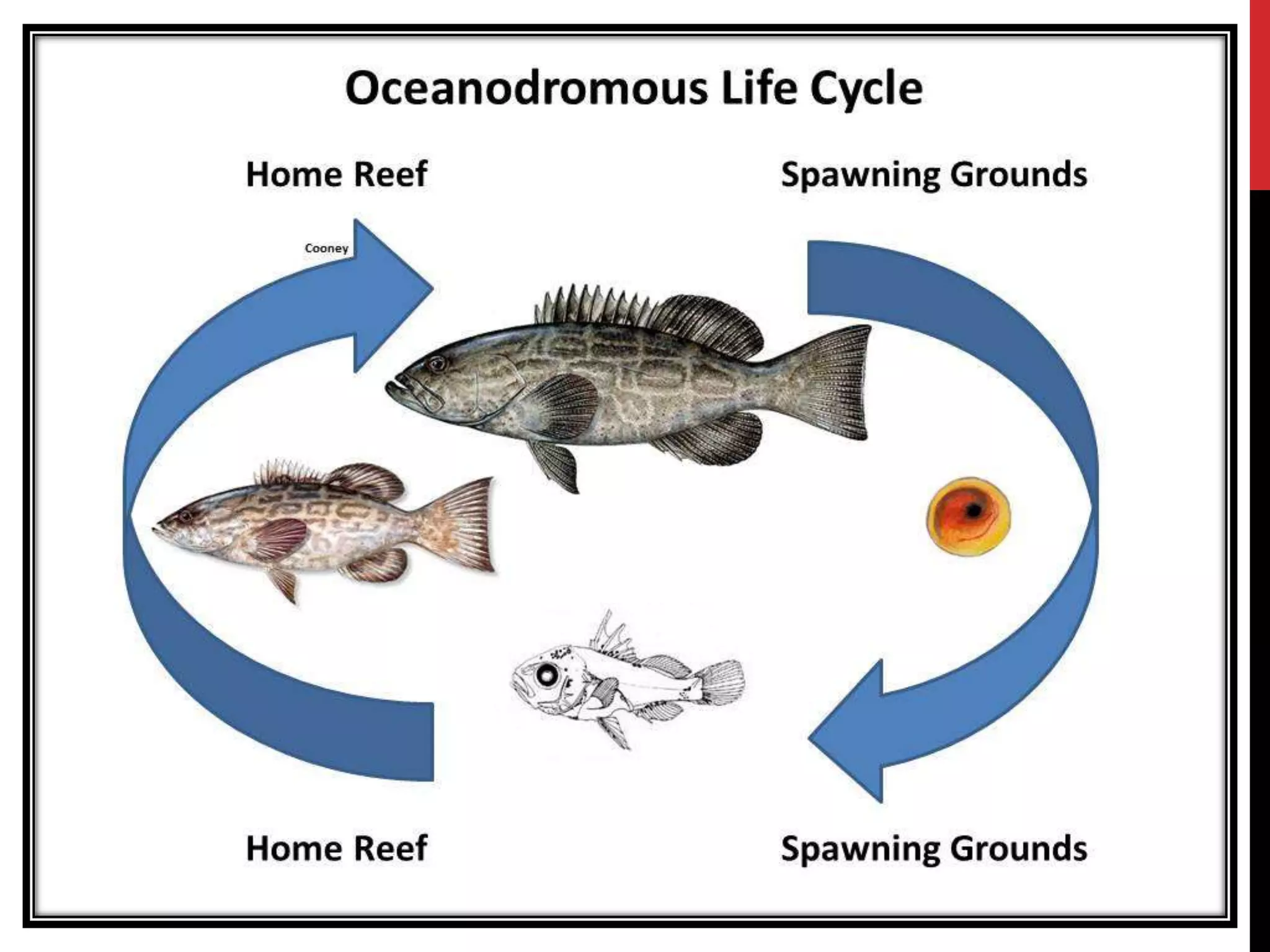
1) Fish migration involves the movement of fish from one area to another, usually for feeding or breeding purposes. Several species migrate long distances for spawning and feeding, including cod, herring, salmon, eel, and tuna.
