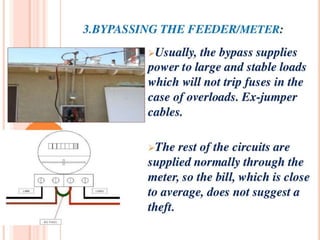
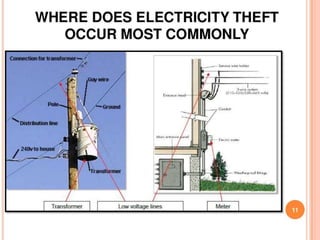
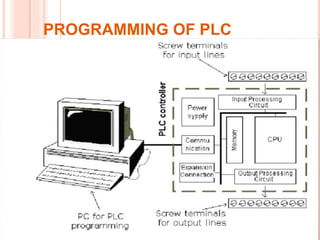
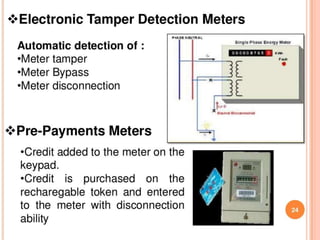
This document summarizes a seminar presentation on a microcontroller-based power theft identification system. It introduces power theft as the illegal use of electrical power without paying the supplier. It then describes two common ways that power theft occurs: slowing down electricity meters with magnets, and inverting meters to make them count backwards. The proposed system architecture integrates a wireless network with the electrical grid to monitor multiple points using data aggregation algorithms. A microcontroller like a PLC would be programmed to detect theft and control the electrical distribution in response.