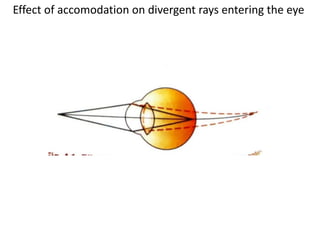
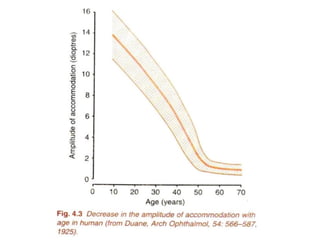
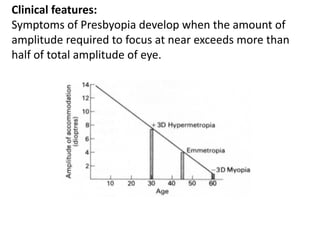
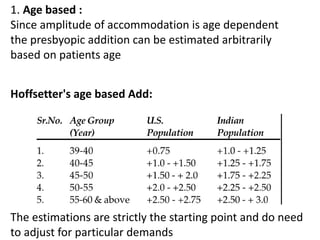
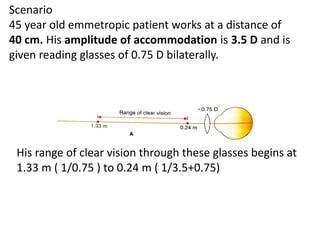
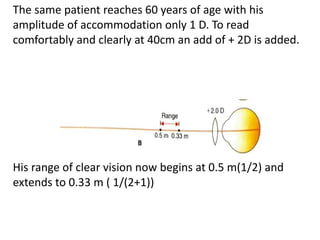
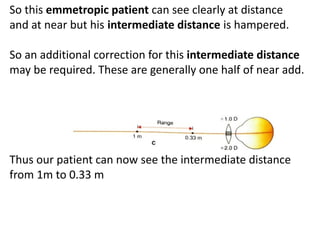
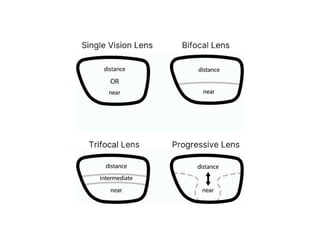
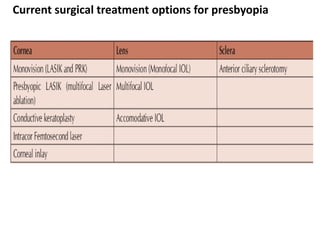
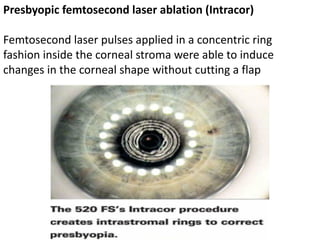
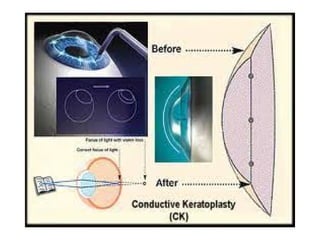
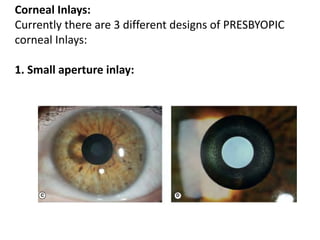
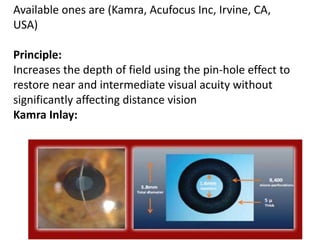
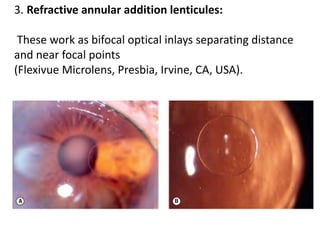
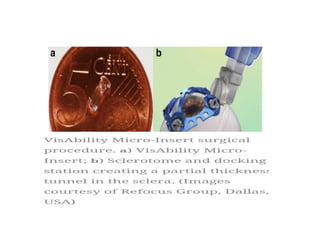
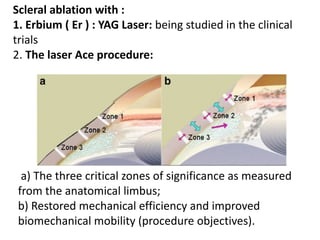
Presbyopia is an age-related condition characterized by a progressive loss of the eye's ability to focus on near objects, beginning around age 40-45. It results from a decrease in the elasticity and flexibility of the lens as we age. Presbyopia can be treated using optical corrections like reading glasses, bifocals, or progressive lenses which supplement the eye's lost accommodation. Surgical treatments include corneal procedures like LASIK to induce multifocality, conductive keratoplasty, or corneal inlays. Lens procedures include multifocal IOL implants during cataract surgery or accommodating IOLs. Experimental scleral procedures also aim to restore accommodation.