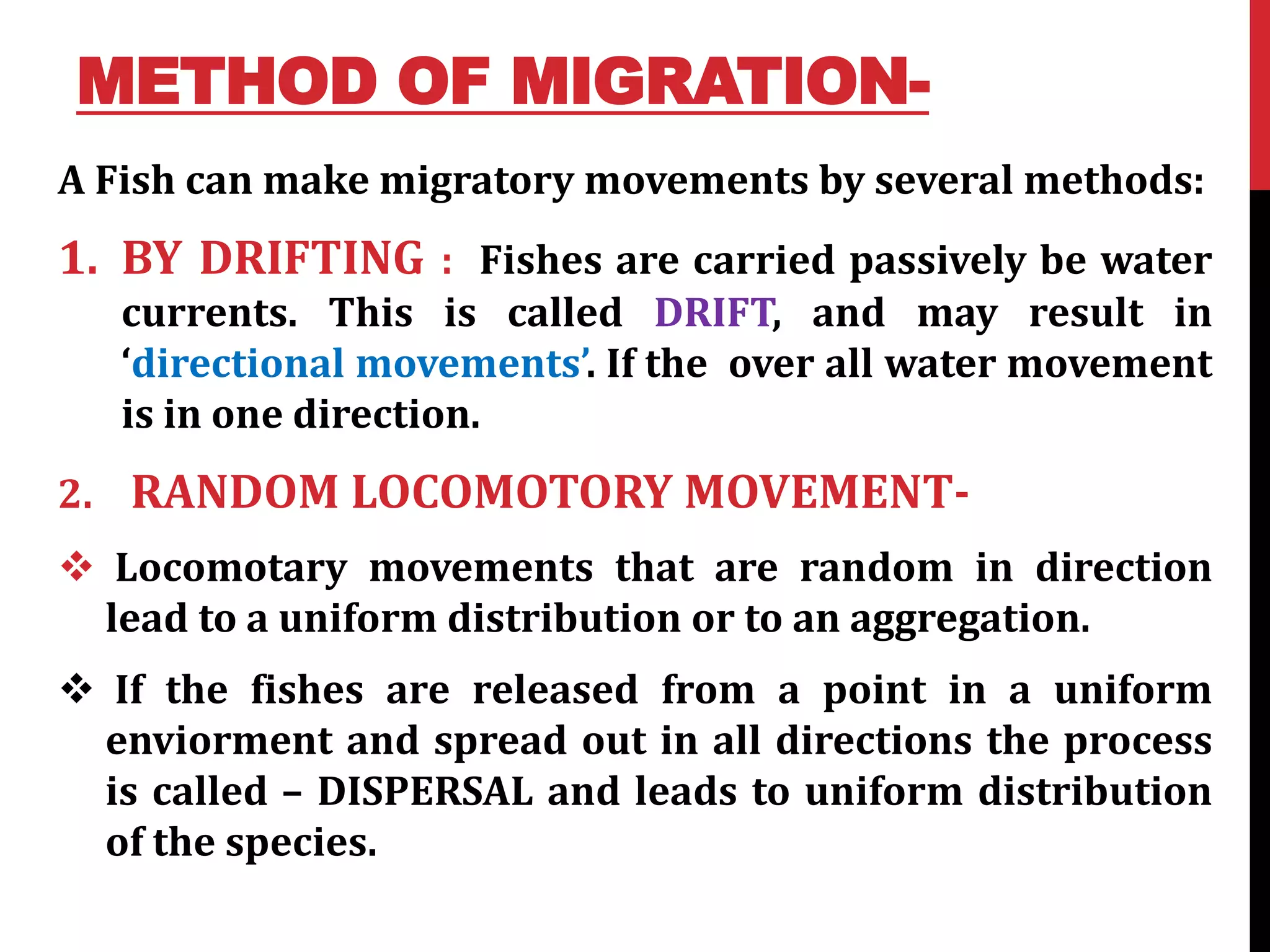
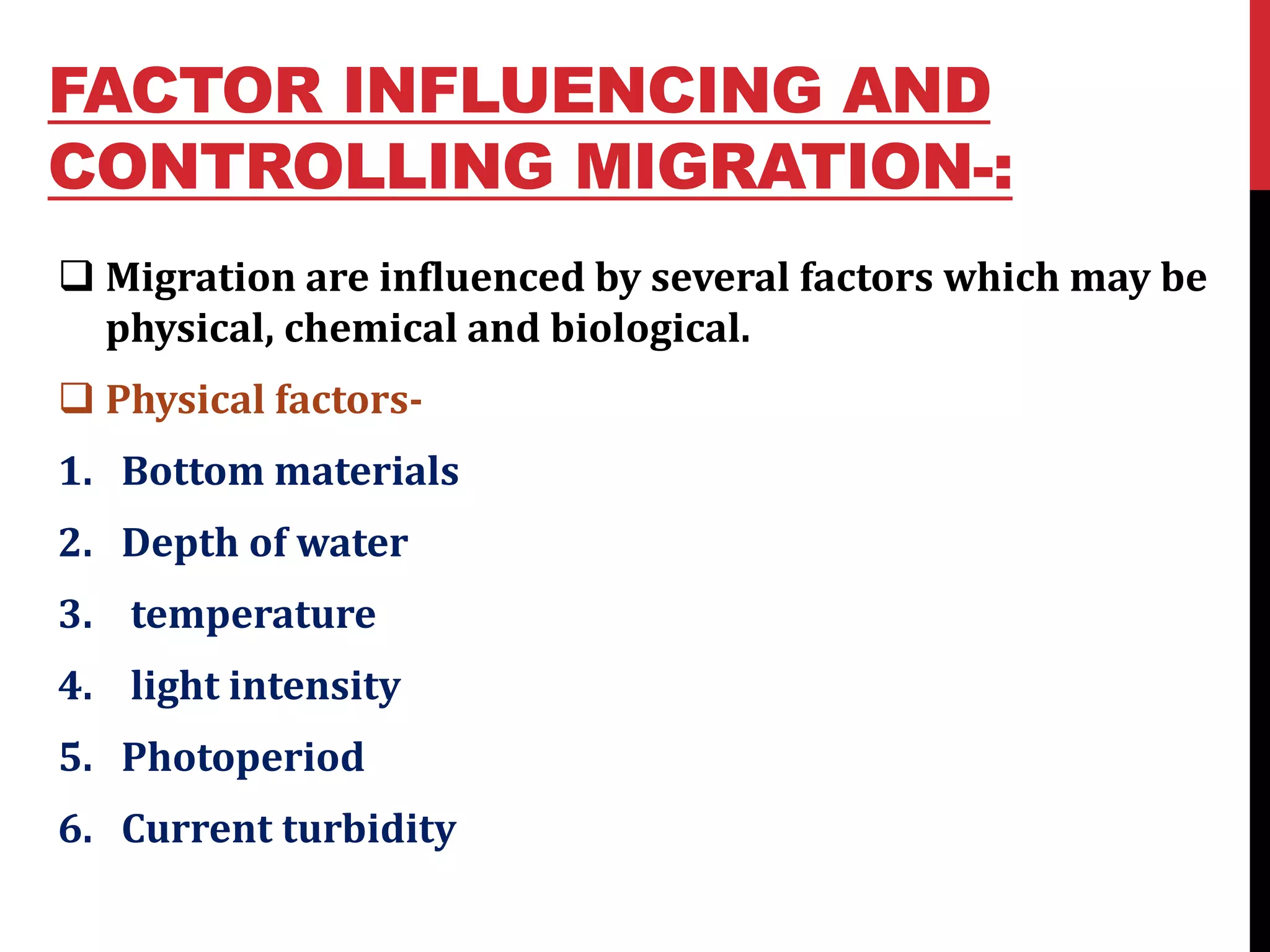
2) There are different types of migration including alimentory (for food/water), gametic (for reproduction), climatic (for suitable climate), and osmoregulatory (for osmoregulation). Fish can migrate through drifting with water currents, random locomotory movement, or orientation swimming in a particular direction.
