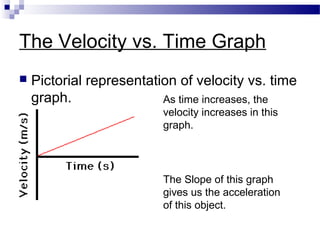
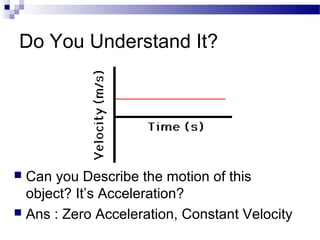
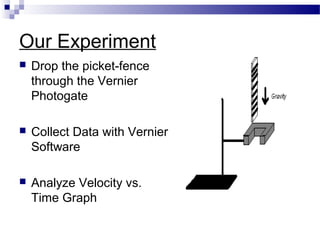
This document discusses free-fall motion and describes an experiment to measure the acceleration due to gravity using a photogate and falling object. The experiment involves dropping an object through a photogate multiple times to collect displacement and time data. Students will then analyze the velocity-time graph to determine the acceleration for each trial and calculate the percent error compared to the accepted value of 9.8 m/s^2. The goal is to perform analysis of free-fall motion and enable students to solve problems involving falling objects.