This document discusses different types of motion including:
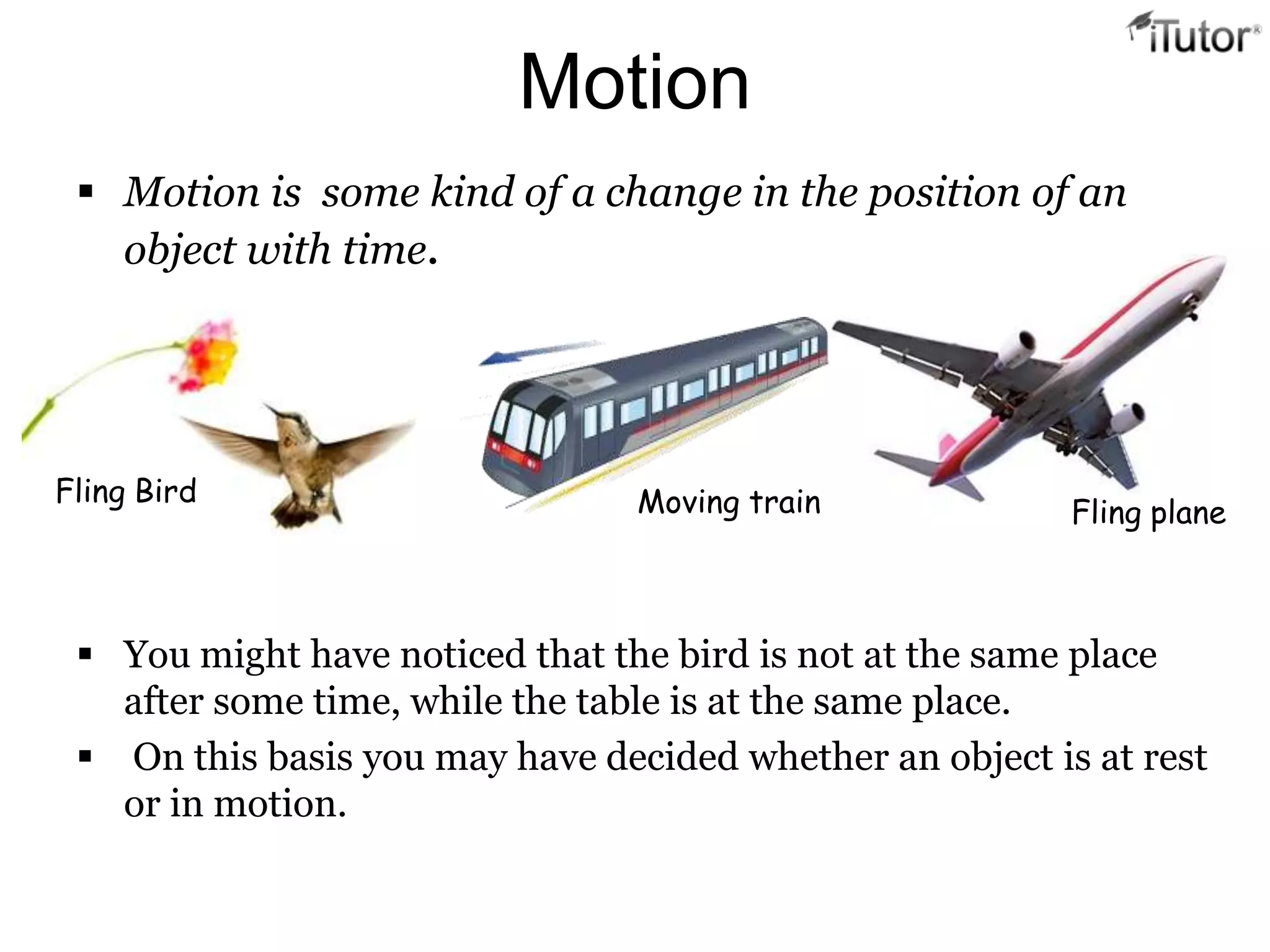
- Motion is defined as a change in an object's position over time.
