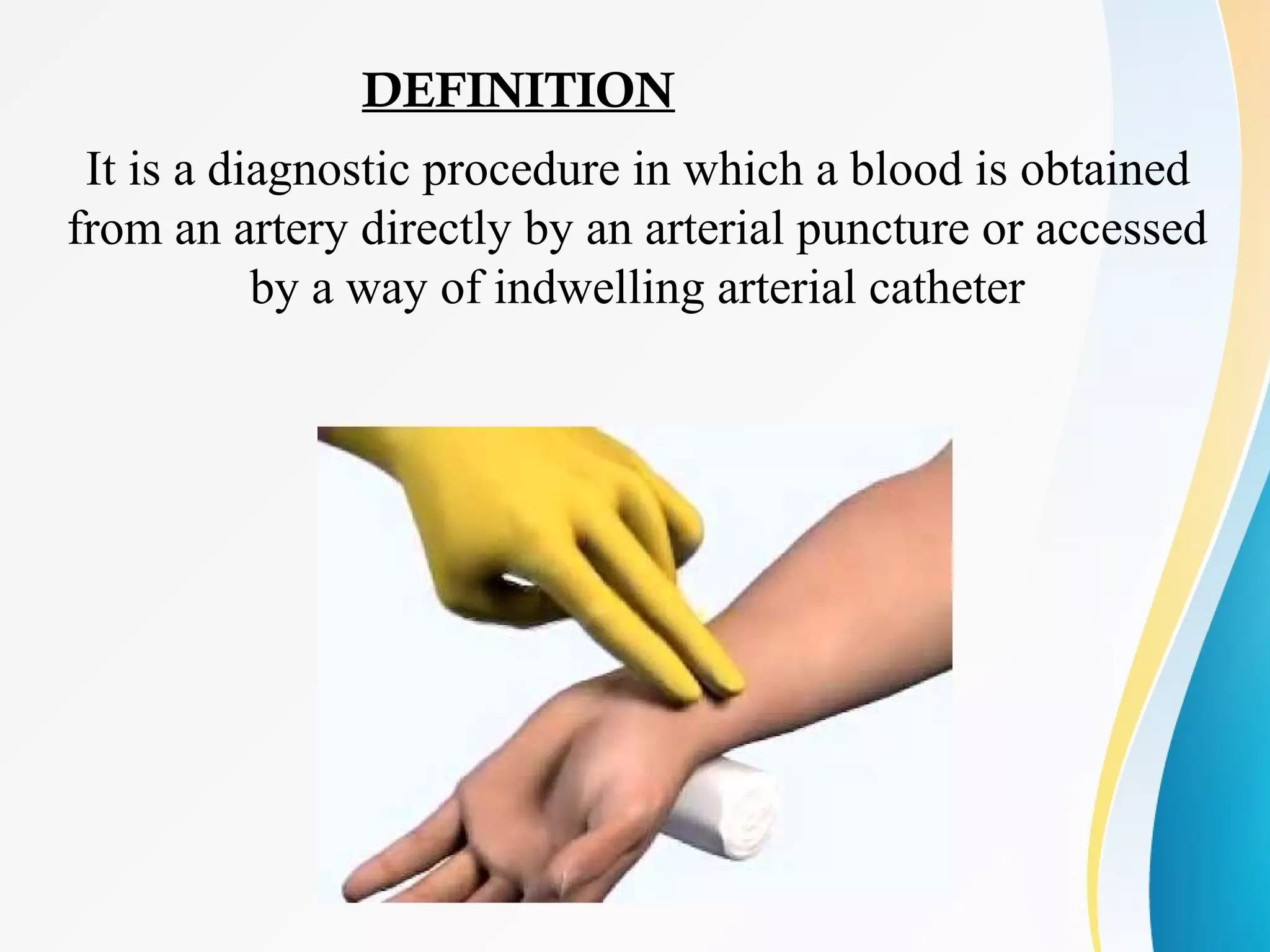