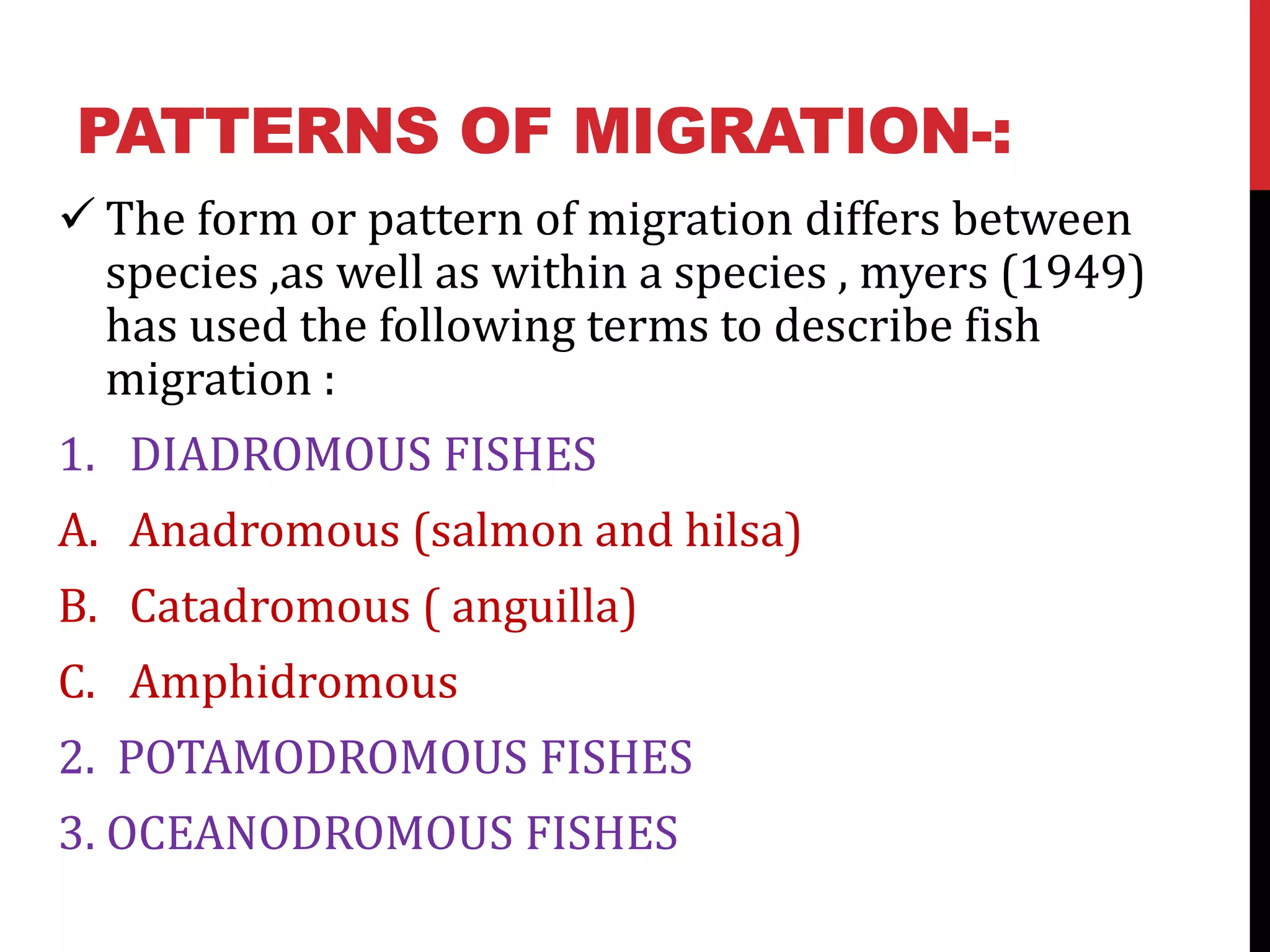
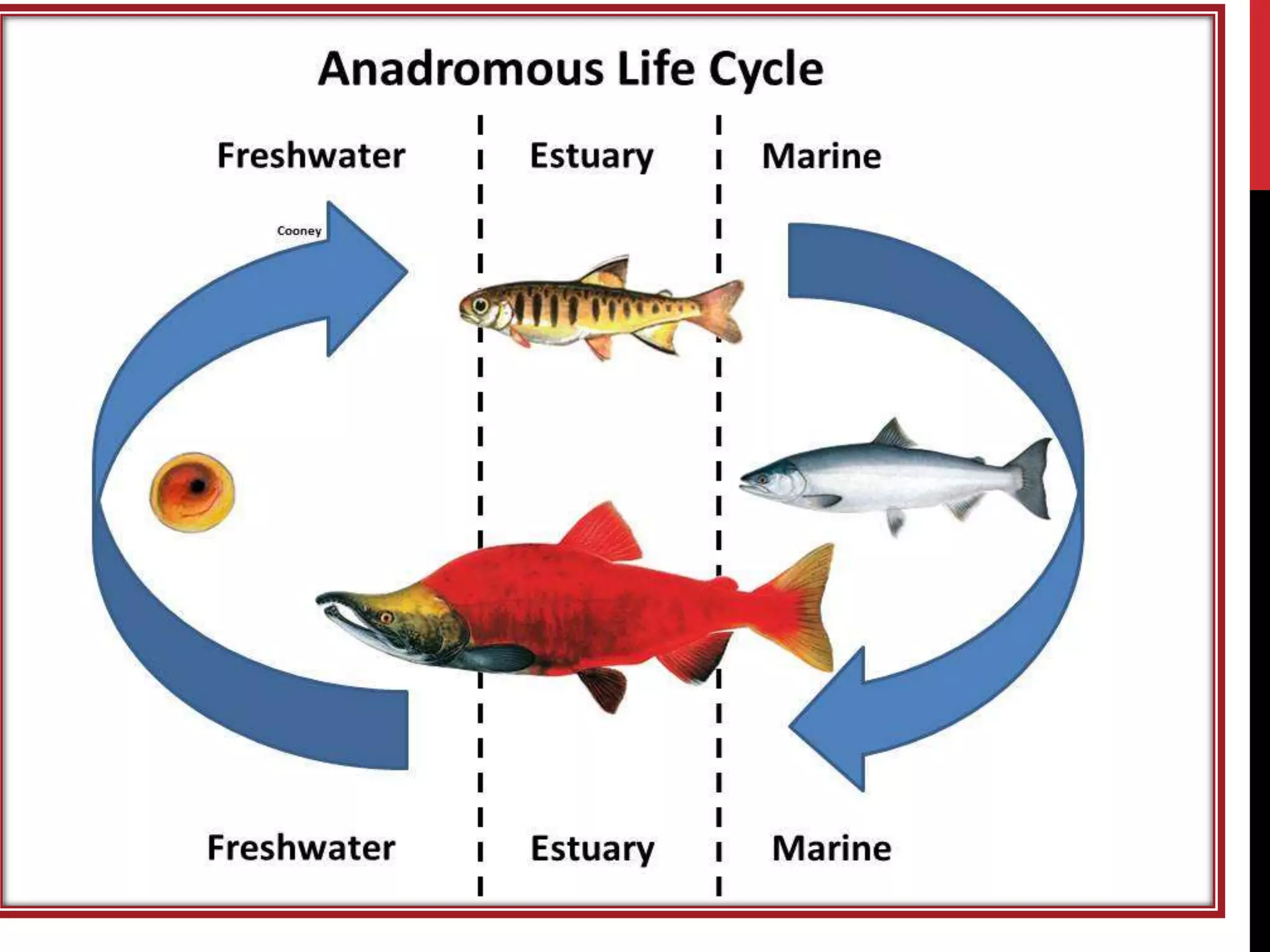
