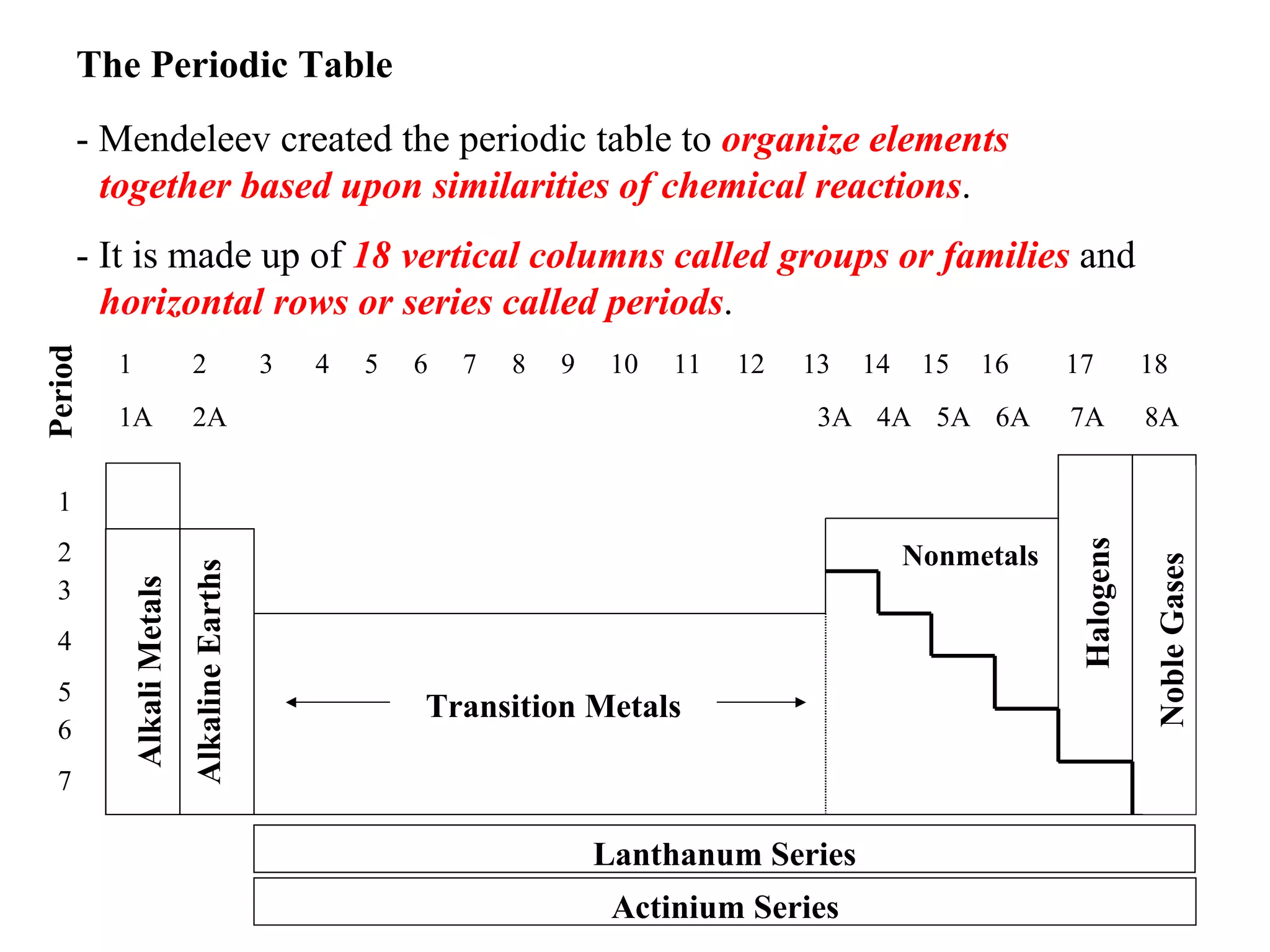
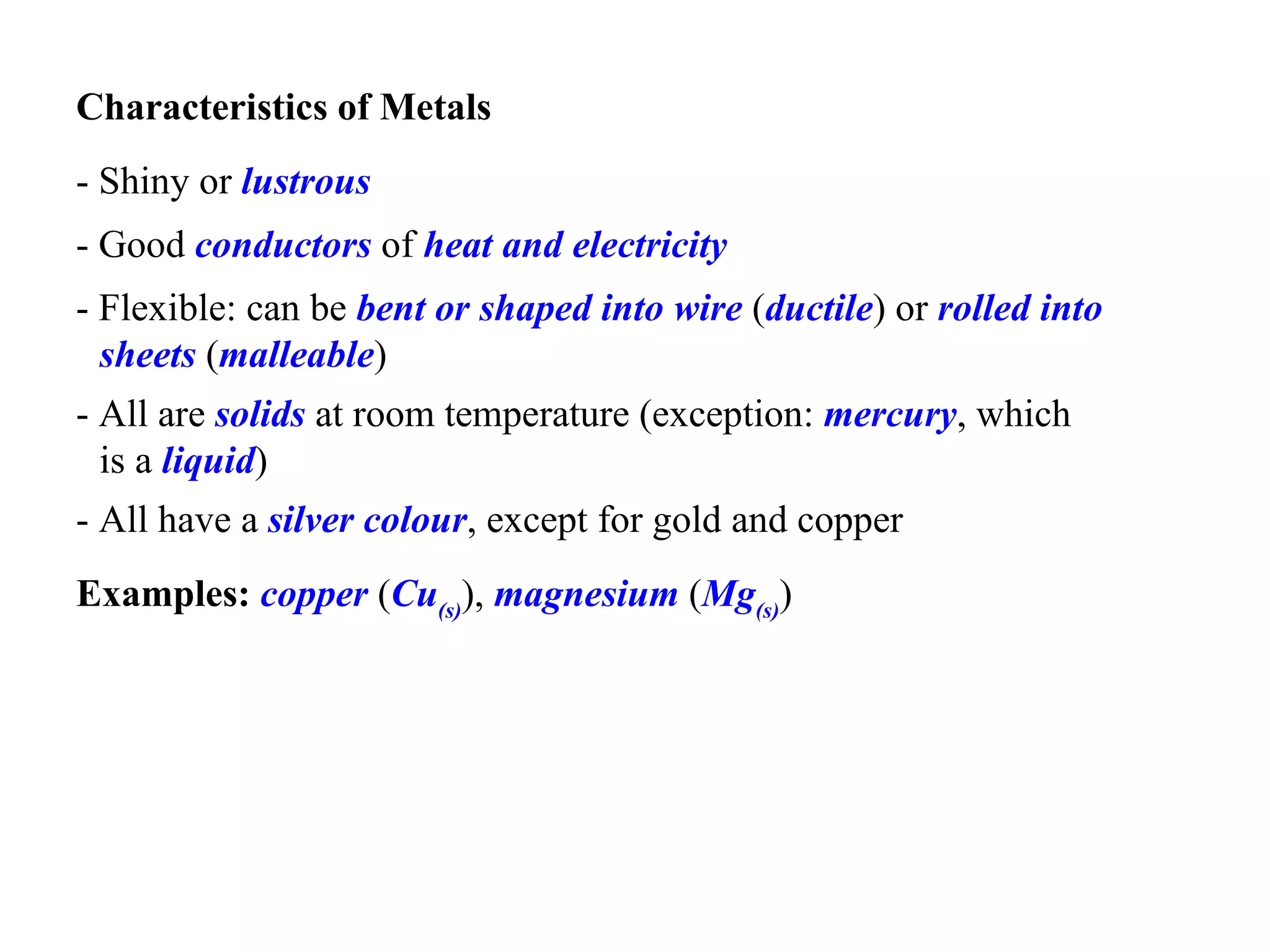- Mendeleev created the periodic table to organize elements based on similarities in their chemical reactions and properties.
- The periodic table is arranged in 18 vertical columns called groups and horizontal rows called periods.
