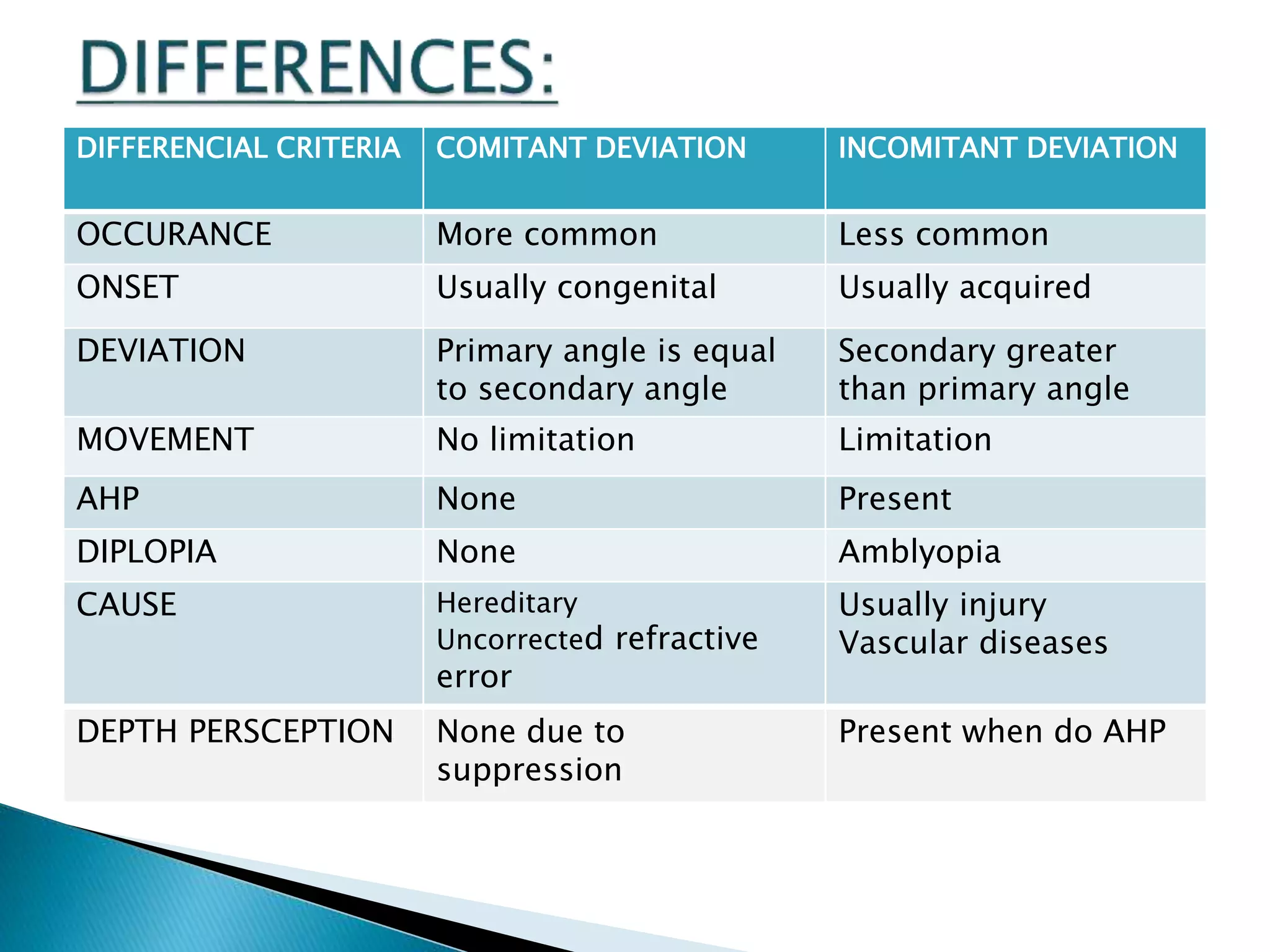
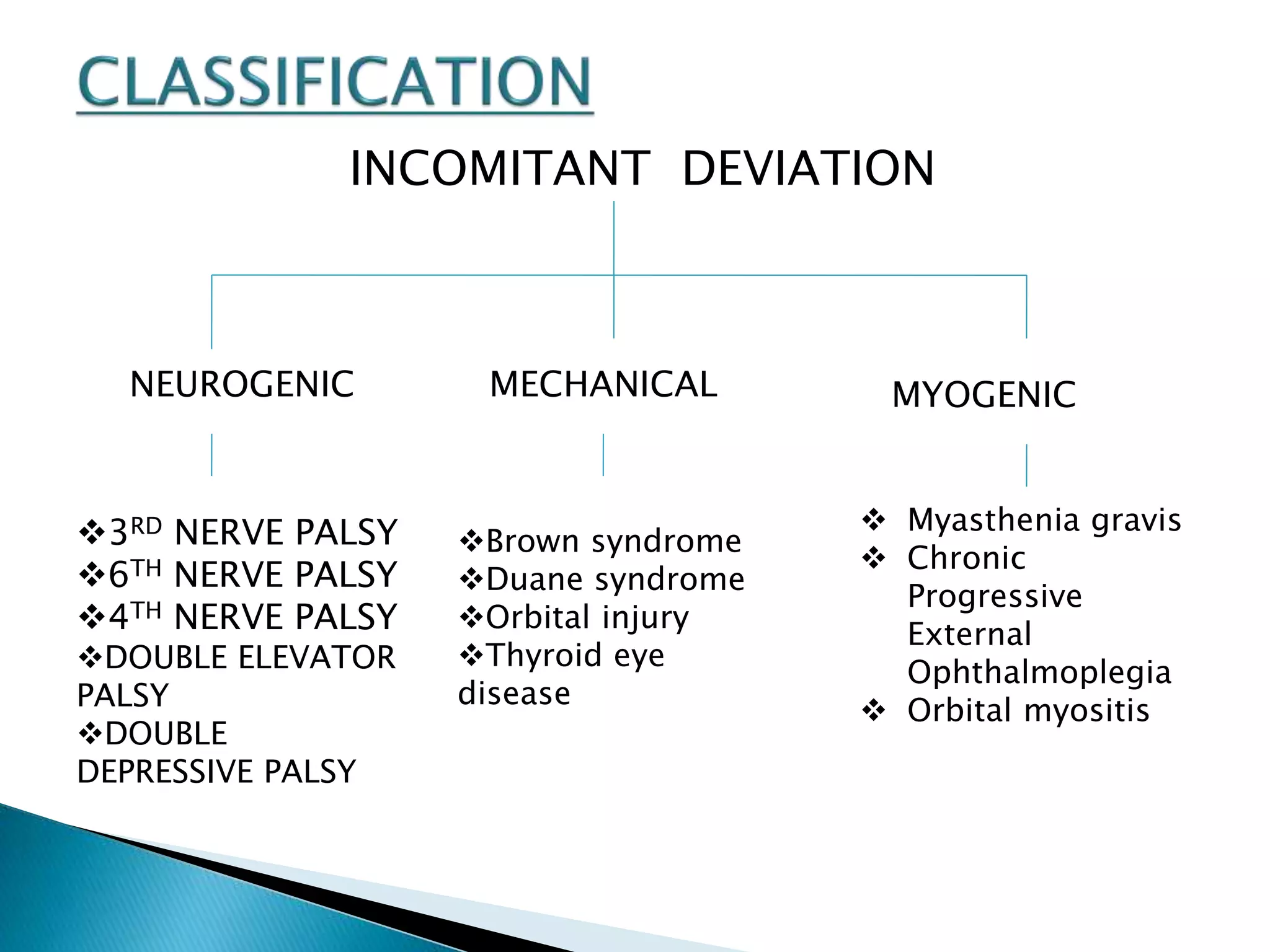
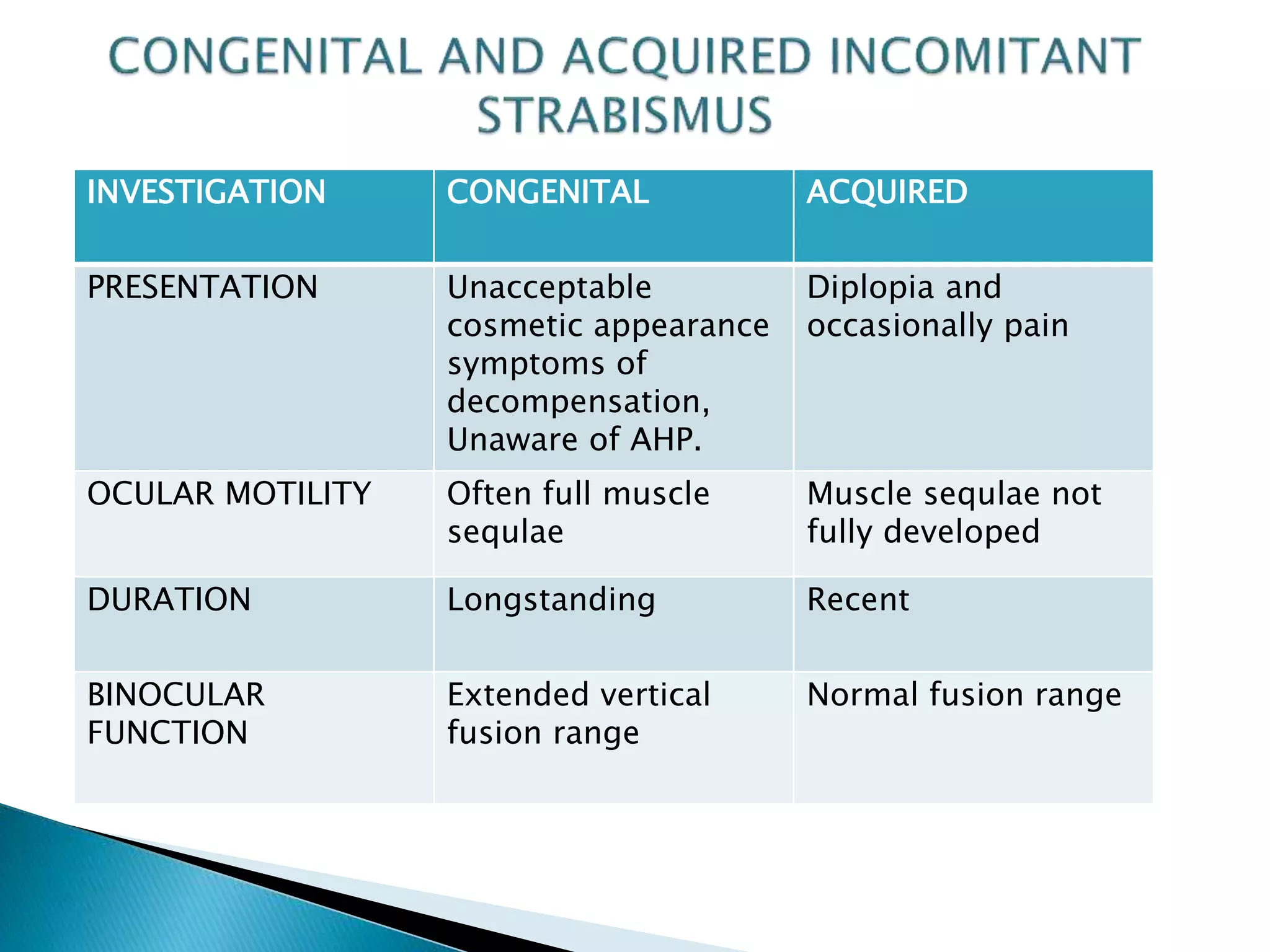