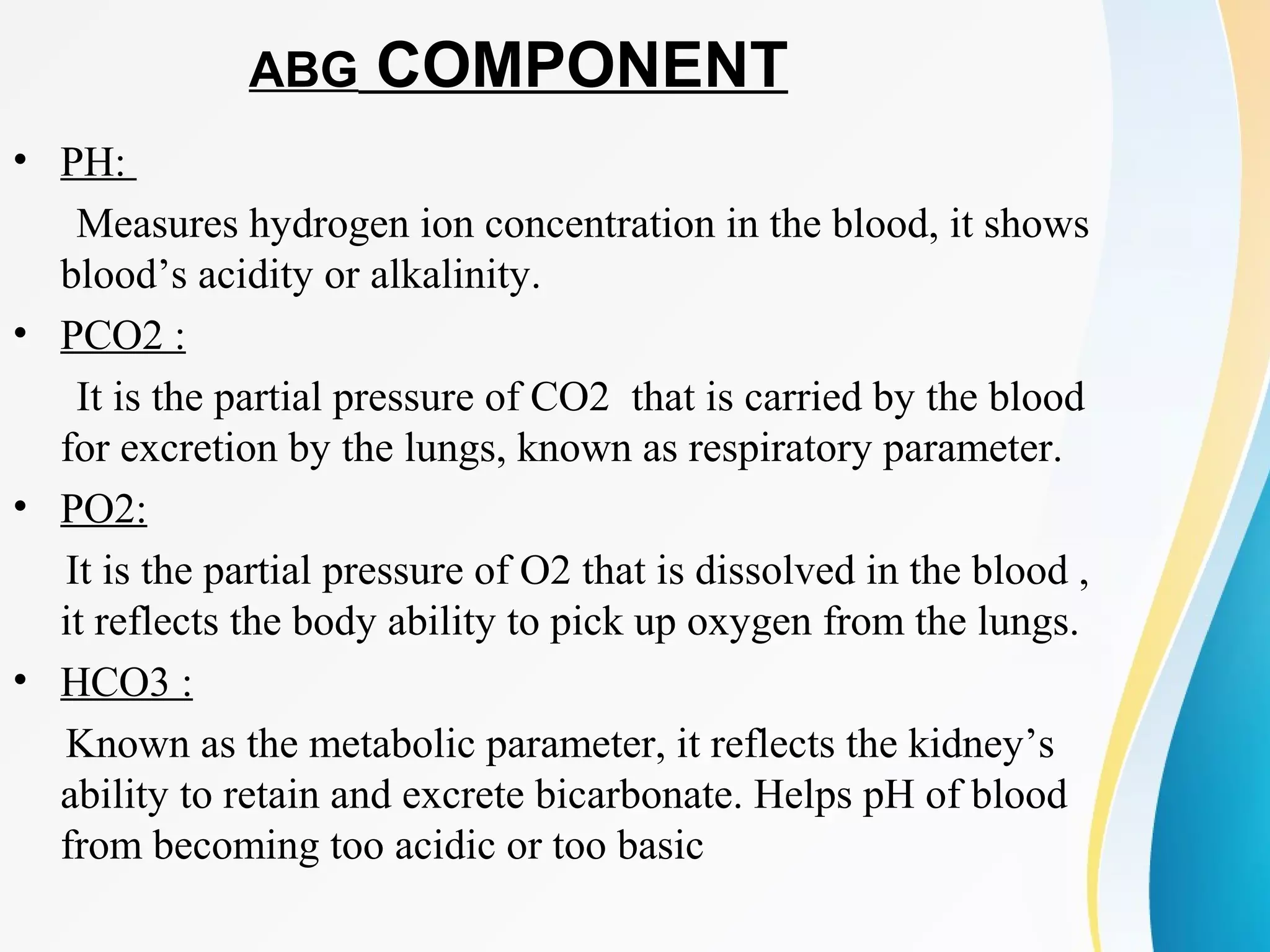