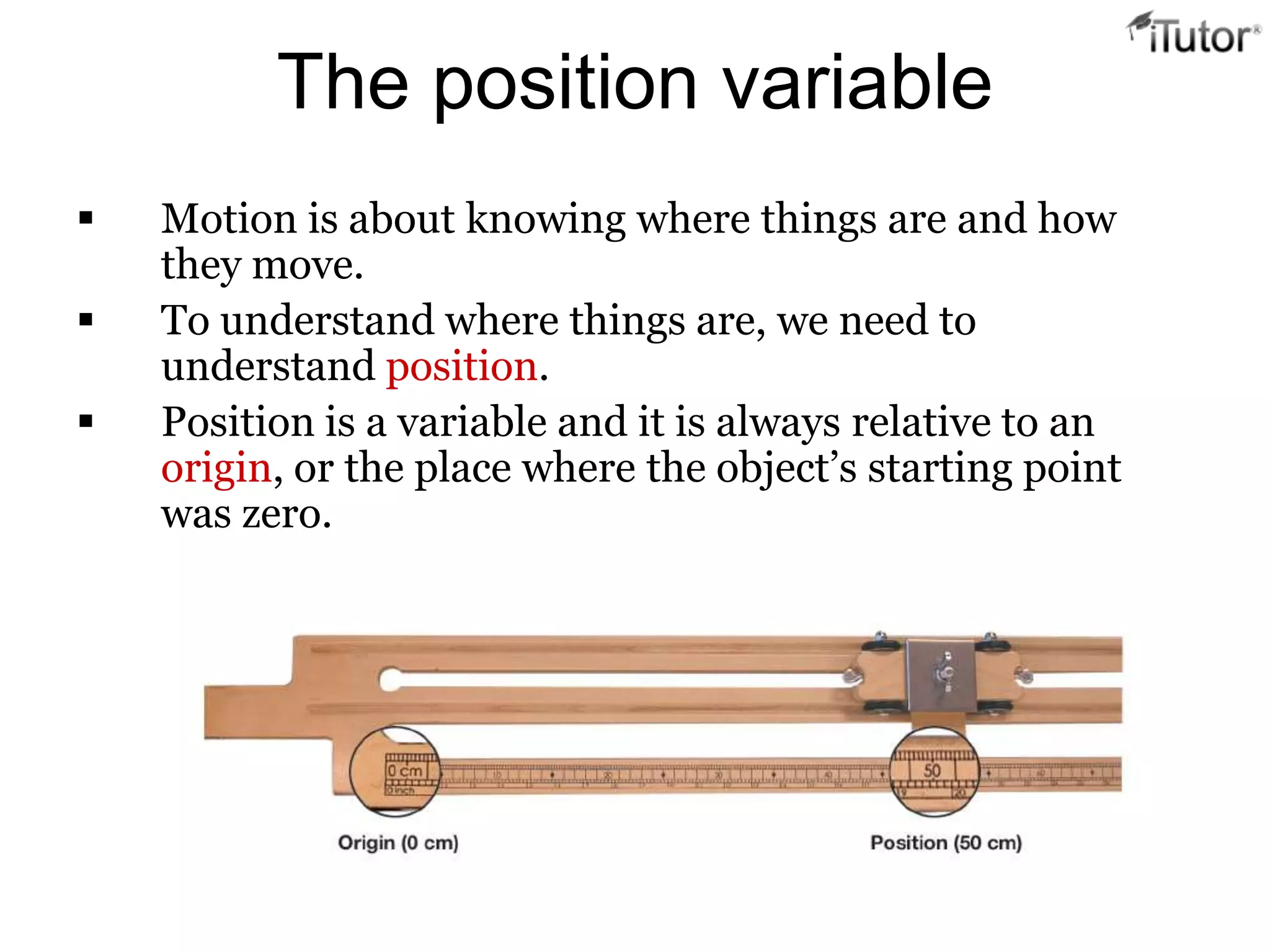
- Position is relative to an origin point and can be positive or negative.