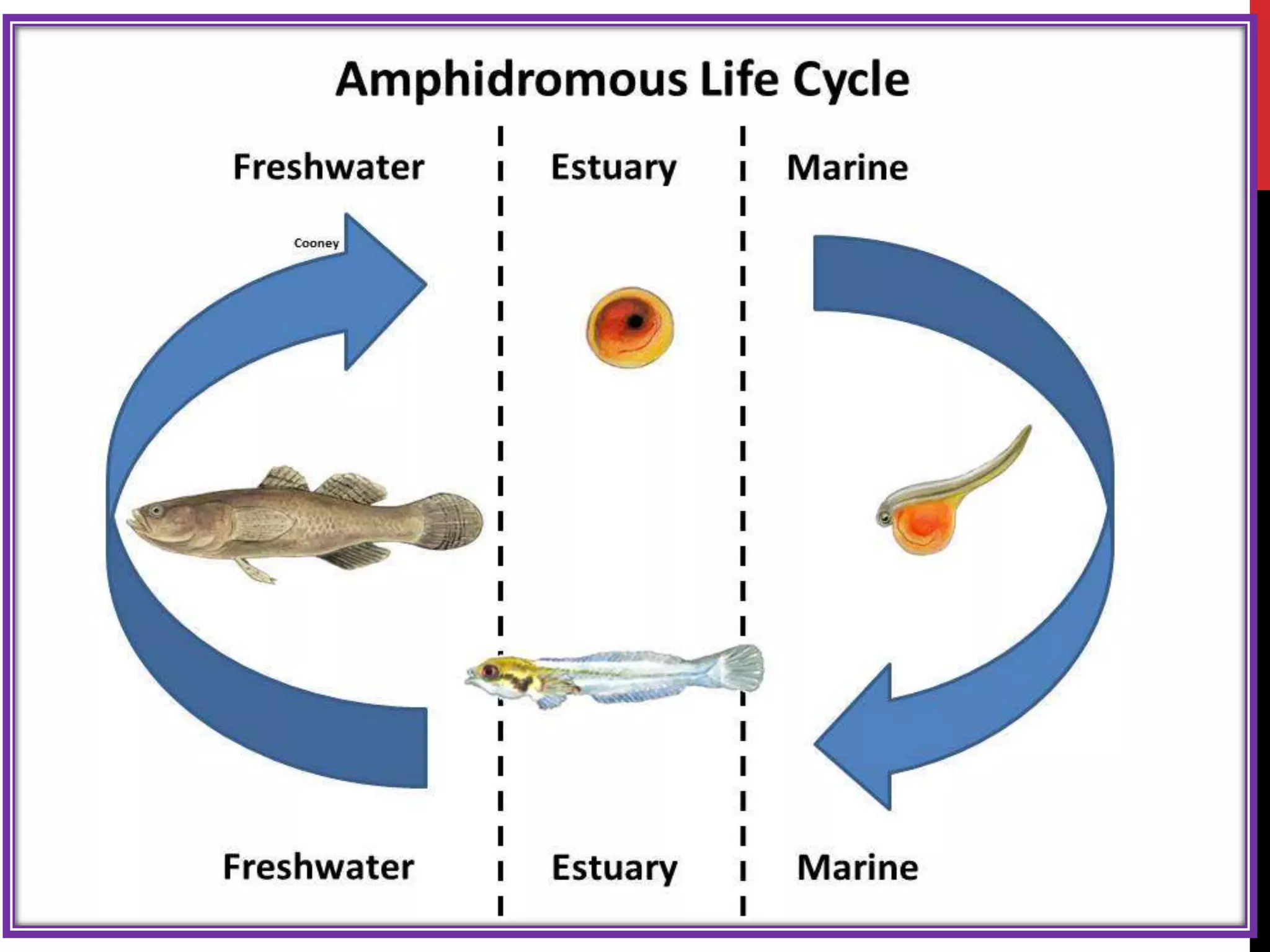
3) Migration patterns vary between species and include diadromous (between fresh and salt water), potamodromous (within fresh