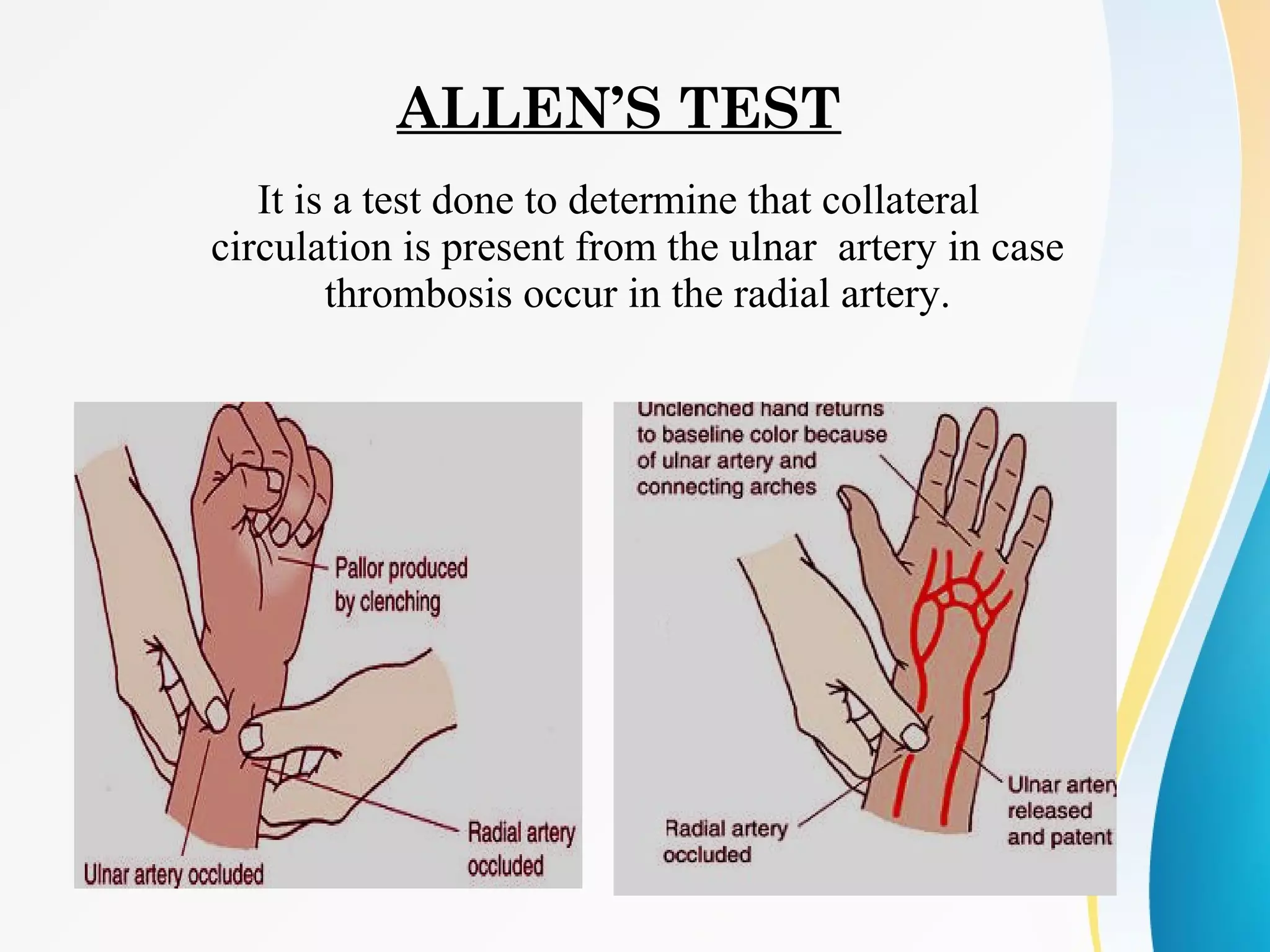
