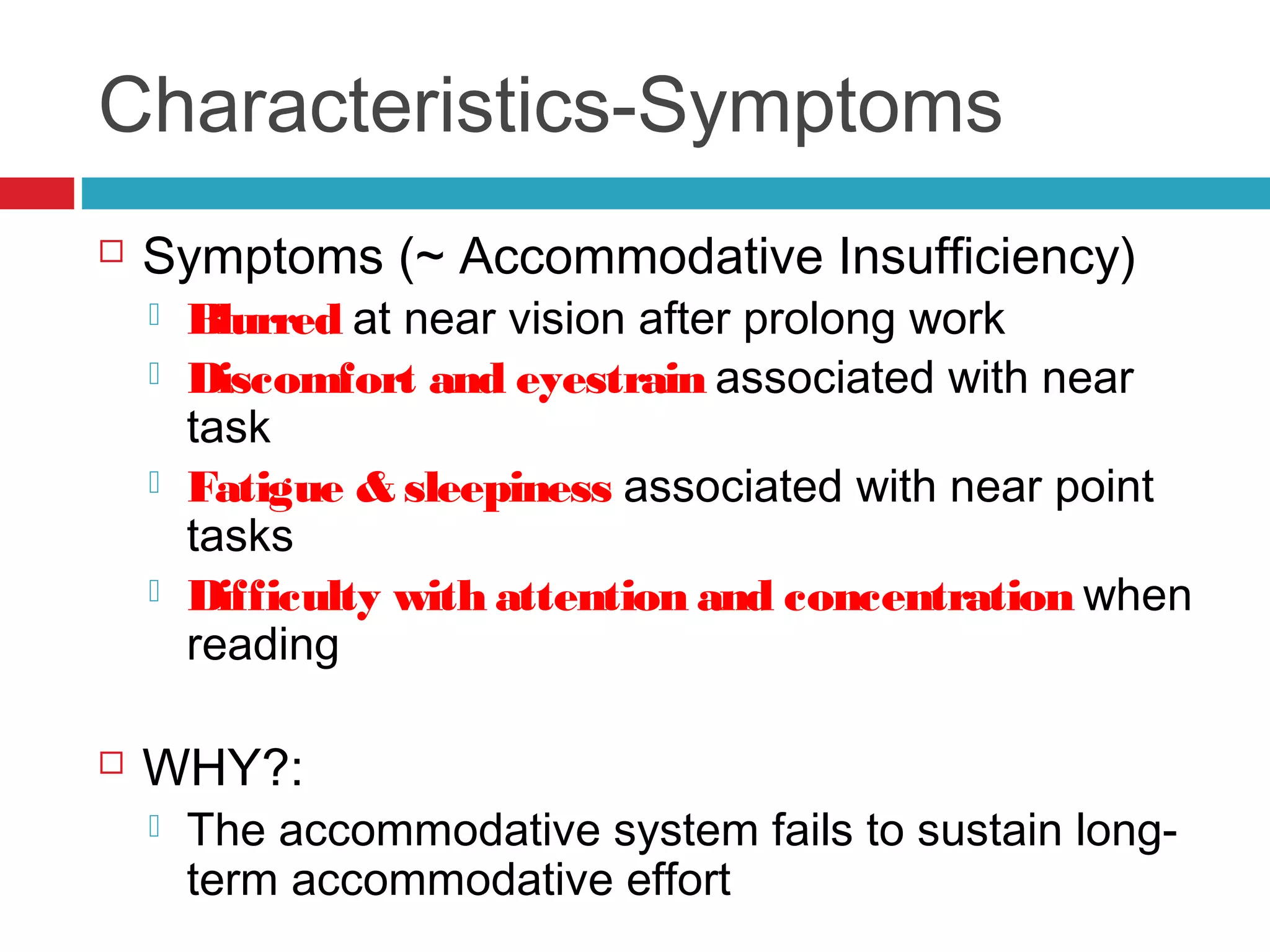
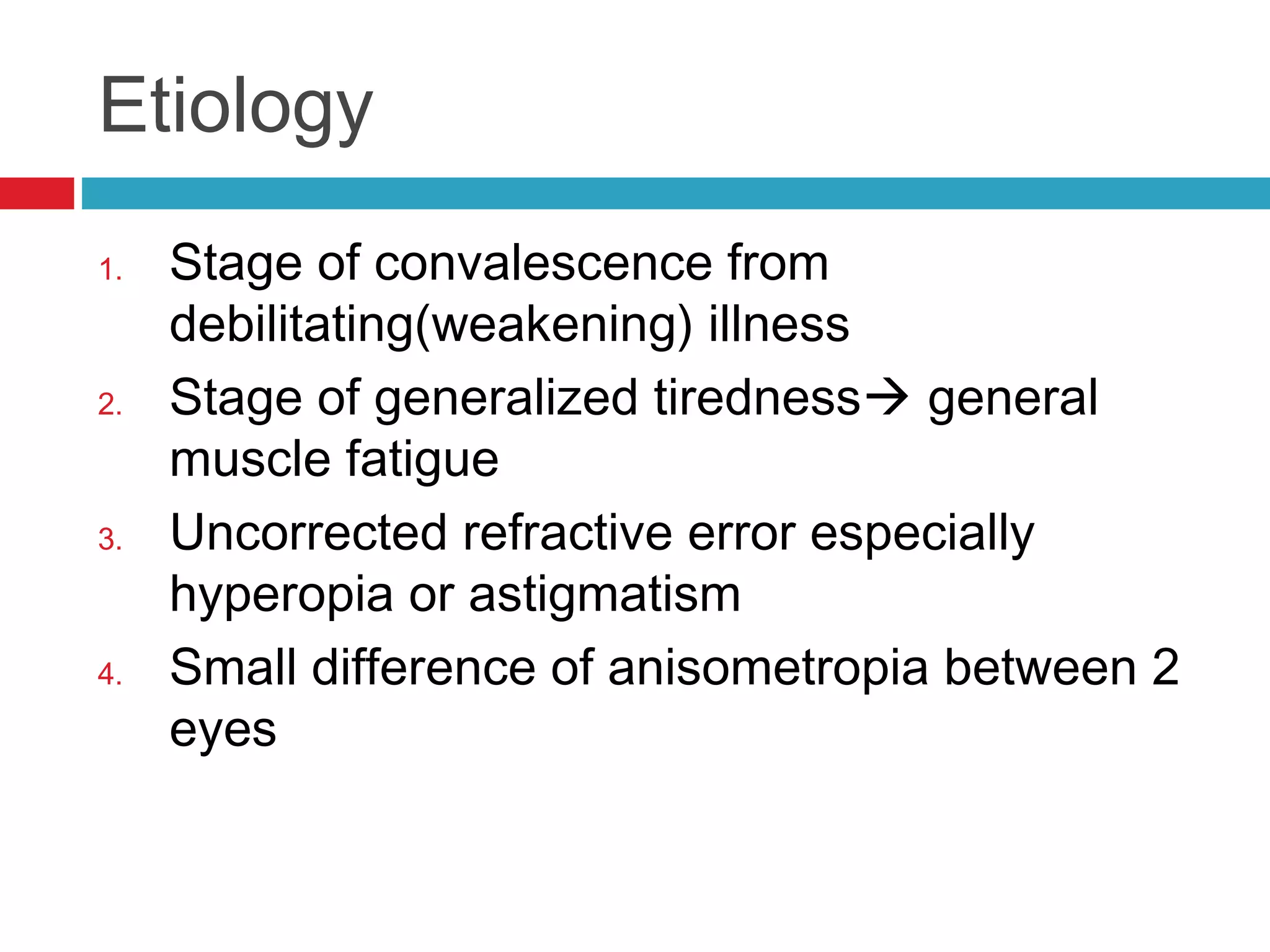
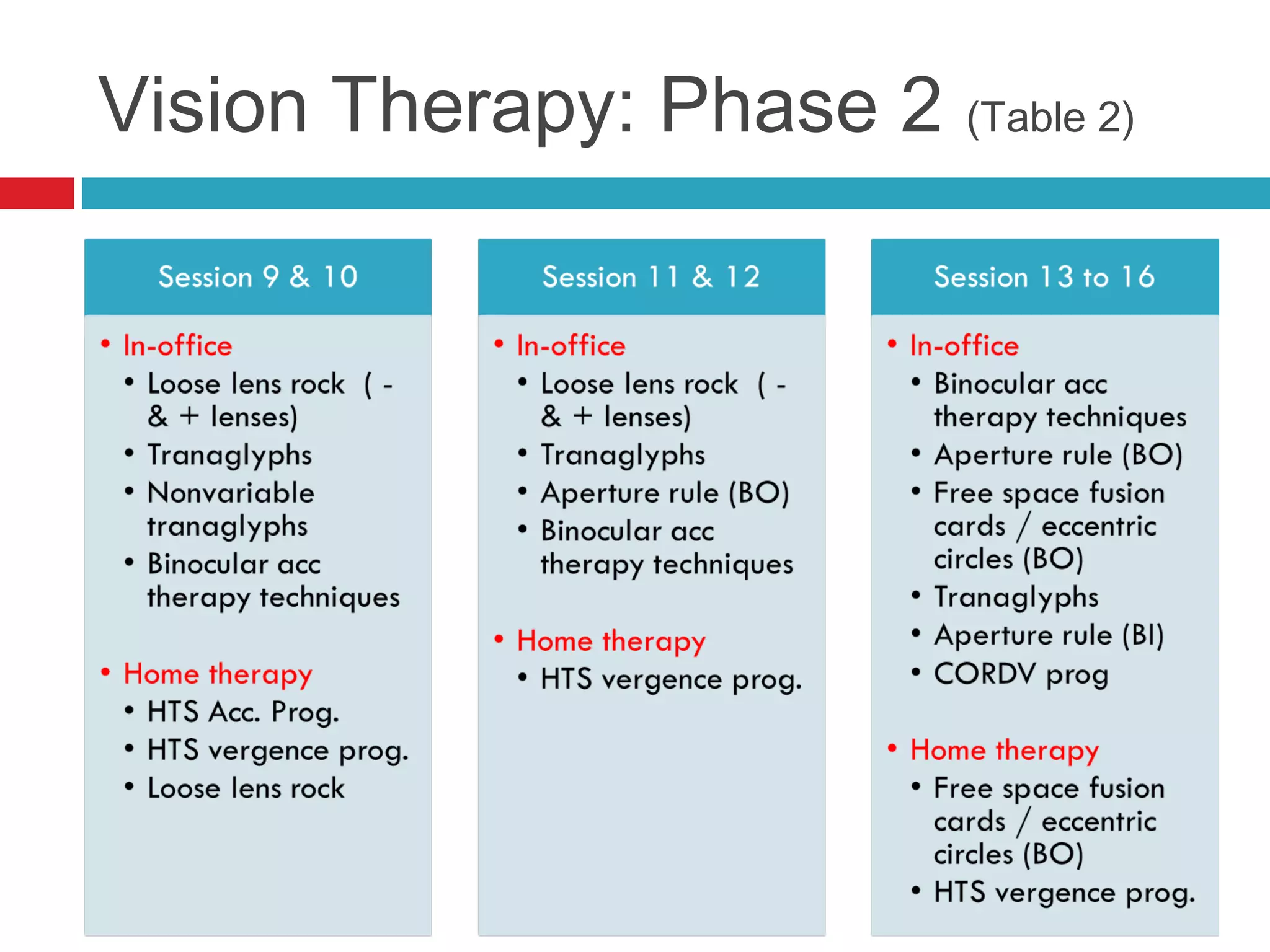
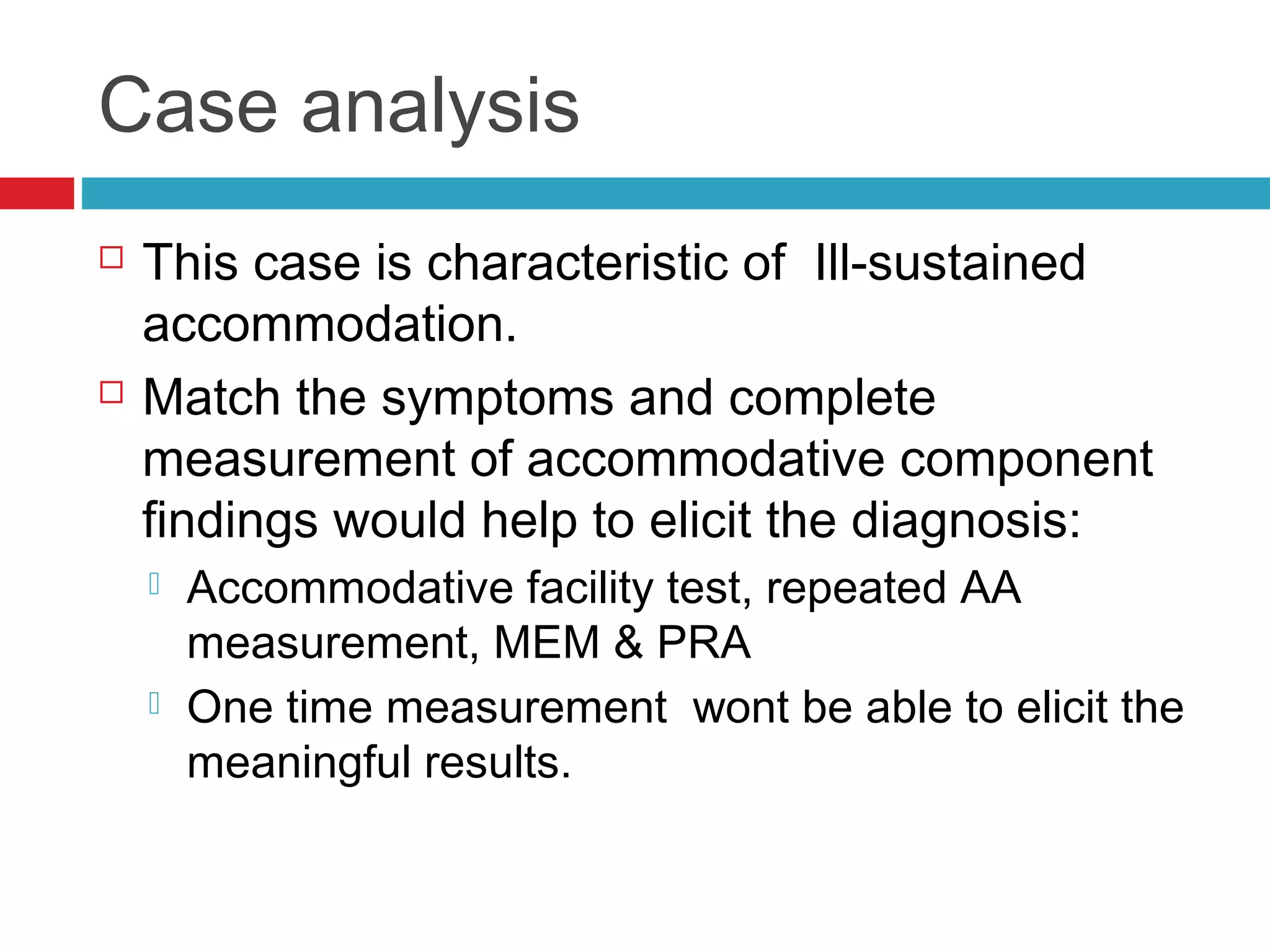
Ill-sustained accommodation is a condition where accommodative ability is normal initially but diminishes with sustained effort, causing blurred vision and discomfort during near tasks. Management options include correcting ametropia, using added plus lenses, and vision therapy to restore normal accommodation. A case study illustrates successful treatment through vision therapy, resulting in improved symptoms and function.