A student is able to:
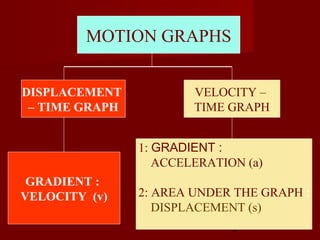
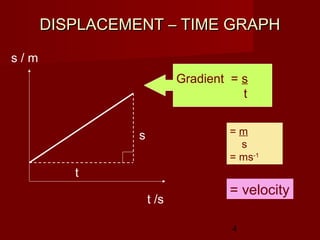
- Plot and interpret displacement-time and velocity-time graphs
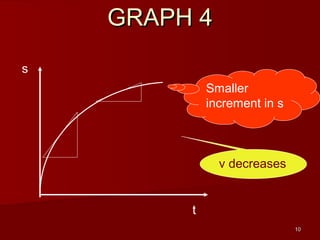
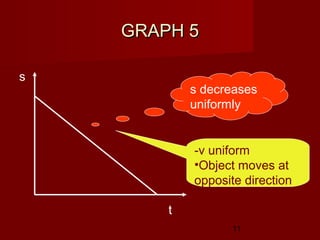
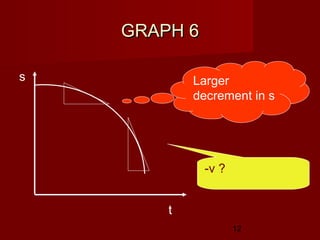
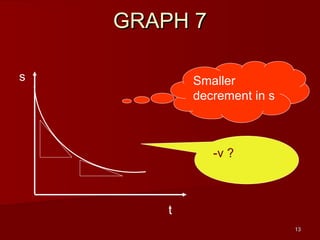
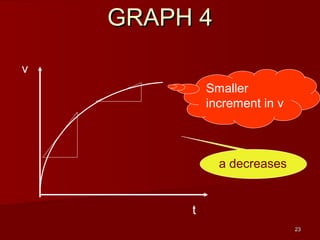
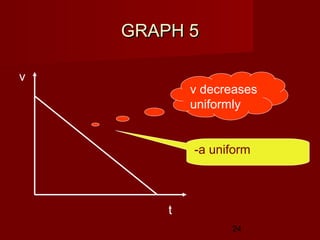
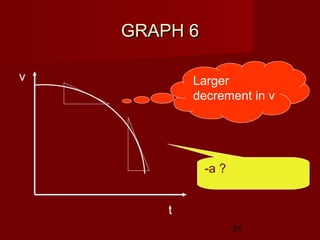
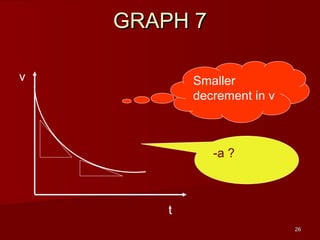
- Determine an object's motion from the shape of the graphs, including whether it is at rest, moving with uniform or non-uniform velocity/acceleration
- Calculate distance, displacement, velocity, and acceleration from displacement-time and velocity-time graphs
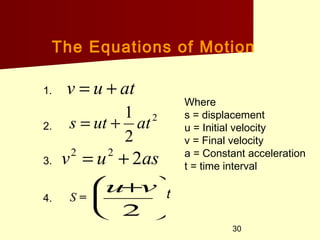
- Solve problems involving linear motion using the equations of motion


