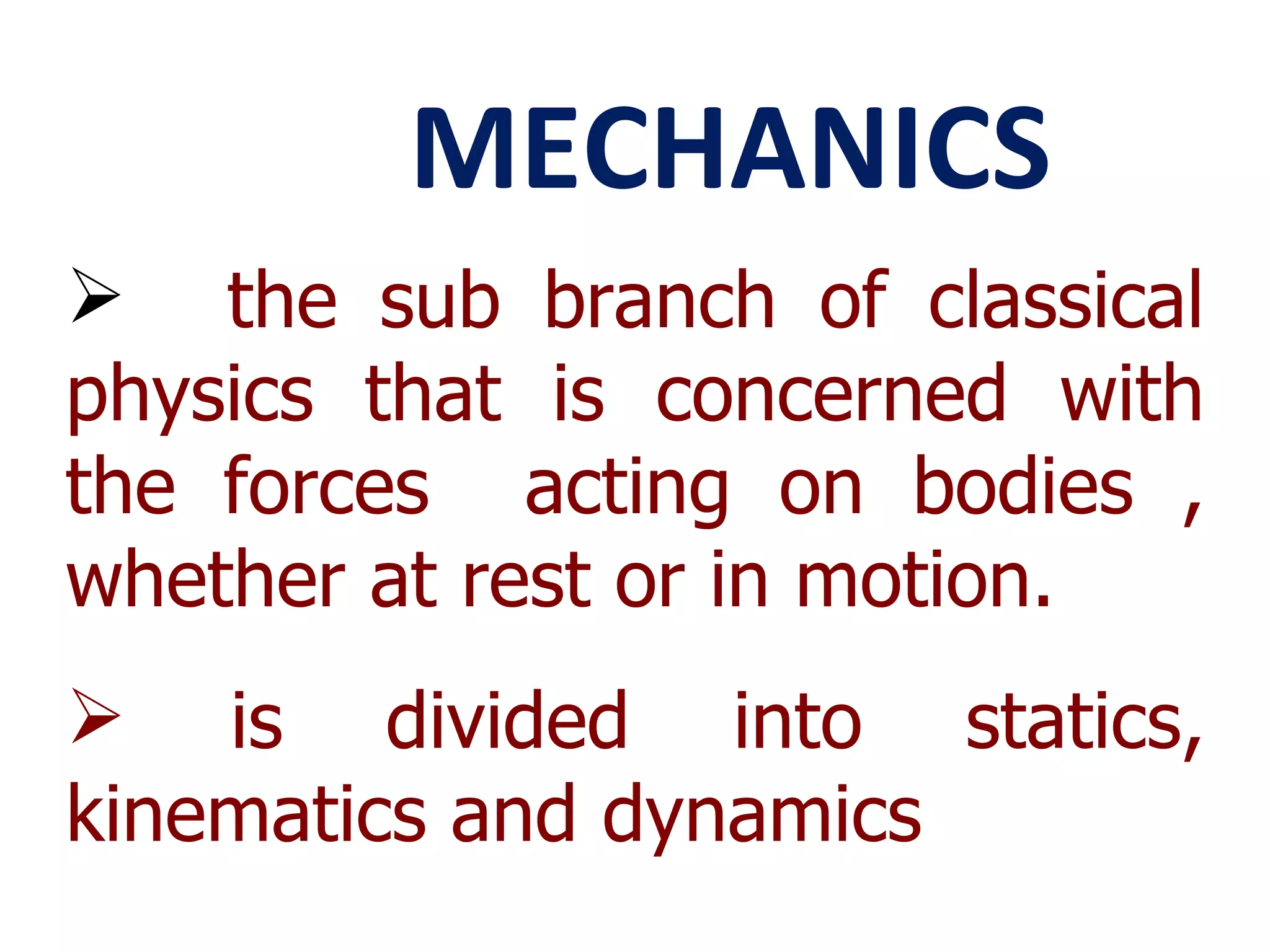
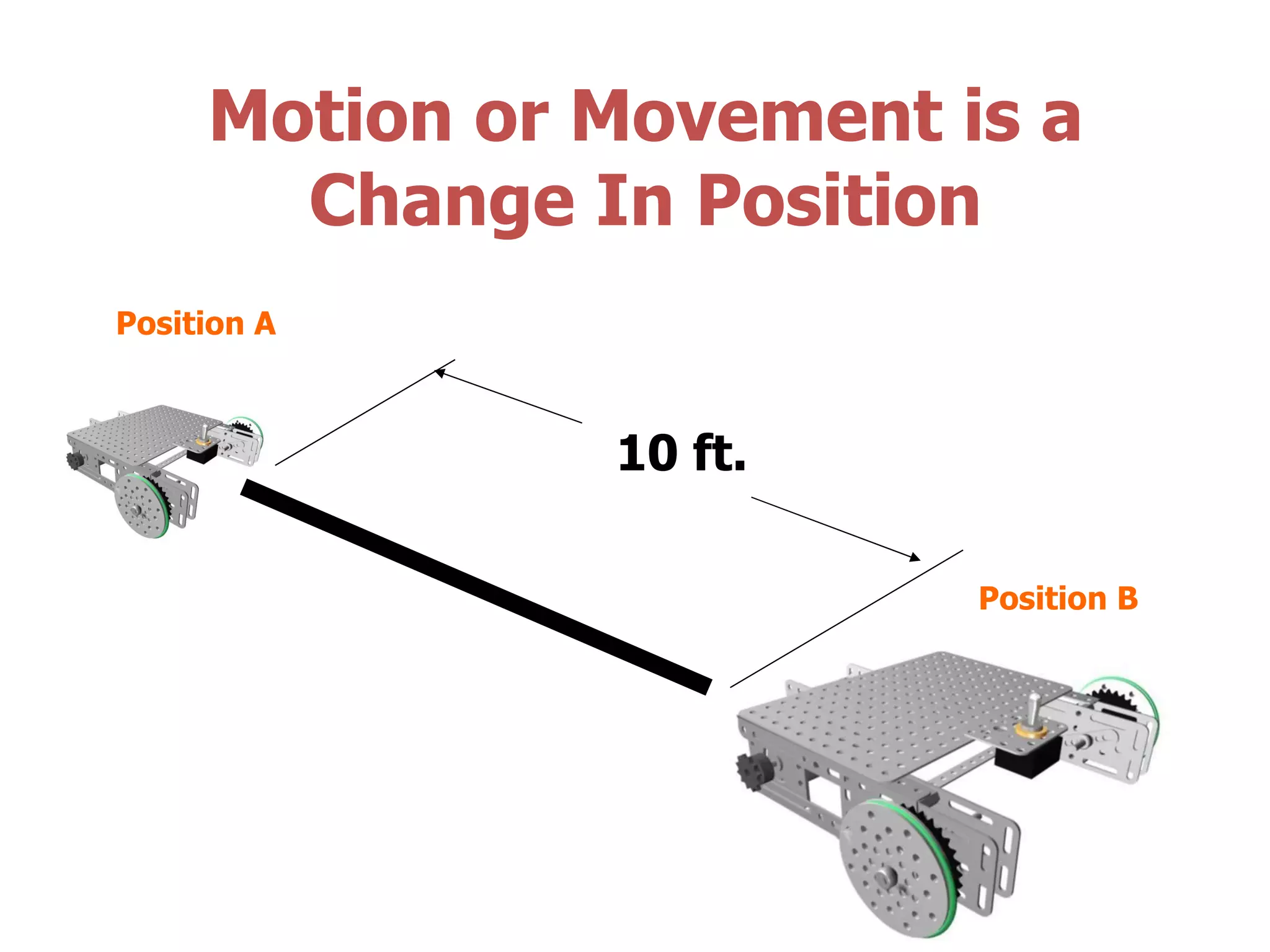
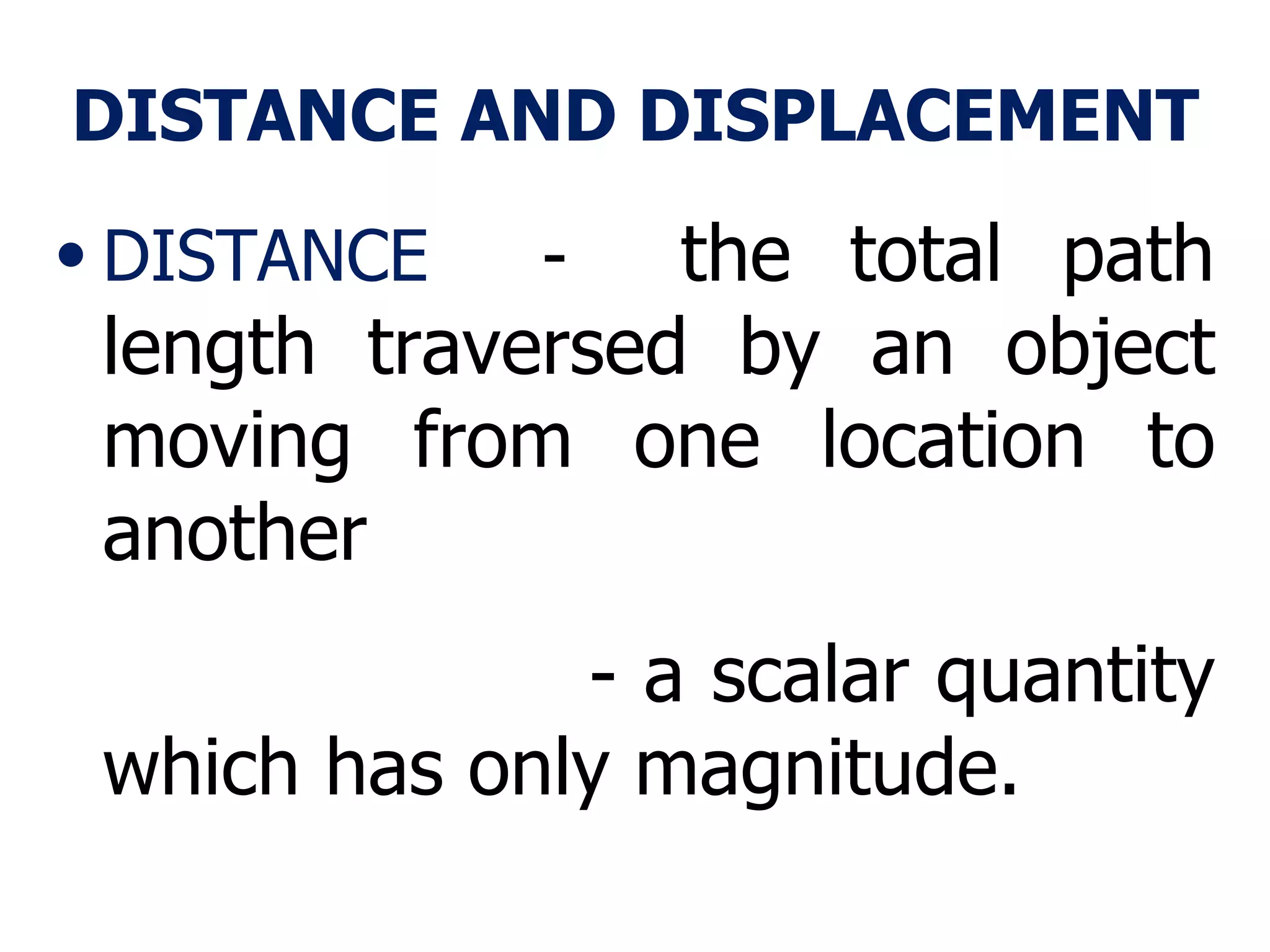
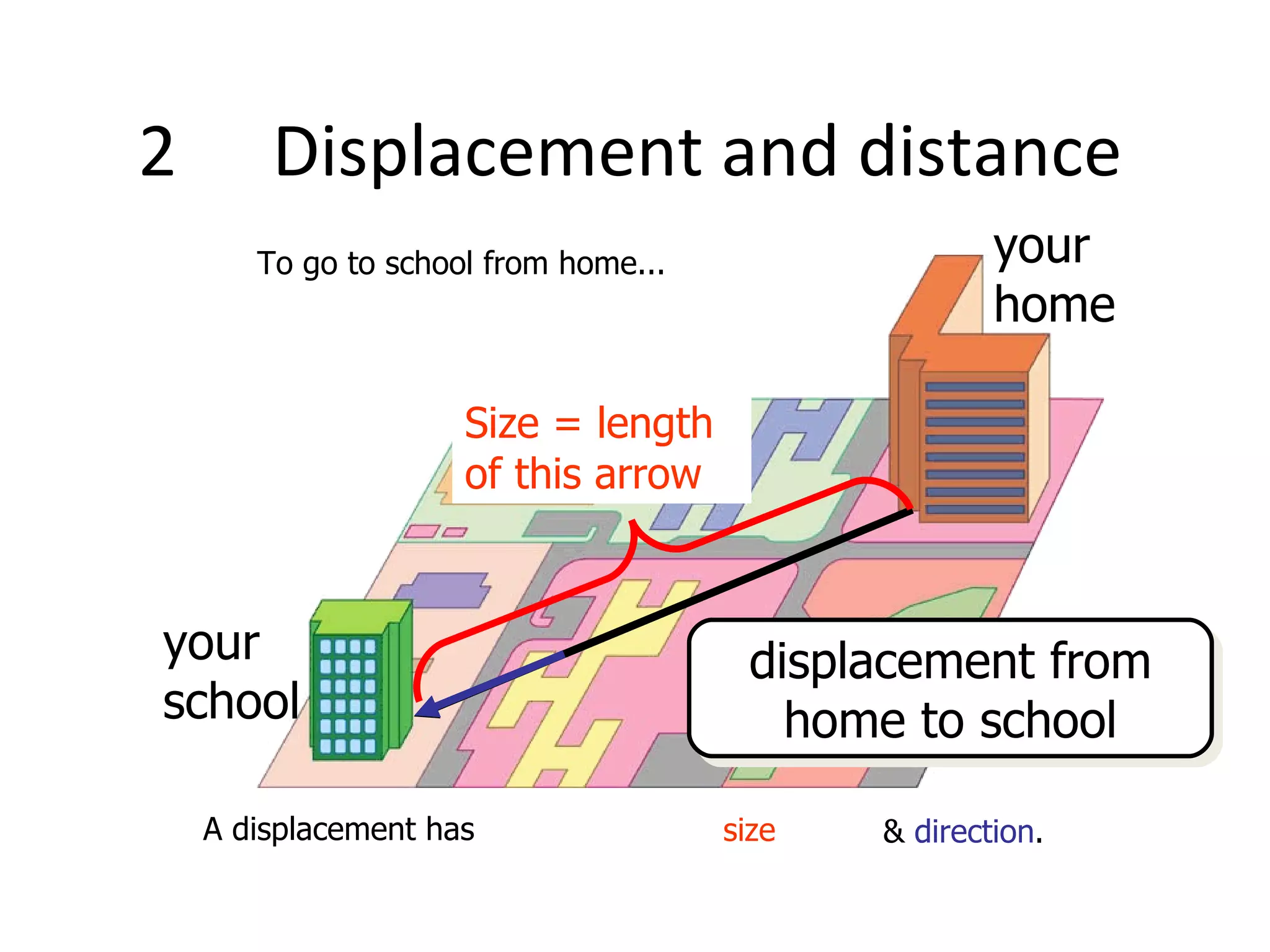