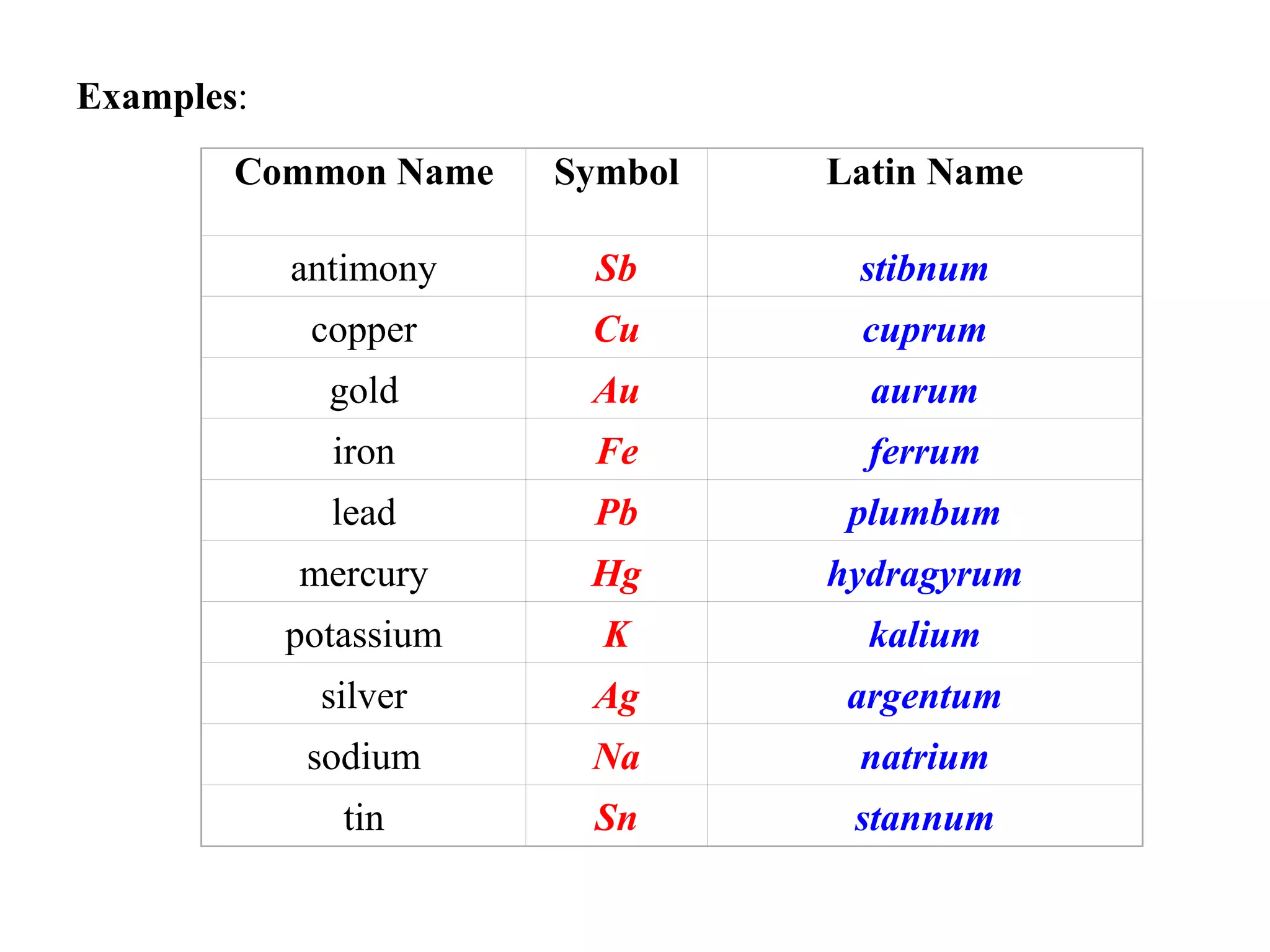
- Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, metalloids, or noble gases based on their physical properties such as appearance, conductivity, state of matter, and reactivity.