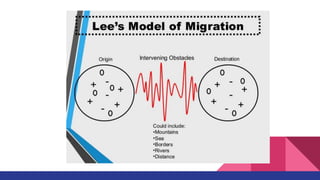
Lee's migration model predicts migration patterns based on push factors that induce people to leave an area, pull factors that attract people to a new area, and intervening obstacles that block migration. It shows that more positive pull factors than negative push factors must outweigh intervening obstacles for migration to occur. While the model works in theory, it does not perfectly account for real-world human behaviors and limitations that can prevent migration even when conditions seem favorable.