- The document discusses substances found in nature which can be categorized as natural or artificial/man-made substances. Natural substances such as coal and petroleum are further divided into metals and non-metals. Artificial substances are those made by humans like chairs and tables.
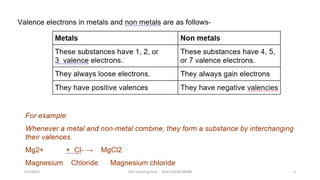
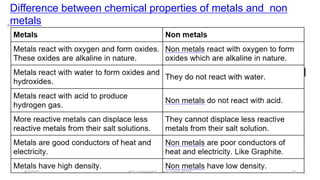
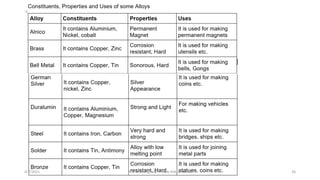
- The document then discusses atoms, elements, and molecules. Atoms are made up of electrons, protons, and neutrons. Valence electrons determine how atoms bond together. Metals and non-metals are introduced along with their properties. Corrosion of metals is discussed along with methods to prevent corrosion like painting, greasing, and electroplating.