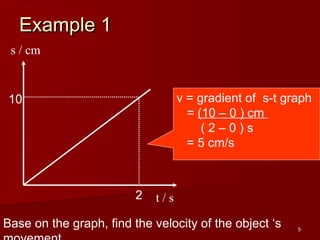

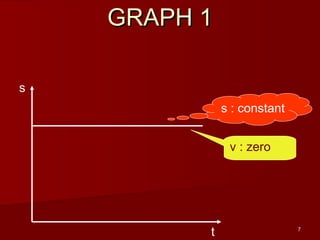
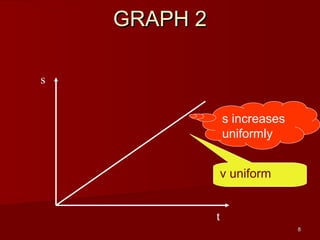
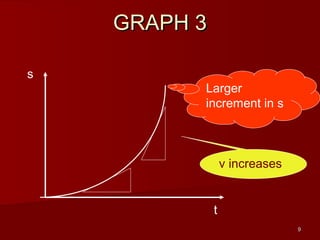
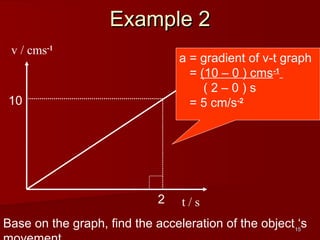
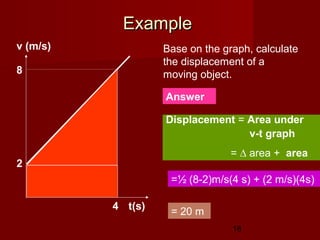

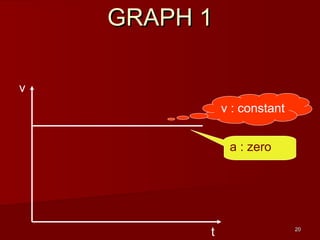
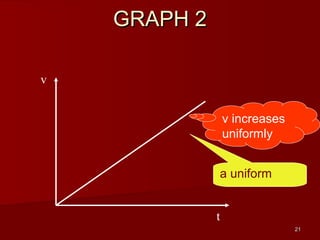
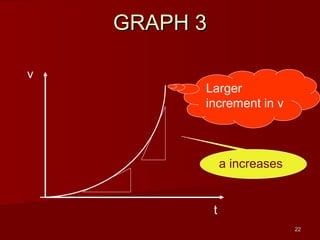
![28
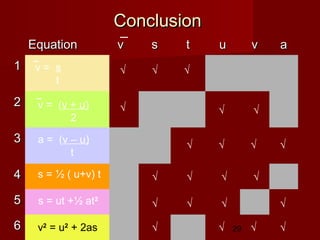
Derived the equations
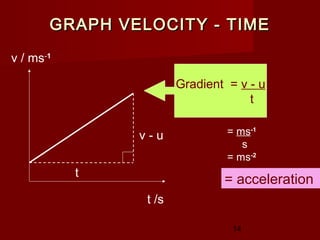
Acceleration = Gradient of
v-t graph
Rearrange [1]
Final velocity v = u+at …….[1a]
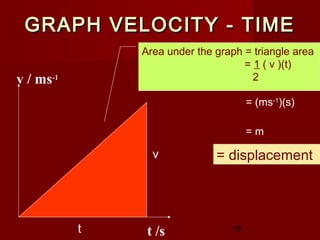
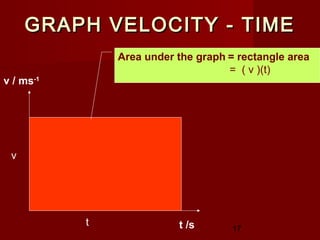
Displacement, s = area under v-t
graph
s = ½ ( u+v) t ……..[2]
Substitute [1a] into [2]
velocity
time
u
t
v
s = ½ ( u+ u+at) t
s = ut +½ at2
……...[3]
Substitute [1b] into [2]
Rearrange [1] again
s = ½ ( u+v) (v – u)
a
v2
= u2
+ 2as …….[4]
t = (v – u) ……..[1b]
a
a = (v – u) ……..[1]
t
v = (v + u) ……..[5]
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-170404135342/85/Motion-Graph-equations-28-320.jpg)