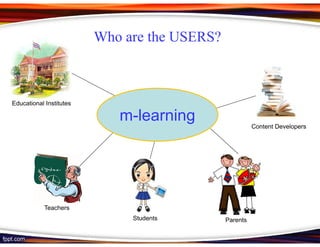
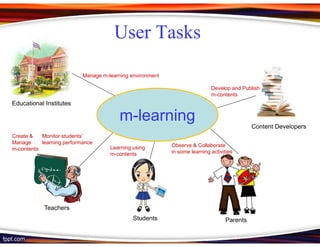
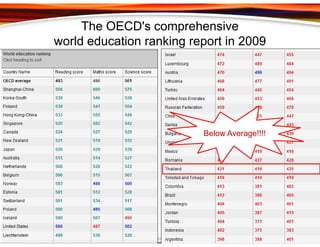
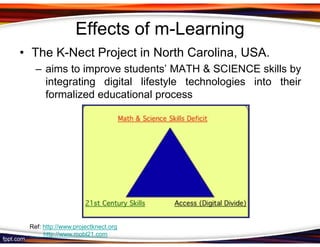
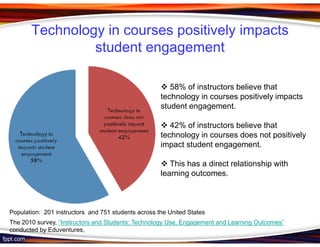
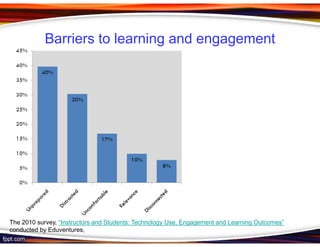
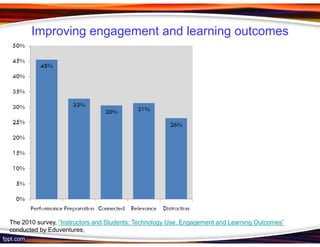
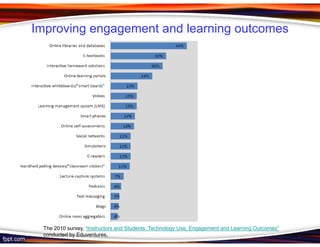
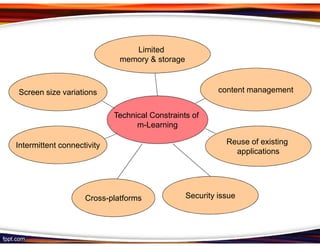
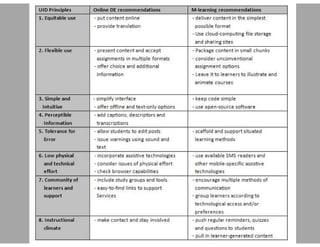
This document discusses principles for designing effective m-learning based on software engineering principles. It identifies the key users of m-learning as educational institutions, teachers, students, parents and content developers. To improve learning outcomes, m-learning needs to be more personal, fun, interactive, networked, spontaneous, connected and just-in-time. Content should be delivered in short segments adapted to different devices and lifestyles. User needs and technical constraints also need to be considered in the design.






![Software Engineering Principle
Software engineering (SE) is an application of a
systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the
development, operation, and maintenance of
software. [WiKi]
Software => solution/tool that fulfills USER NEEDs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/m-learning-design-by-drsasipornusanavasin-120529021018-phpapp01/85/M-Learning-8-320.jpg)