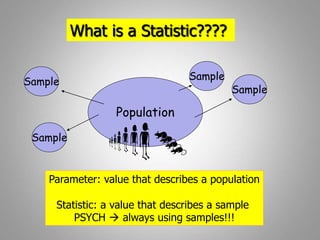
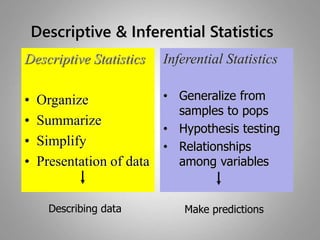
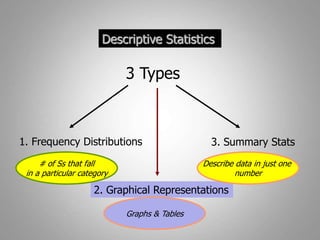
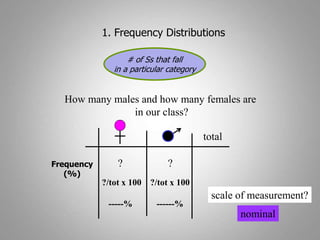
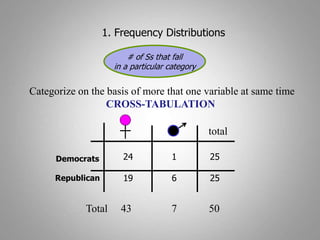
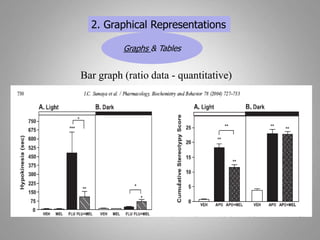
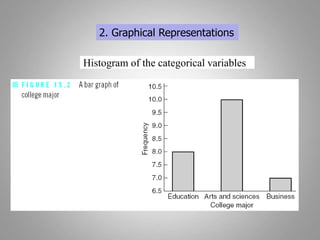
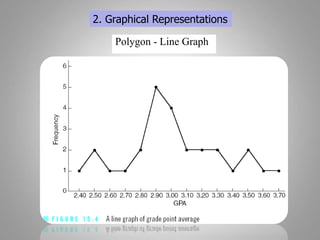
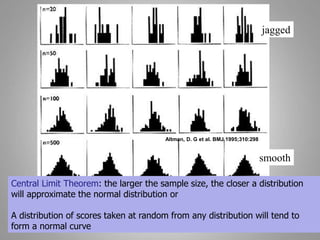
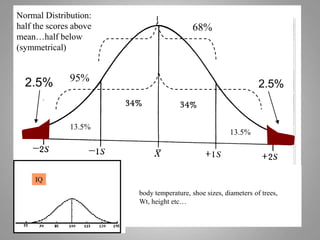
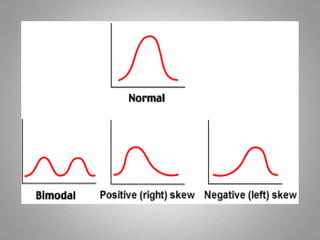
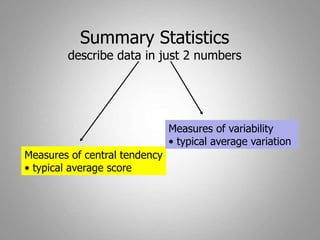
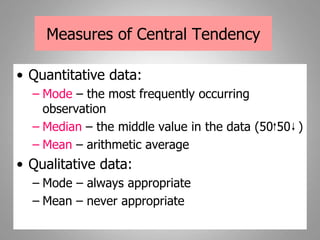
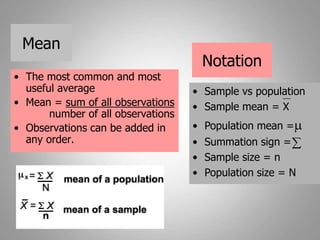
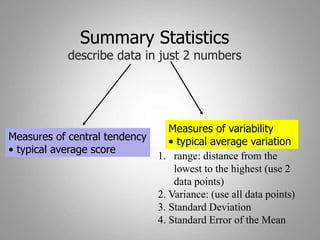
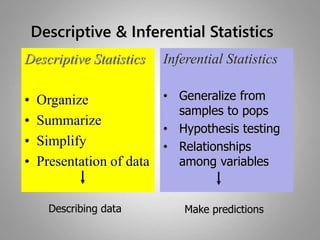
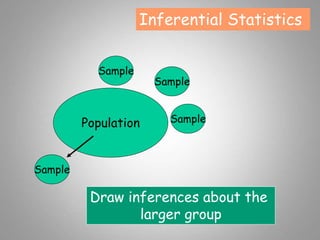
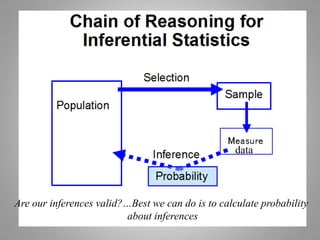
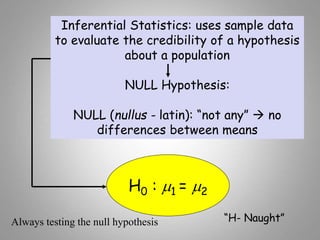
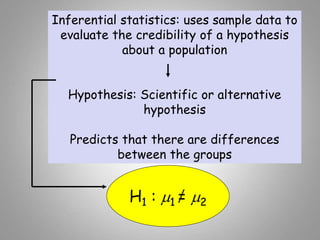
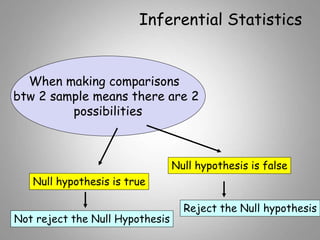
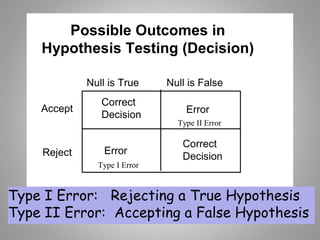
