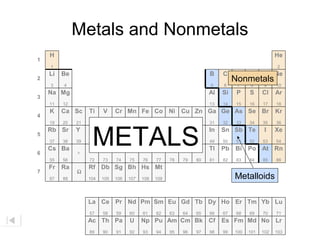
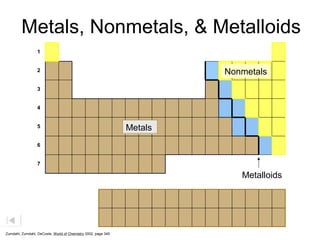
The document discusses metals, nonmetals, and metalloids according to their placement on the periodic table. Metals are located on the left side of the zigzag line, nonmetals are on the right side, and metalloids are along the zigzag line. Metals are malleable, ductile, good conductors while nonmetals are brittle, poor conductors. Metalloids exhibit properties between metals and nonmetals.