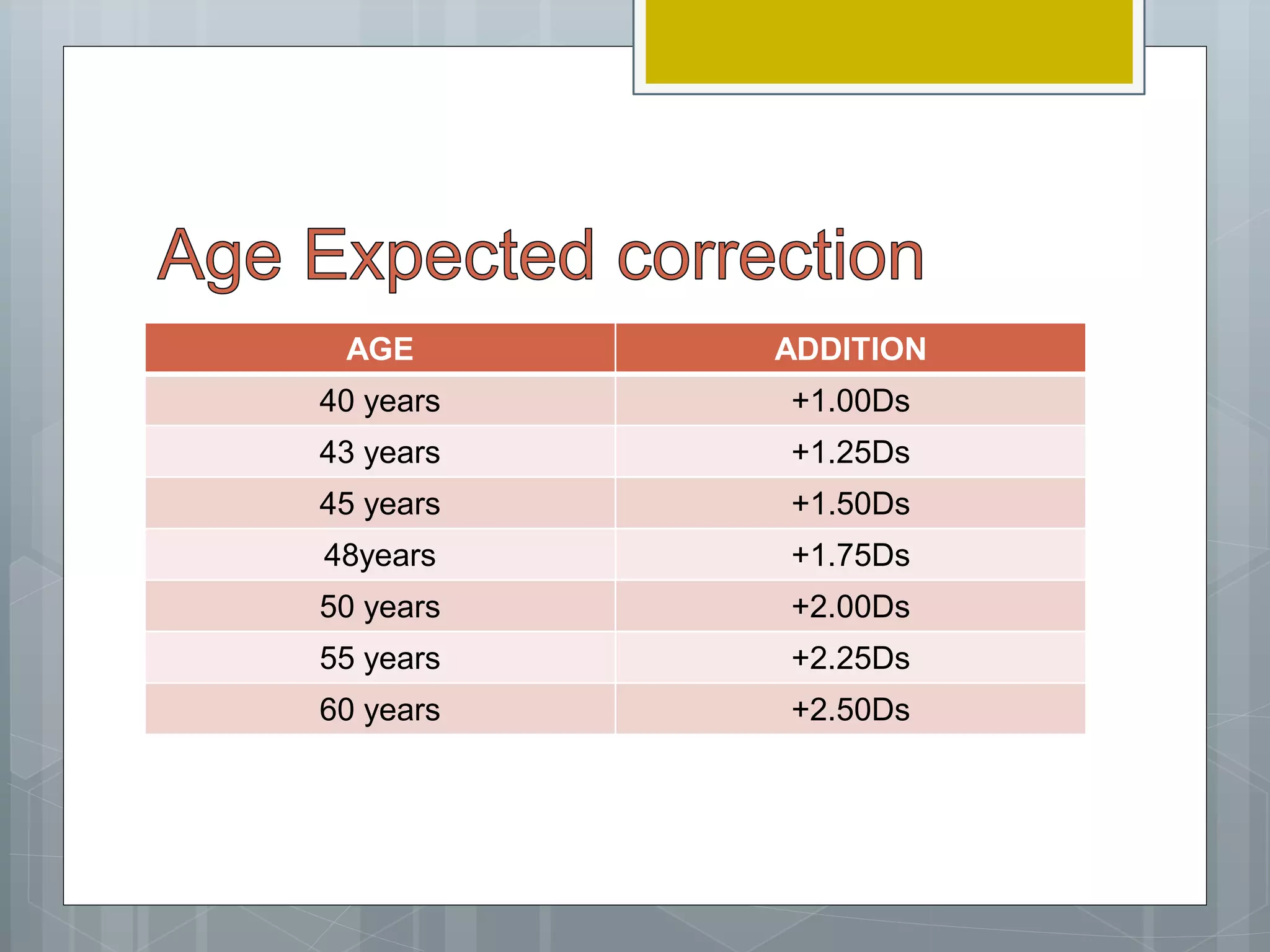
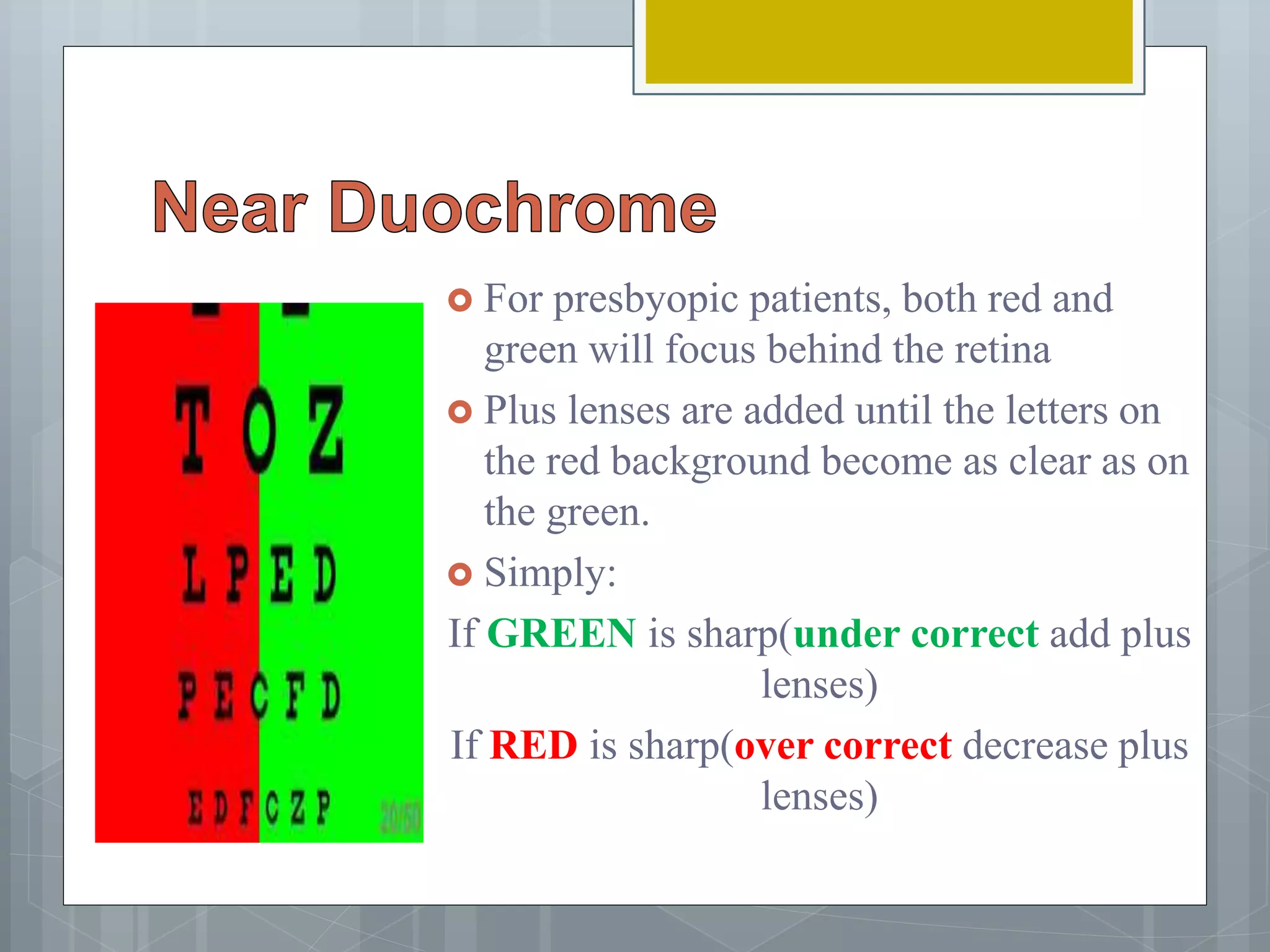
This document discusses various methods for determining the near addition required for presbyopia correction, including dynamic retinoscopy, determining the tentative addition, and age-expected additions. It provides details on techniques like determining the near point of accommodation, using cross cylinders and near duochromes to refine the prescription, and calculating the near addition needed based on the reading distance and a patient's amplitude of accommodation while leaving some accommodation in reserve.