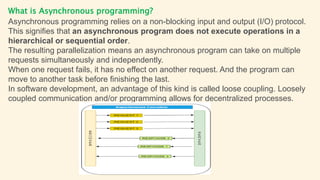
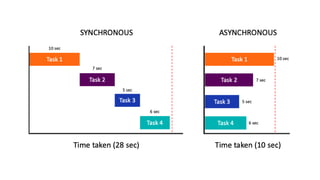
Synchronous and asynchronous programming refer to two different models for executing tasks. Synchronous programming involves executing tasks sequentially in a specific order, blocking other tasks until each one is complete. Asynchronous programming allows tasks to run concurrently without blocking, improving responsiveness. While synchronous programming is simpler, asynchronous programming improves performance for long-running or I/O-bound tasks by making more efficient use of resources through parallelization. Examples of where asynchronous programming is particularly useful include batch processing large amounts of data and long-running background tasks like order fulfillment.