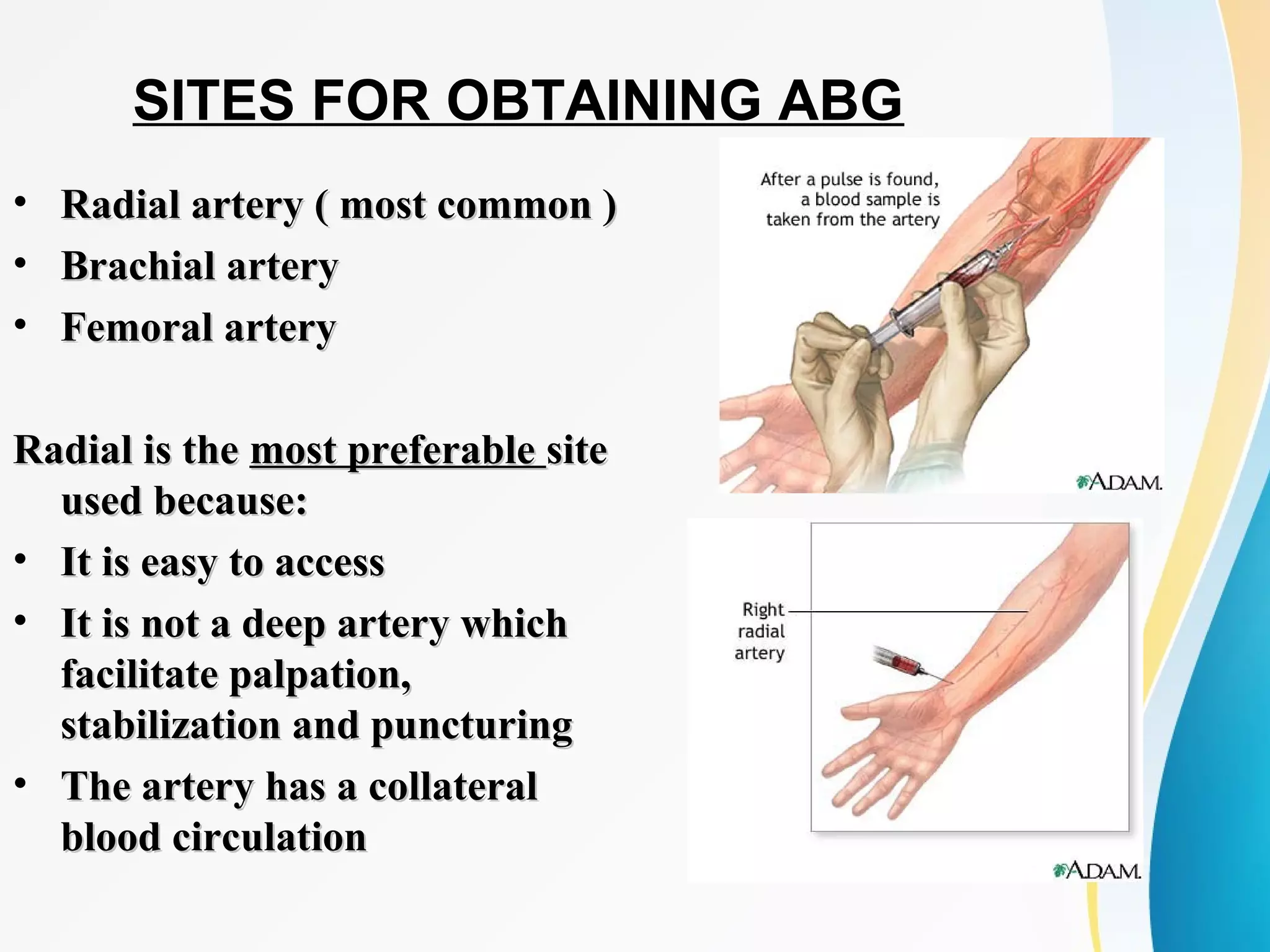
