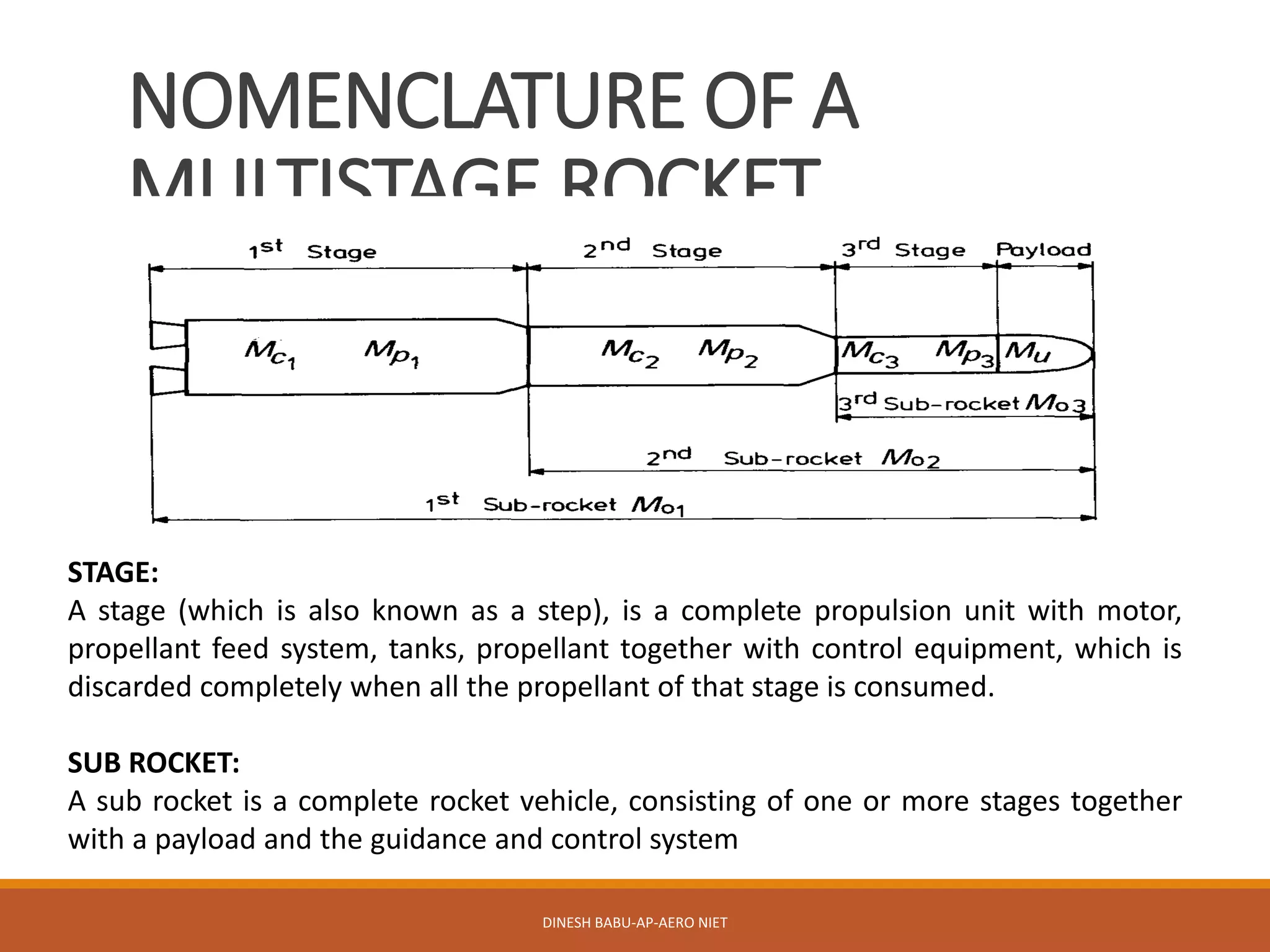
1. A multistage rocket uses two or more stages, each with their own engines and propellant. Stages are discarded completely after their propellant is consumed.
