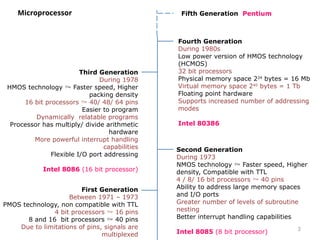
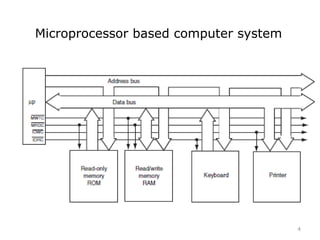
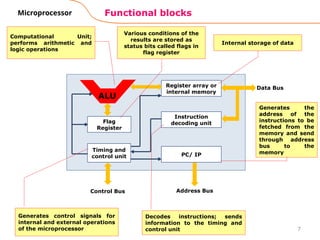
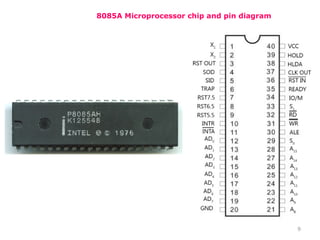
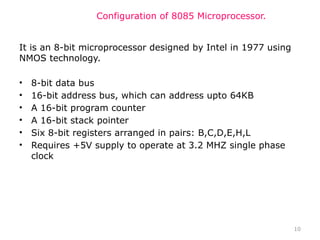
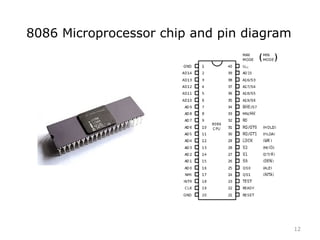
The document provides an overview of microprocessor assembly programming, detailing the evolution and characteristics of various generations of microprocessors from the first generation PMOS technology in the 1970s to the fifth generation Pentium 4 systems. It outlines different types of buses (address, data, and control), peripheral devices, and the functional blocks of microprocessors like the 8085 and 8086. Key specifications and advancements in processing technology, such as speed, internal memory, and addressing capabilities, are also highlighted.