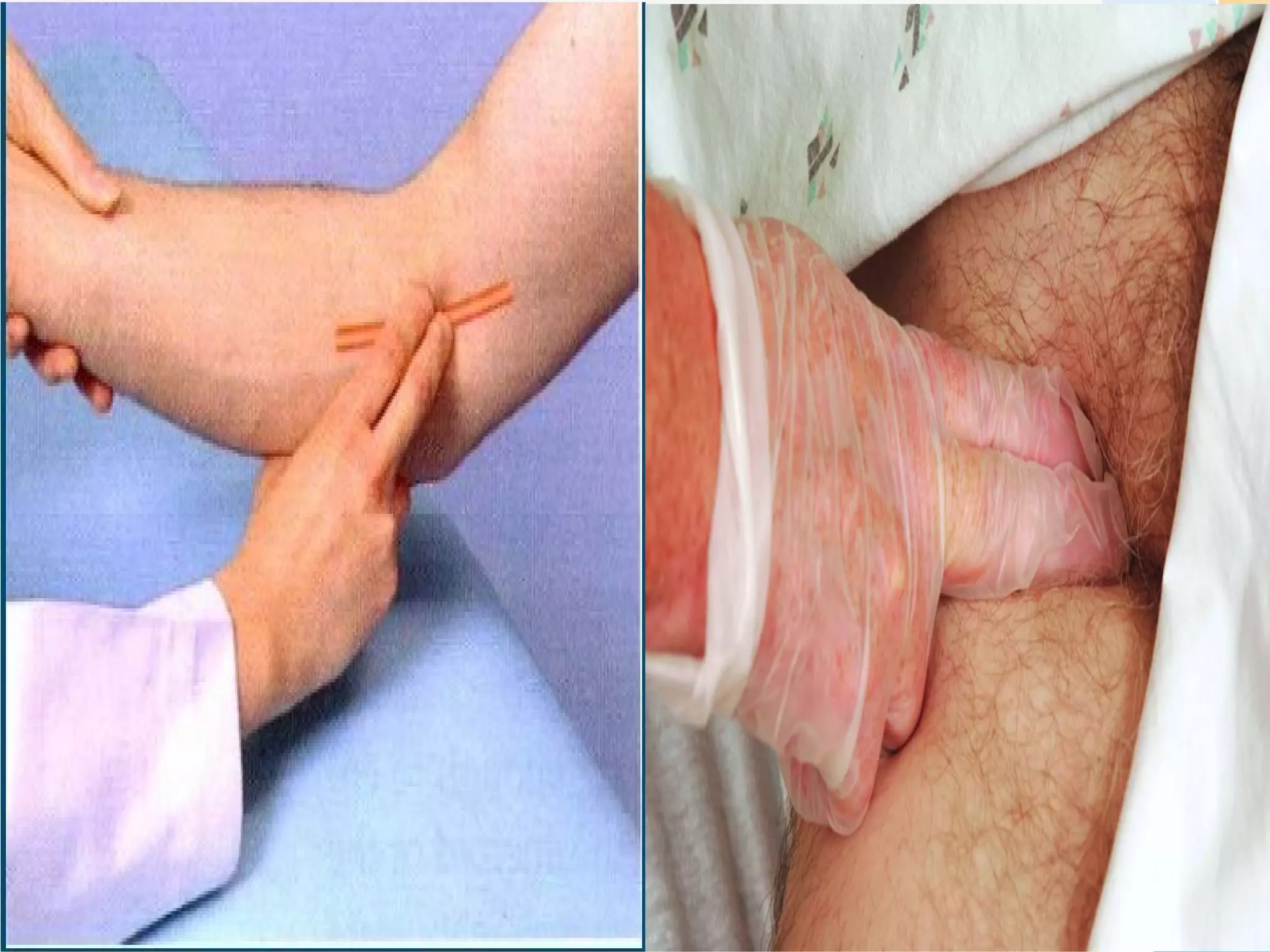