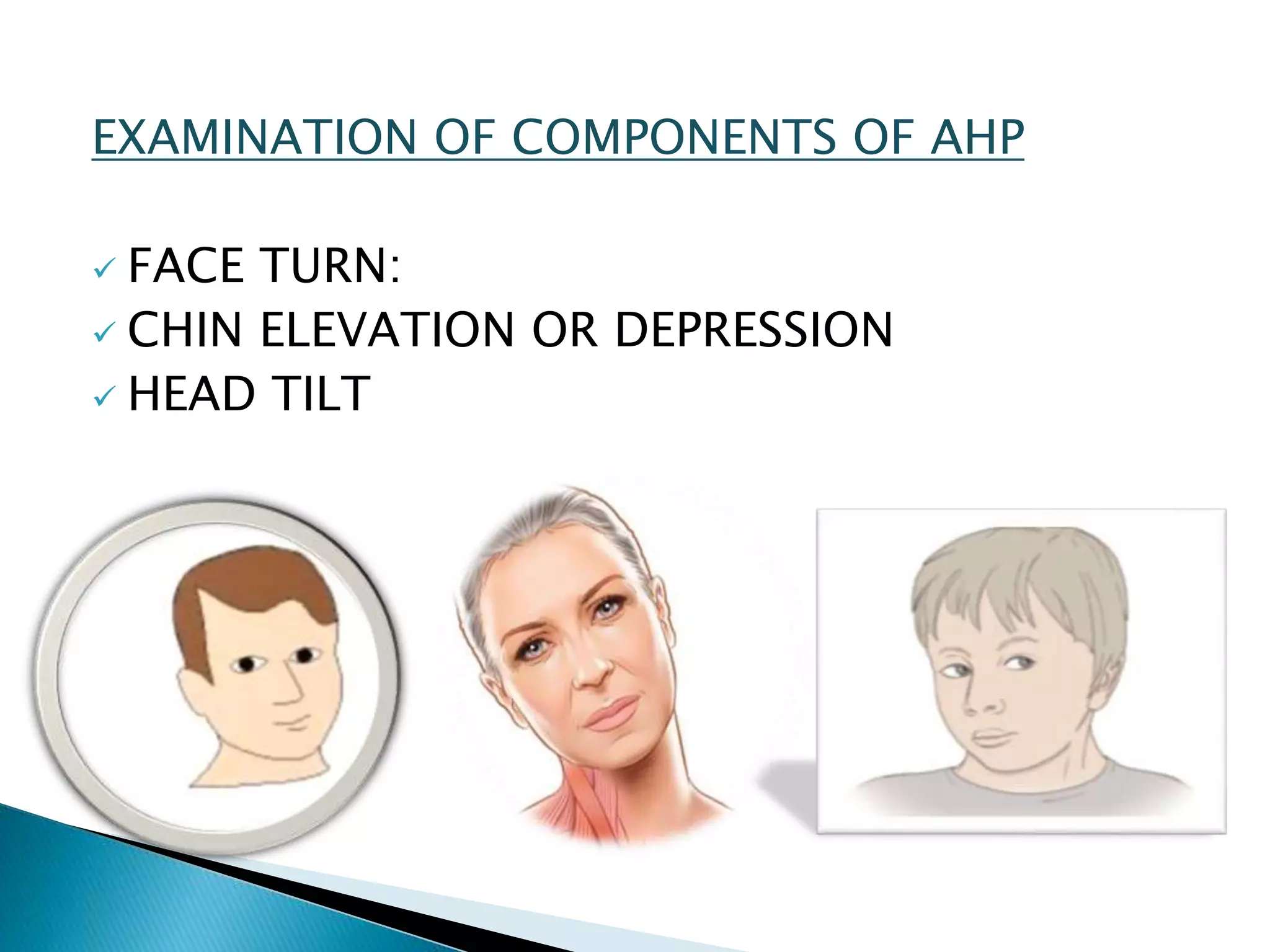
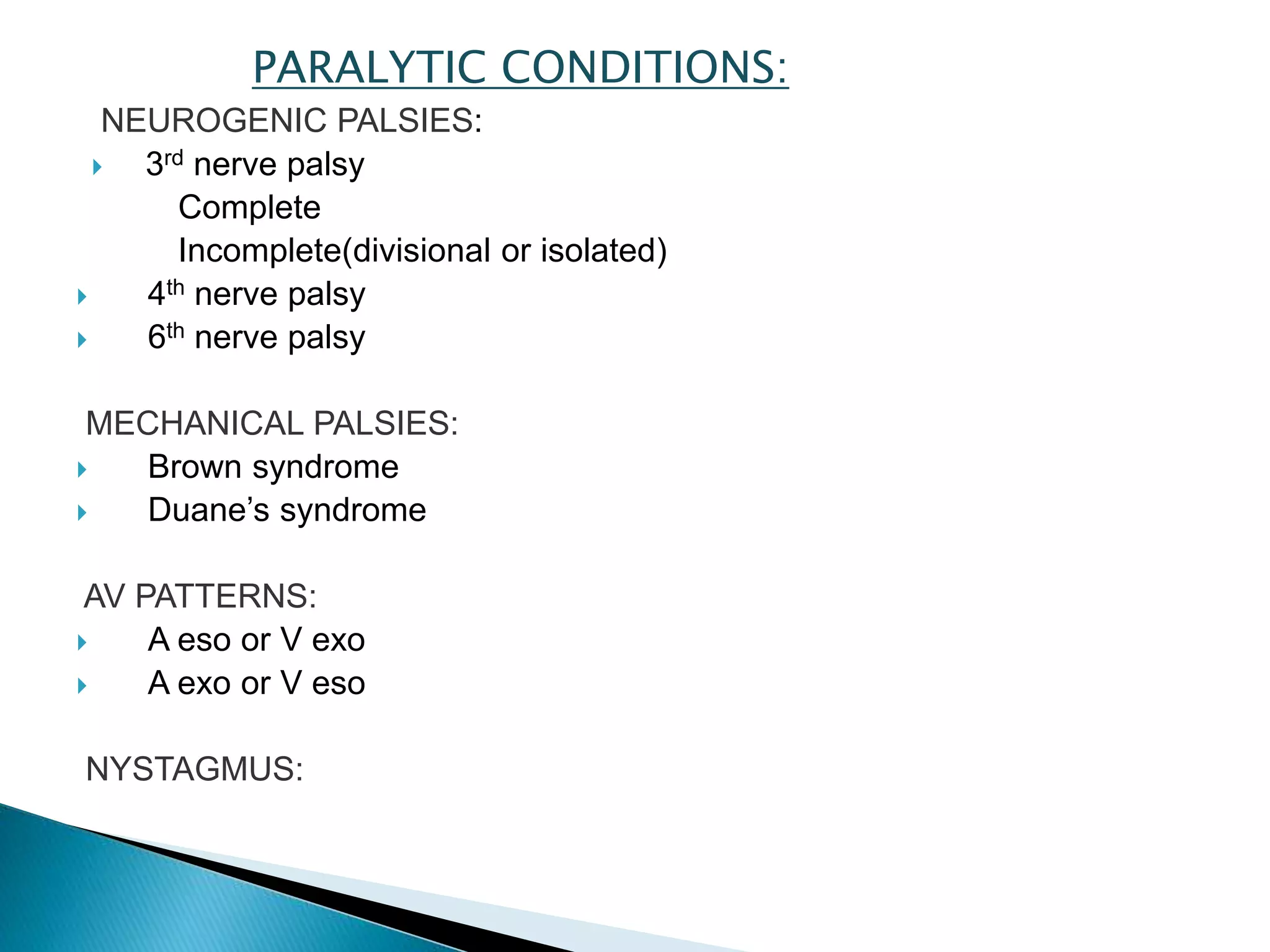
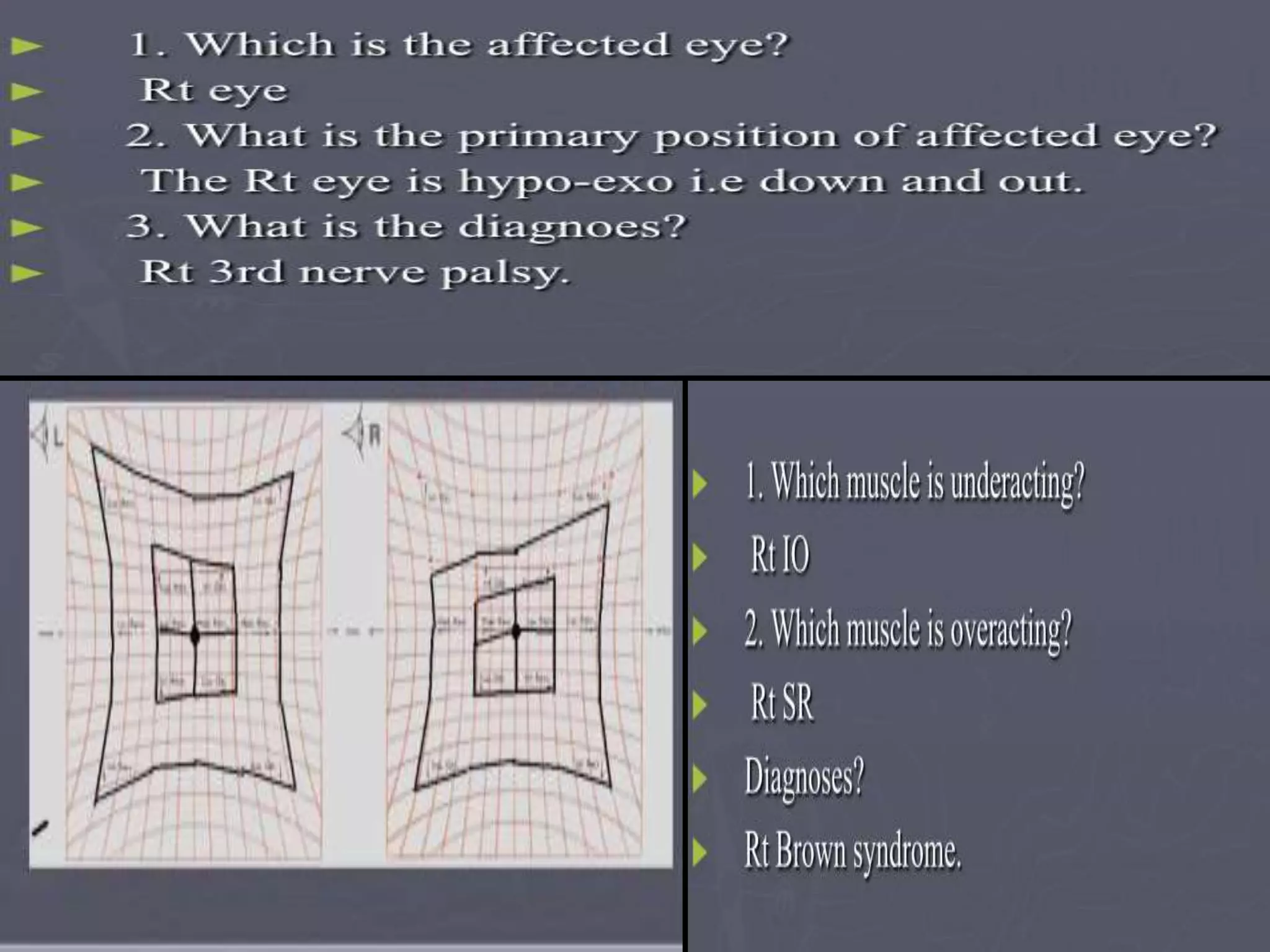
