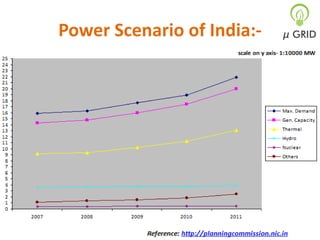
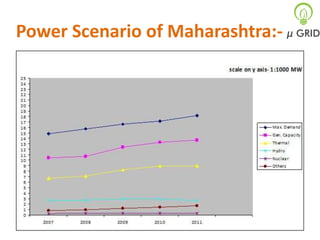
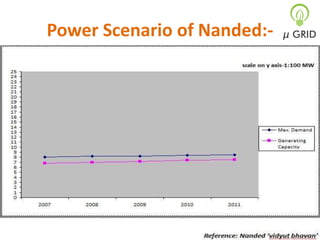
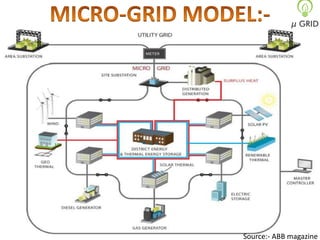
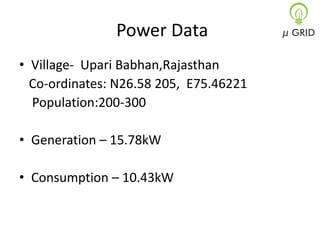
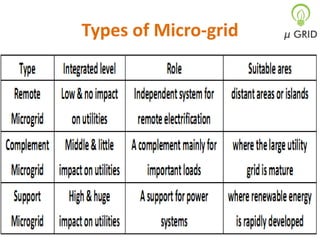
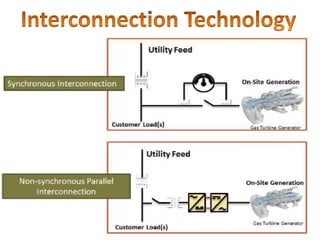
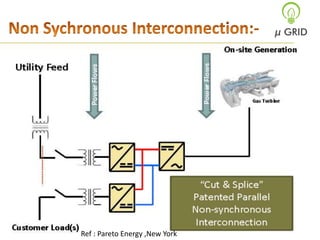
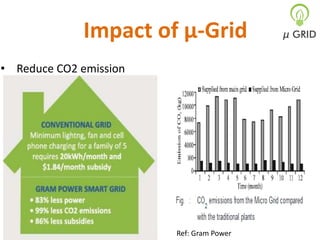
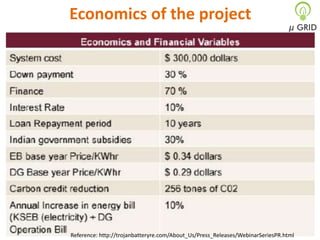
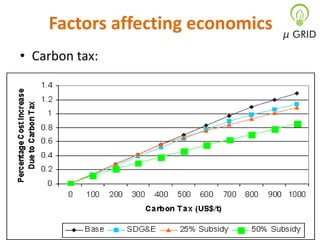
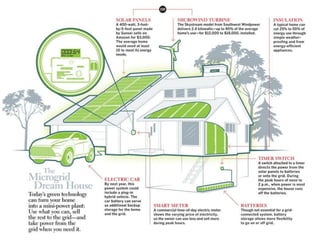
This document discusses microgrids, including their technologies, impacts, and conclusions. It describes the power scenarios of India and some local areas. Microgrids can utilize technologies like combined heat and power, smart metering, efficient batteries, and interconnection systems. They provide sustainable energy and reduce emissions while benefiting communities economically. Microgrids are viable in remote areas lacking transmission infrastructure. Government policies aim to support microgrid development through funding, regulations, and carbon credits.