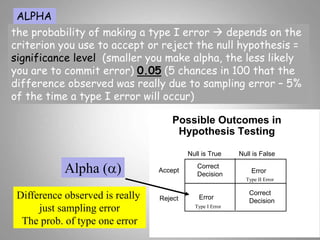
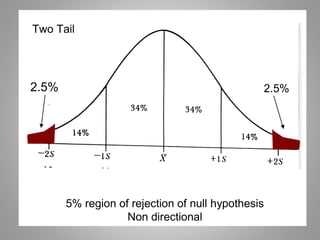
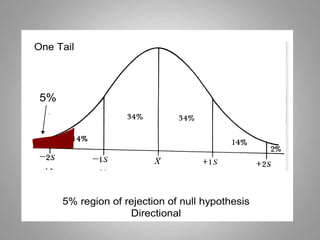
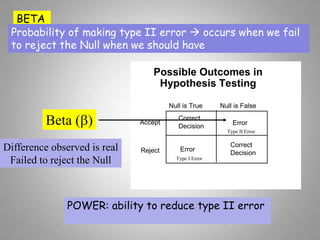
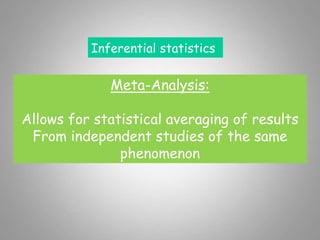
This document discusses descriptive and inferential statistics. Descriptive statistics summarize and organize data through frequency distributions, graphs, and summary statistics like the mean, median, mode, variance, and standard deviation. Inferential statistics allow generalization from samples to populations through hypothesis testing, where the null hypothesis is tested against the alternative hypothesis. Type I and type II errors are possible, and significance tests control the probability of type I errors through the alpha level while power analysis aims to reduce type II errors. Common inferential tests mentioned include t-tests, ANOVA, and meta-analysis.