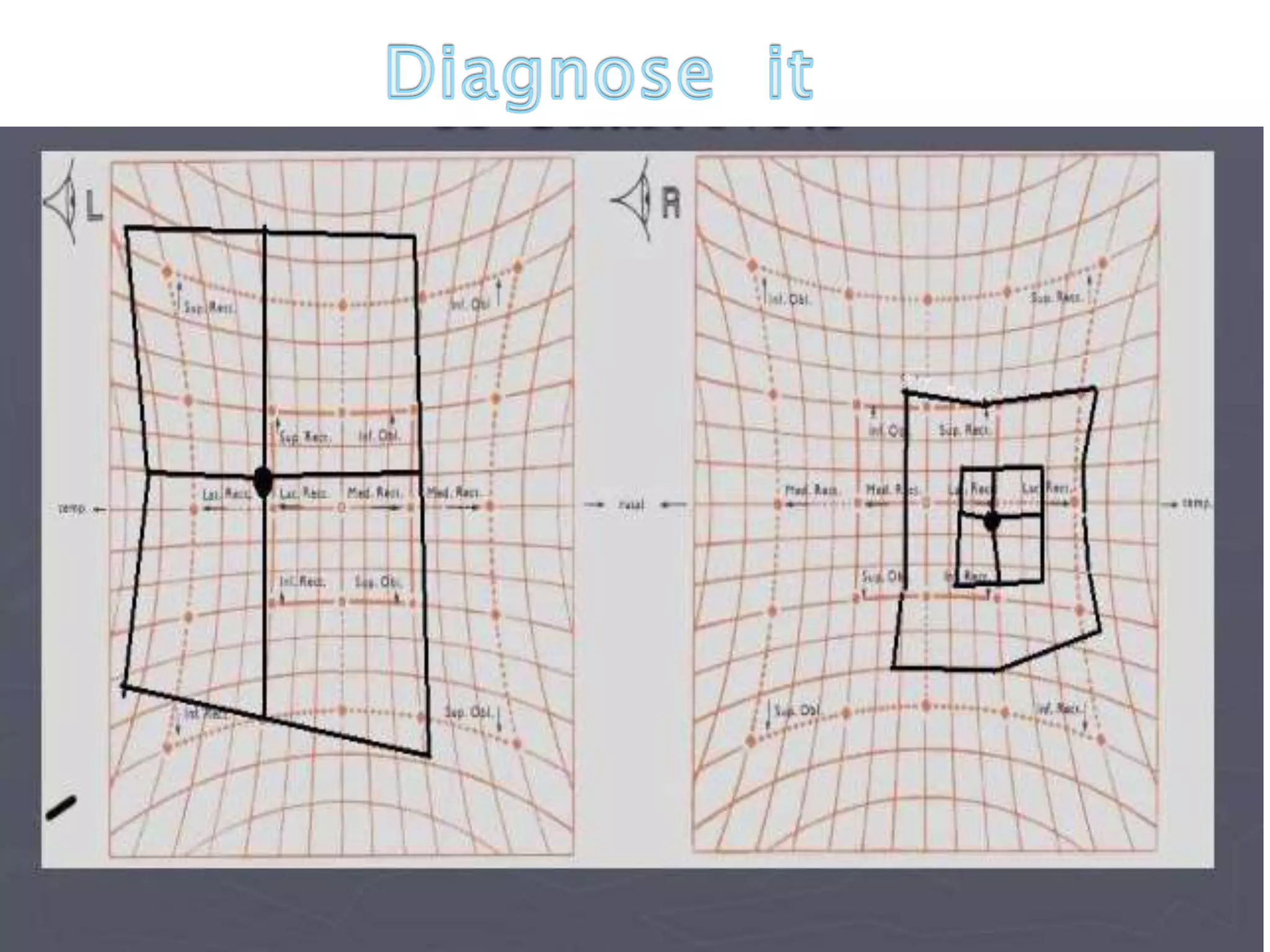
This document discusses abnormal head posture, concomitant and incomitant strabismus, and Hess chart testing. It defines concomitant as having equal angle of deviation in all gazes, while incomitant deviation varies between gazes. Incomitant can be neurogenic from nerve palsies or mechanical from conditions like Brown syndrome. Abnormal head posture is a motor adaptation to maintain comfortable vision and includes face turns, chin elevation/depression, and head tilts. Hess chart testing uses red/green filters or mirrors to dissociate the eyes and identify muscle weaknesses or palsies.