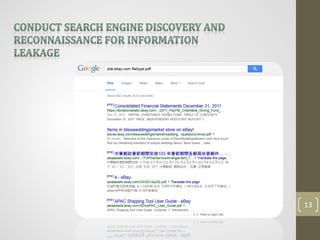
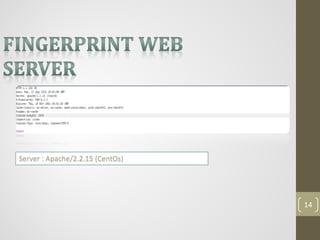
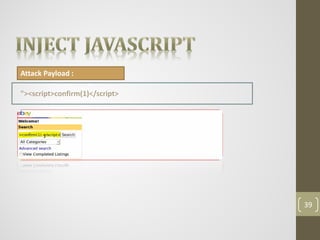
This document provides an agenda for a presentation on comprehensive web application attacks. The presenter, Ahmed Sherif, has over 5 years of experience in penetration testing and web application security. The agenda includes an overview of security in corporations and web technologies, the OWASP security testing methodology, common web attacks like XSS and SQL injection, and a demo of these attacks. The goal is to educate attendees on how to identify and address vulnerabilities in web applications.