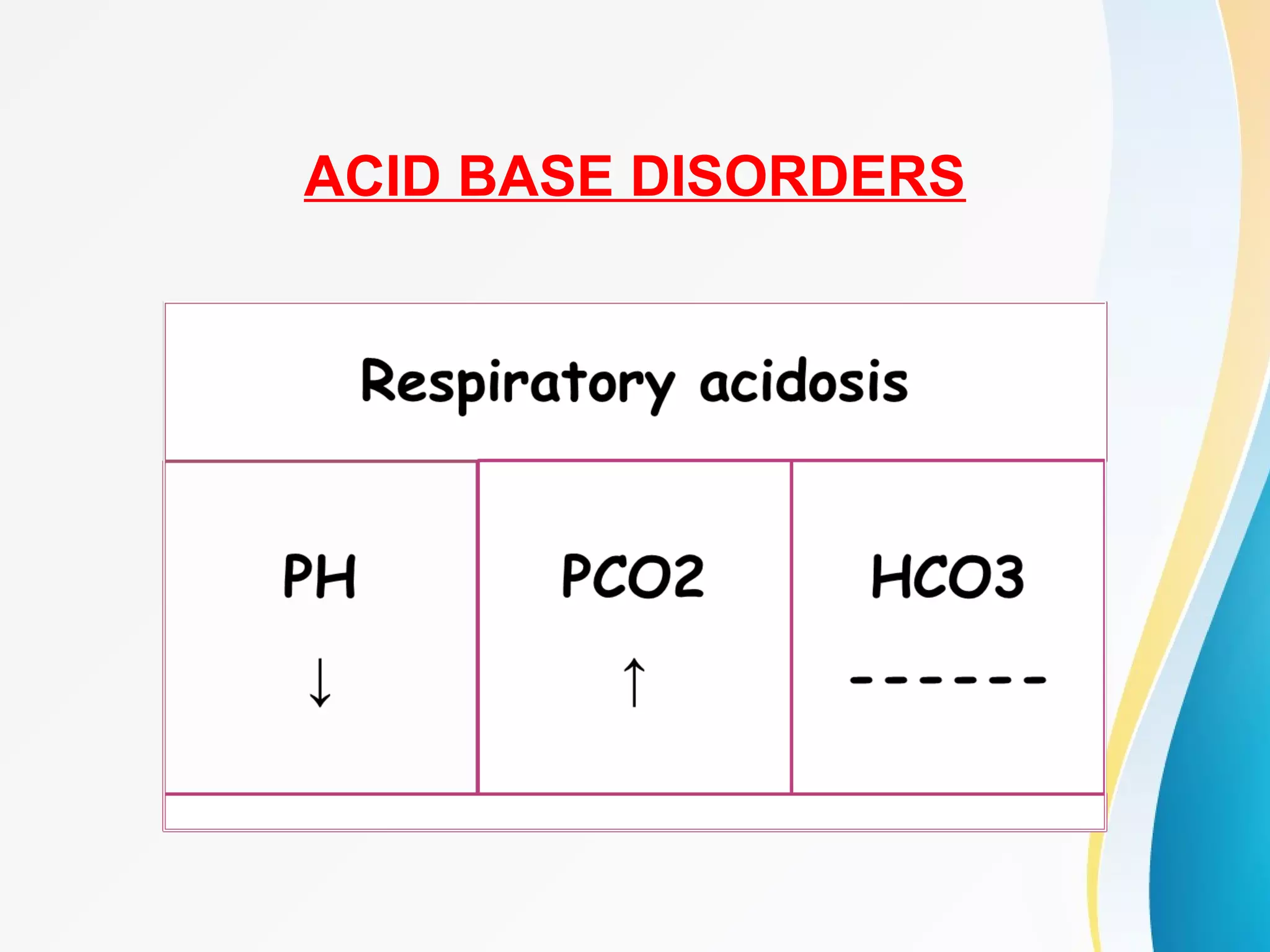