- Types of motion include rectilinear, circular, and periodic motion.
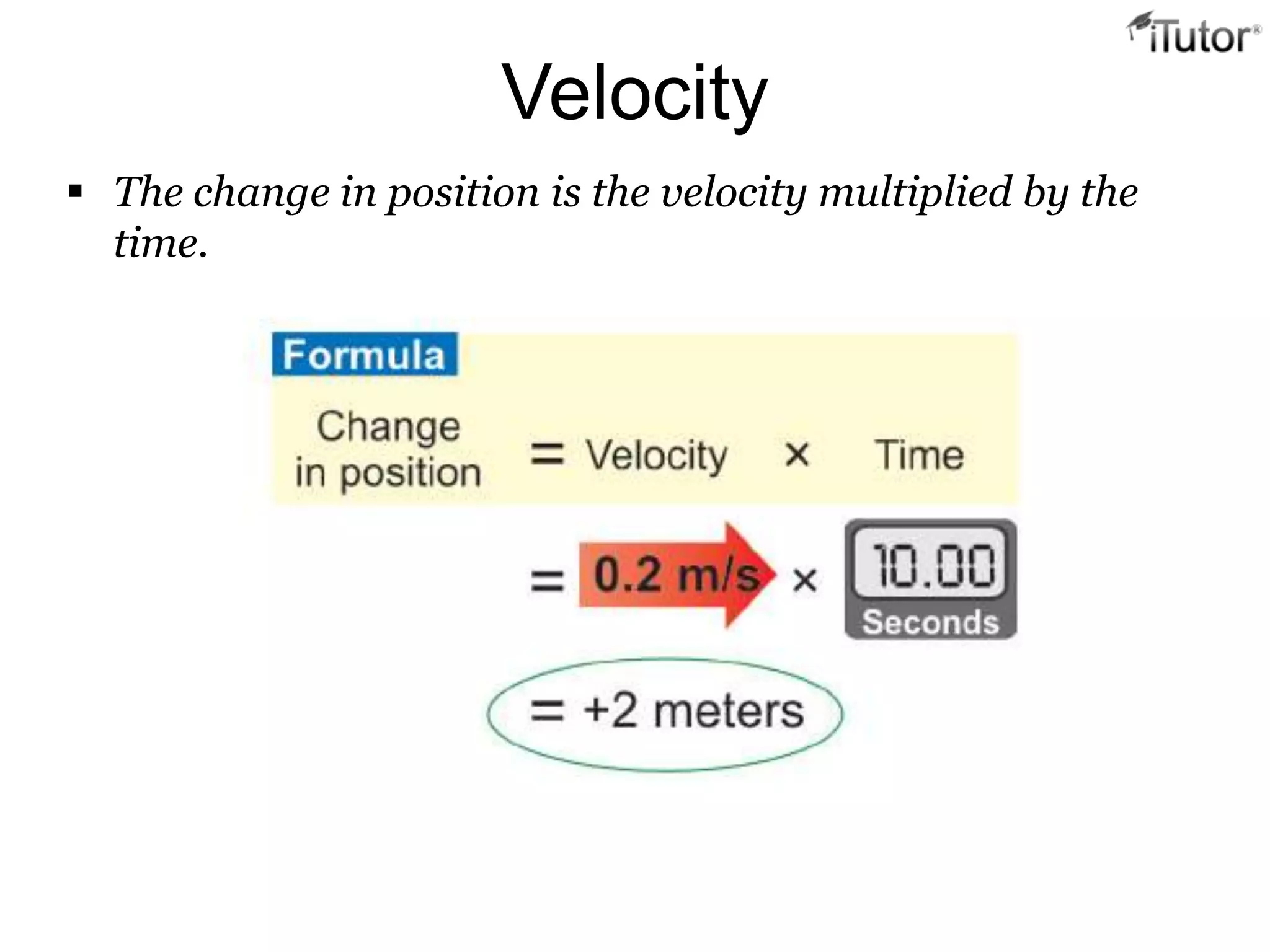
- Velocity refers to an object's speed and direction of motion.