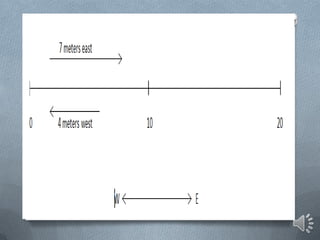
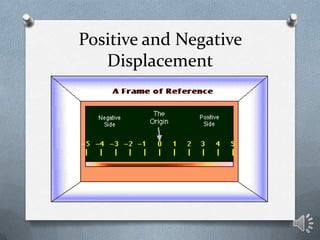
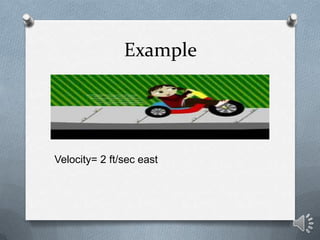
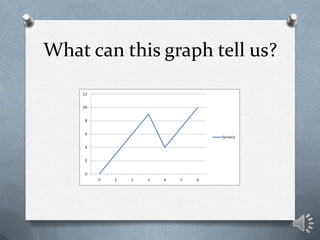
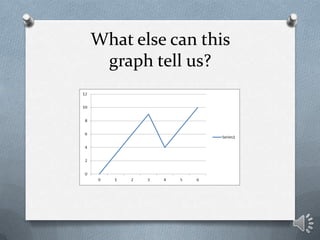
This document discusses key concepts in one-dimensional motion physics including displacement, distance, velocity, speed, and average velocity. It provides examples and problems to illustrate the differences between scalar and vector quantities as well as distance and displacement. Graphs are used to represent motion data and calculate instantaneous and average velocities from slopes of the position-time graphs at different time intervals. Students are prompted to practice examples, self-assess their understanding, and complete a lab assignment.