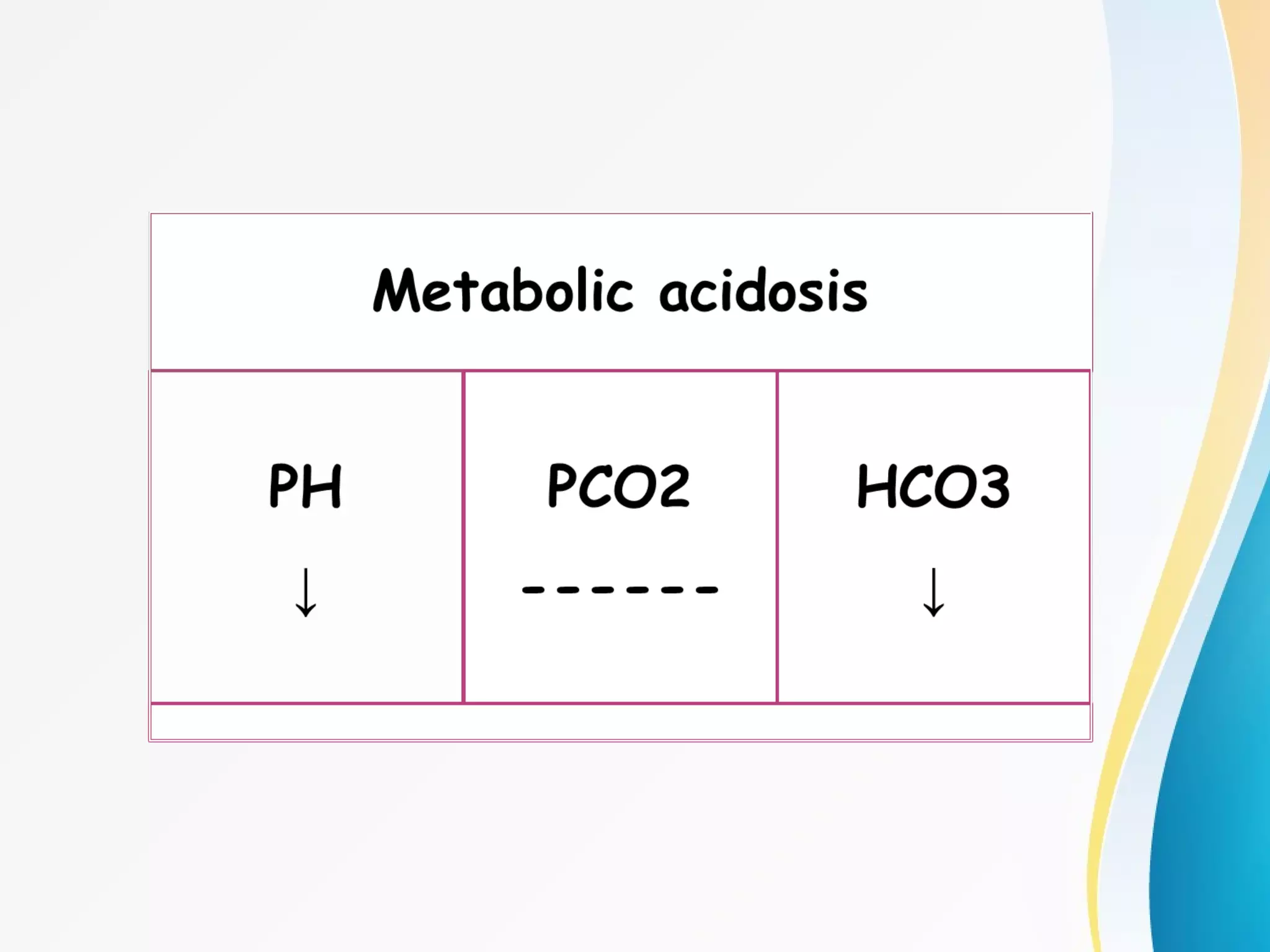