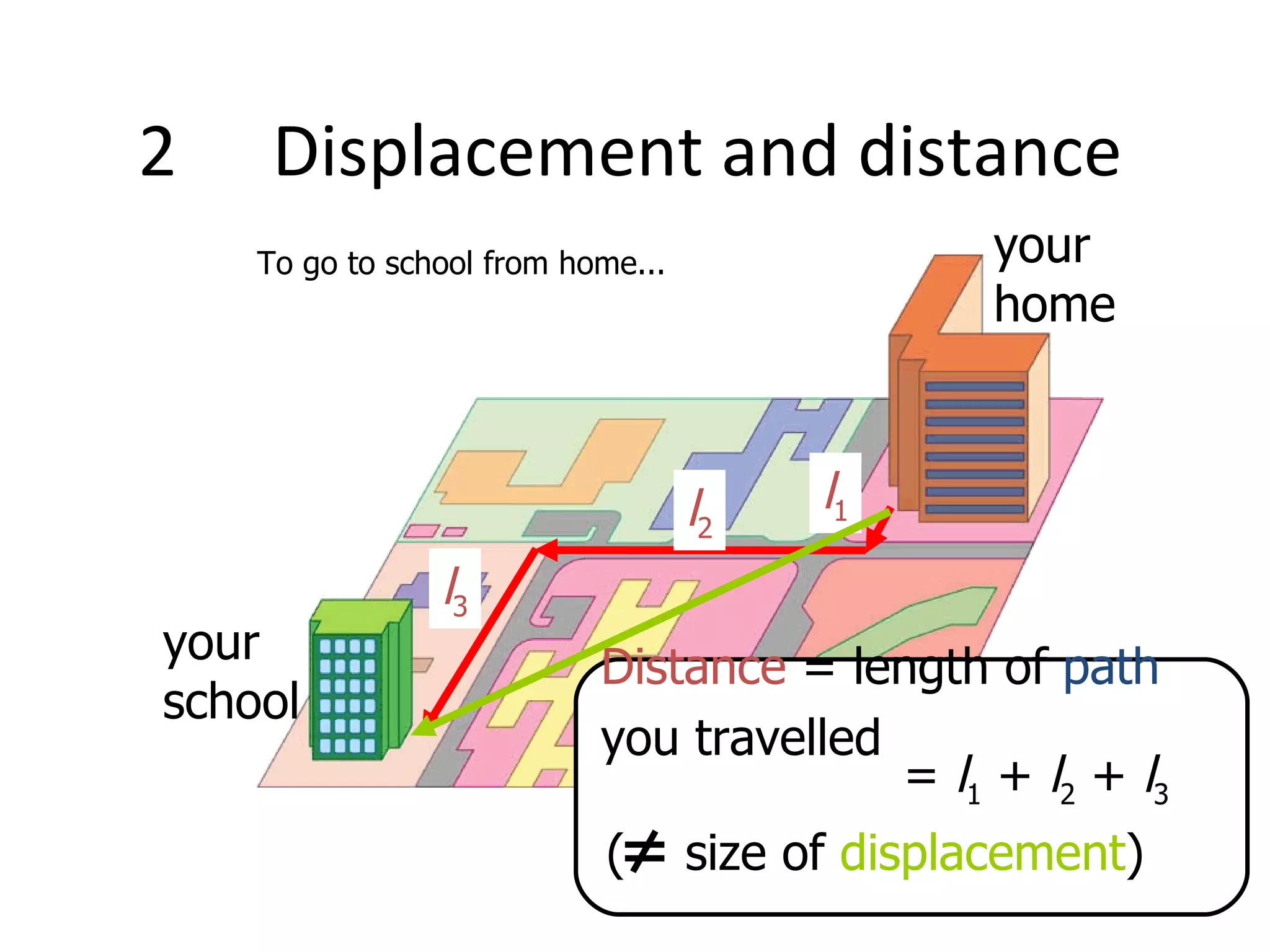
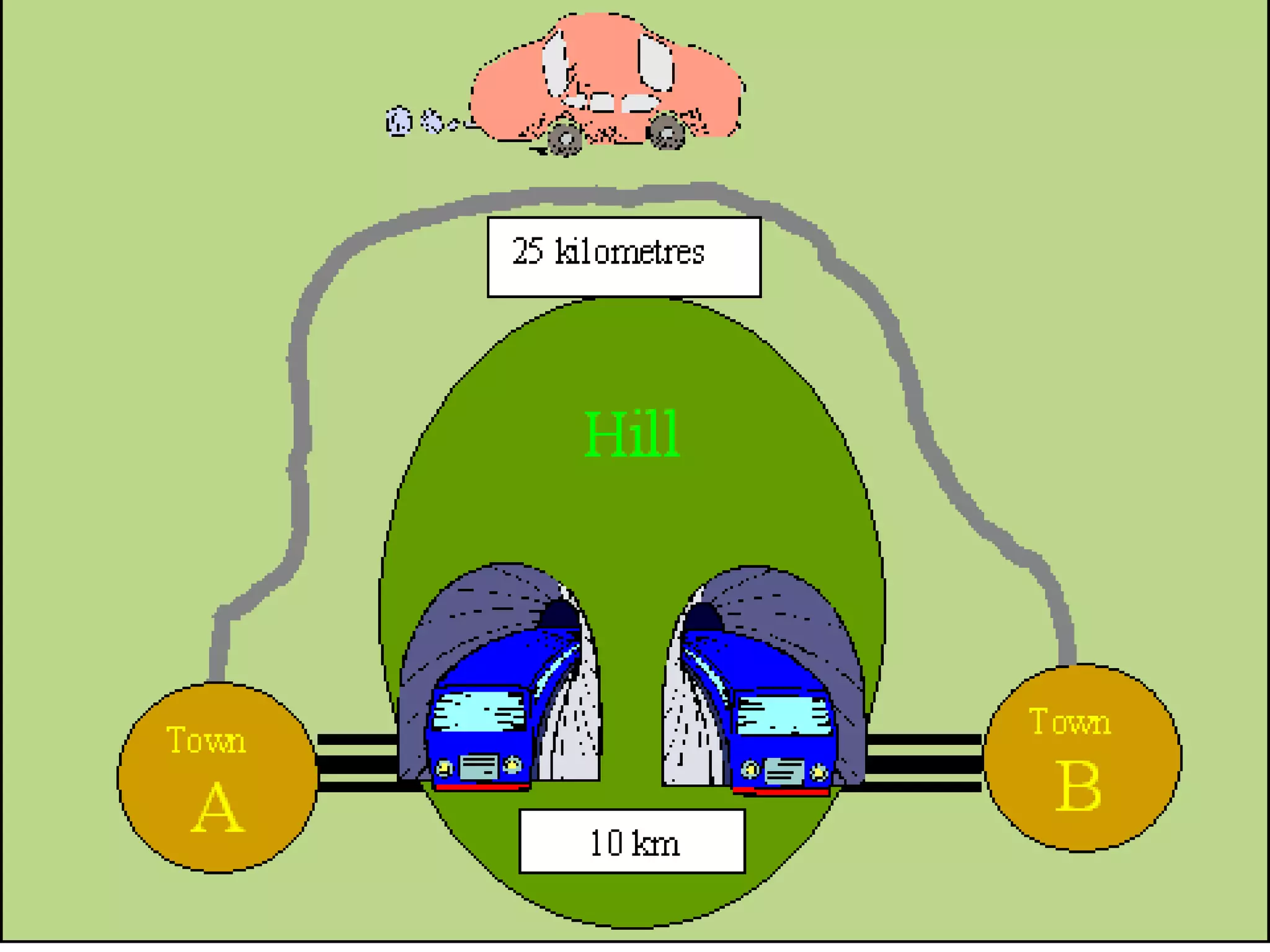
Mechanics is the branch of physics concerned with forces and motion. It is divided into statics, kinematics, and dynamics. Statics deals with forces in equilibrium, kinematics with motion without forces, and dynamics with the relationship between forces and motion. Motion refers to a change in an object's position over time and can be described in terms of distance traveled, displacement, speed, and velocity. Distance is a scalar quantity representing total path length, while displacement is a vector quantity referring to straight-line distance between start and end points. Speed is a scalar measure of distance covered per unit time, and velocity is a vector measure representing rate of change of displacement over time.