This document provides an introduction to computers, including:
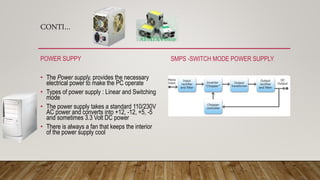
- The basic components of a computer like the CPU, RAM, motherboard, power supply, hard drive, and connectors.
- Classification of computers into supercomputers, mainframes, minicomputers, and microcomputers.
- Computer processing speeds measured in milliseconds, microseconds, nanoseconds, and picoseconds.
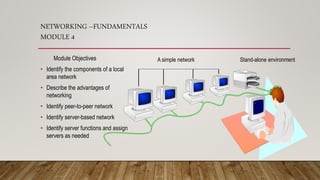
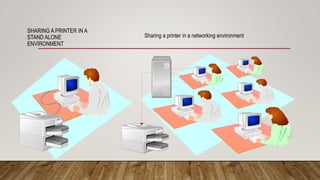
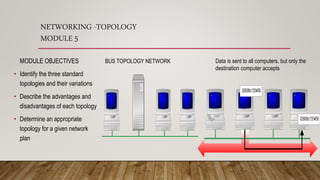
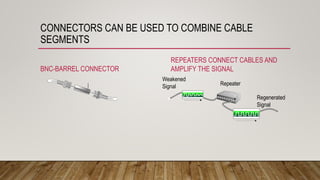
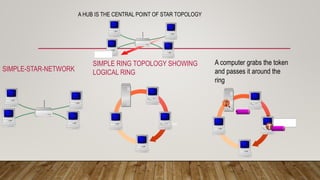
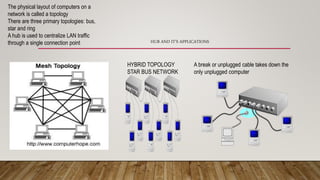
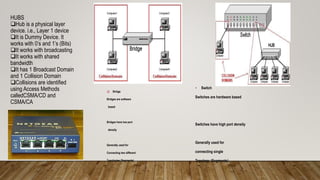
- Networking fundamentals like topologies, cabling, IP addressing, and network devices like hubs, switches, and routers.