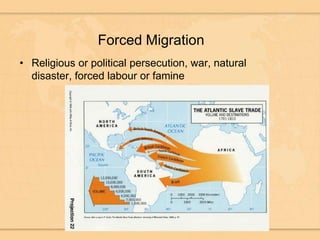
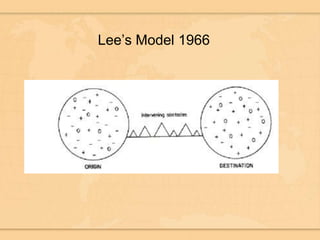
Cities grow due to both push and pull factors related to migration. Key push factors driving rural to urban migration include lack of land, food, and opportunities in rural areas, as well as the pull of potential work and higher wages in cities. Migration leads to changes in birth and death rates in cities as people adopt an urban lifestyle with better access to education, healthcare, and family planning services compared to rural areas. Cities also depend on wealth inequality as migrants have a wide range of incomes and access to services.