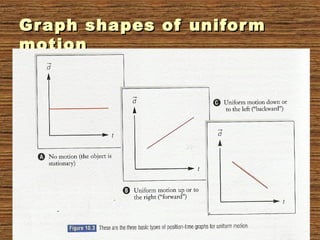
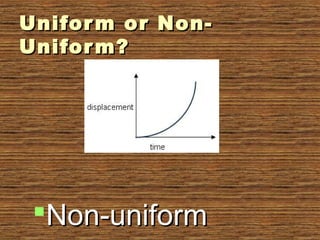
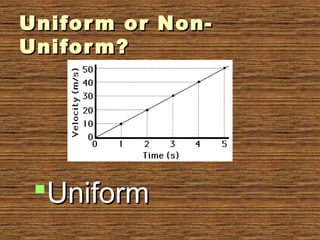
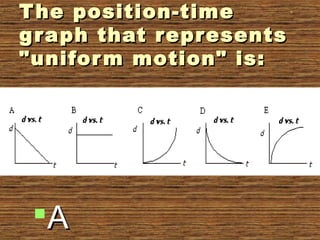
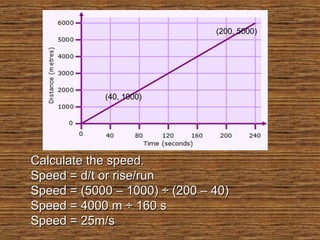
The document provides information about uniform and non-uniform motion through text and diagrams. It defines uniform motion as when an object moves equal distances in equal intervals of time with constant speed, and non-uniform motion as when distances covered are unequal in equal time intervals with varying speed. Graphs are used to illustrate the difference between uniform and non-uniform motion based on whether the distance-time graph is a straight line or not. Speed, velocity, average speed, and instantaneous speed are also defined and distinguished. Real-world examples are given to explain the concepts.