2. There are two types of multistage rockets: series staging where the second stage fires after the first is finished, and parallel staging where upper stage engines are used during lower stage operation by arranging stages alongside each other.
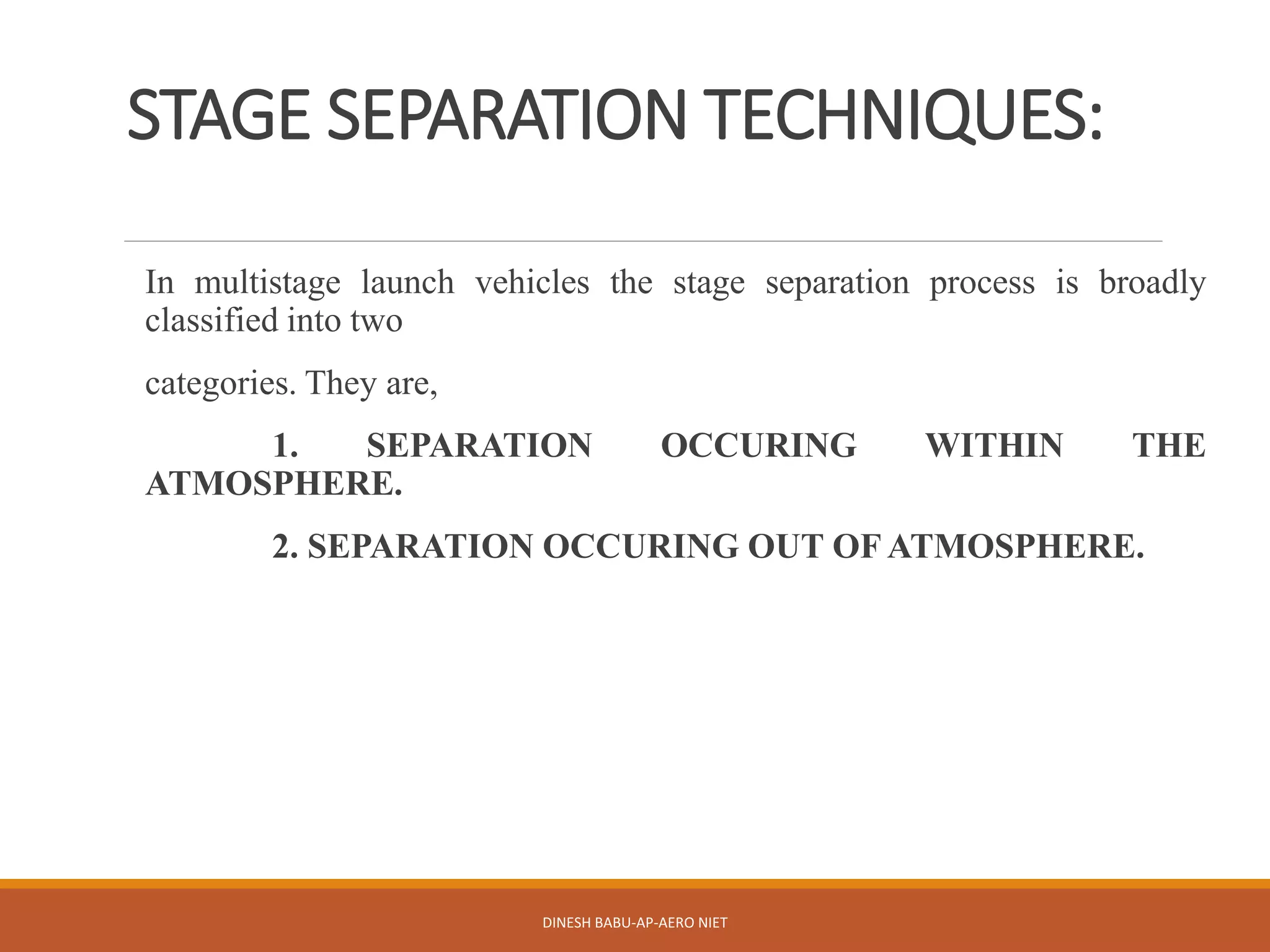
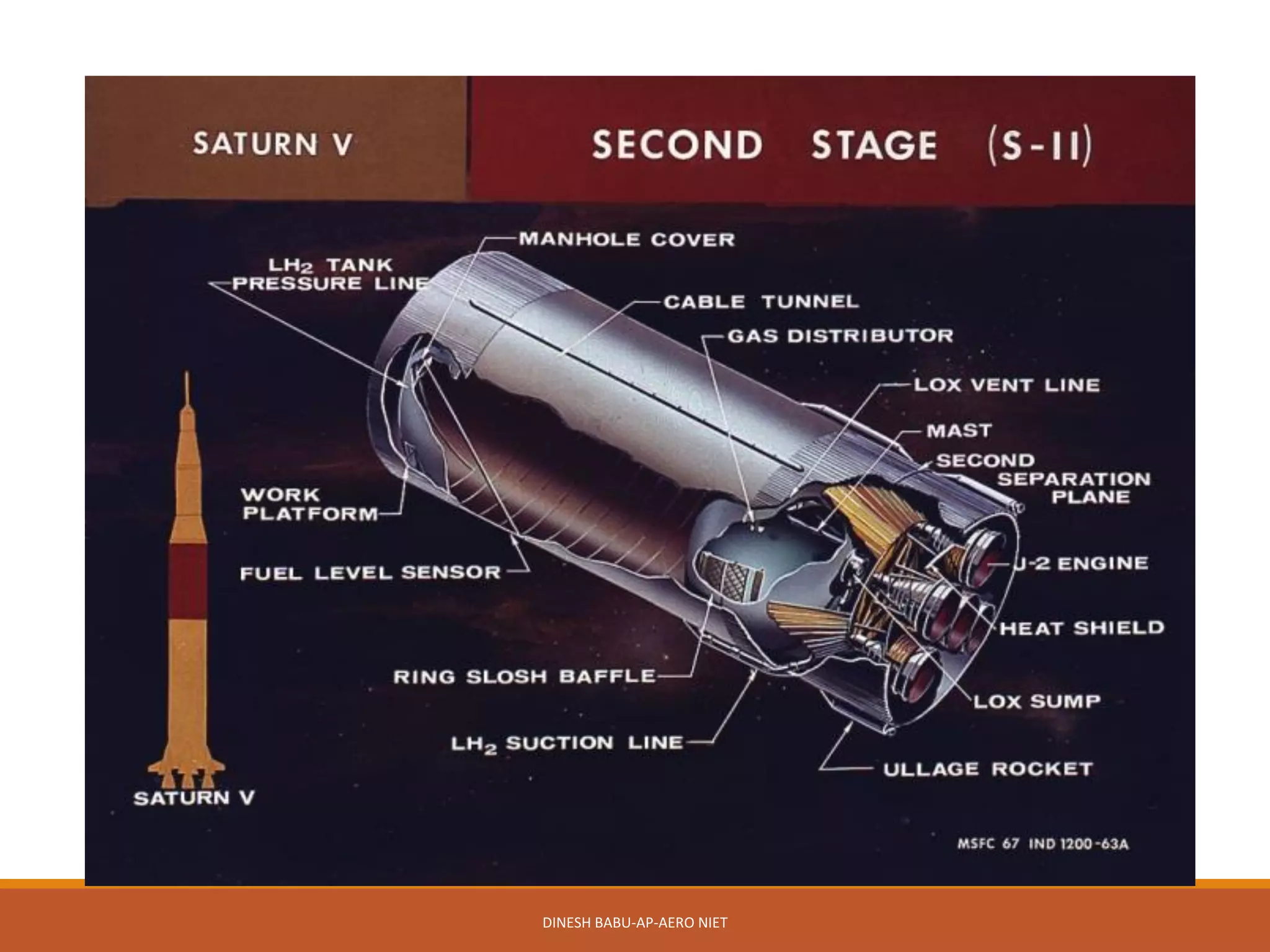
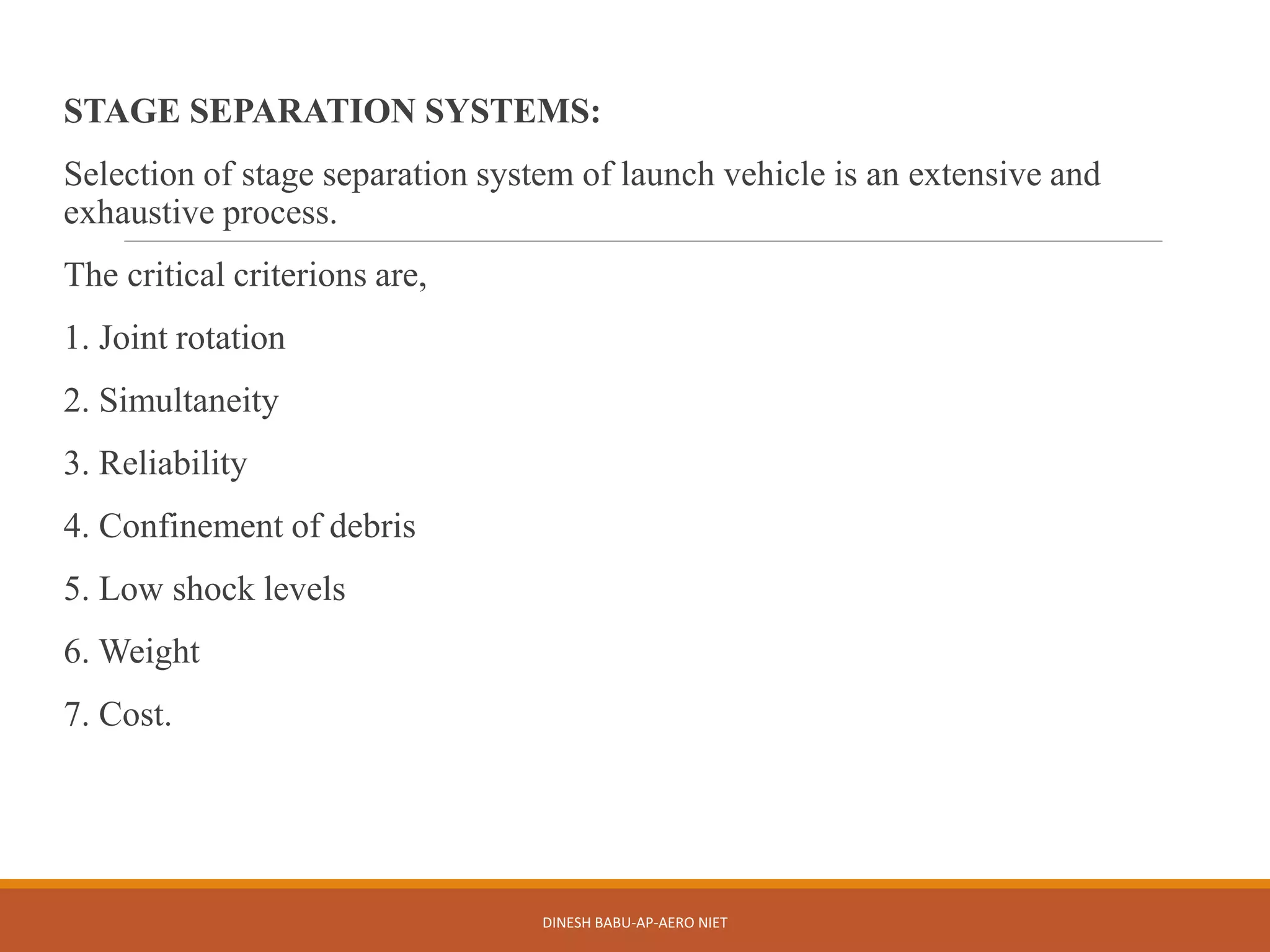
3. Stage separation can occur within the atmosphere using techniques like firing holes or ullage rockets, or out of the atmosphere in space using springs or solid propellant rockets. Selection of separation systems considers factors like joint rotation, reliability, and debris confinement.