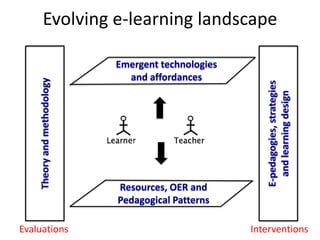
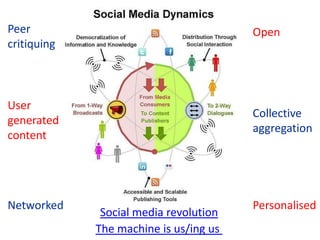
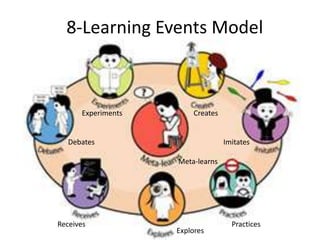
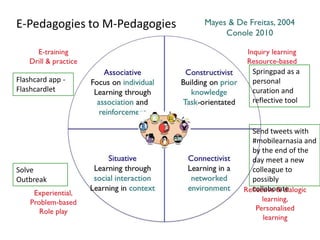
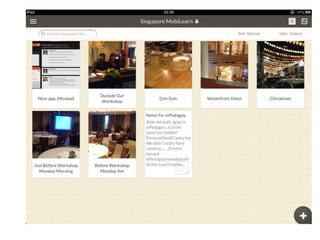
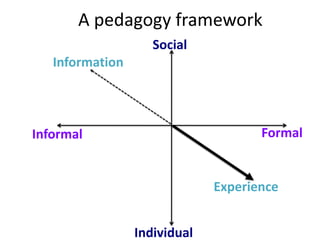
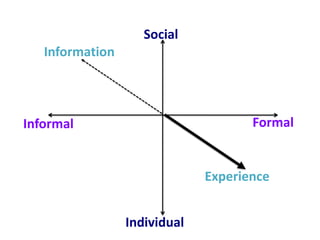
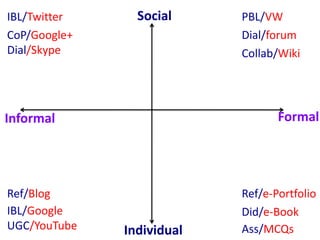
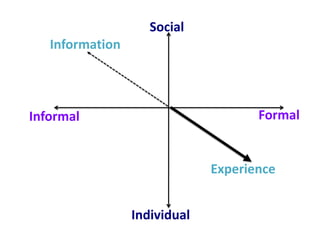
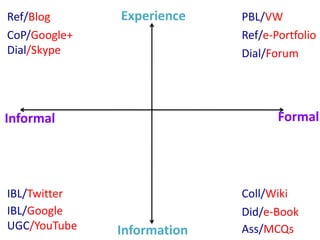
This document discusses the evolution from e-learning to m-learning using mobile technologies. It outlines key drivers for the shift to mobile, including student expectations, marketing, and employers seeking mobile skills. New affordances of mobile devices allow for learning anywhere and capturing multimedia. This enables new m-pedagogies focused on tasks, experiential learning, and social/collaborative approaches. The document maps different e-pedagogies to mobile technologies and applications. It presents frameworks for matching pedagogies to informal/formal and social/individual learning. Examples from the University of Leicester demonstrate personalized mobile learning environments. The future of m-learning is discussed as an emerging norm, with new business models, sophisticated