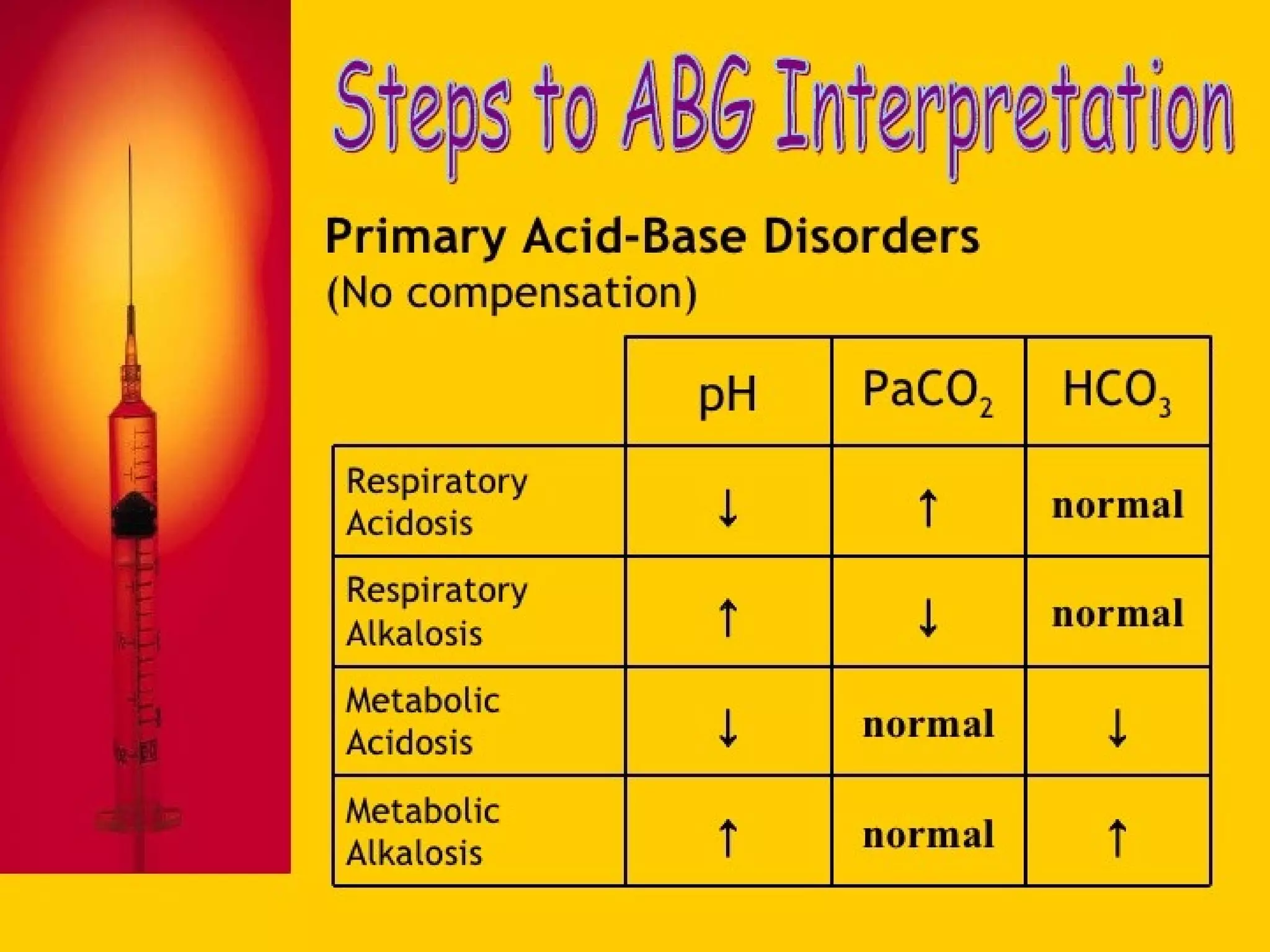
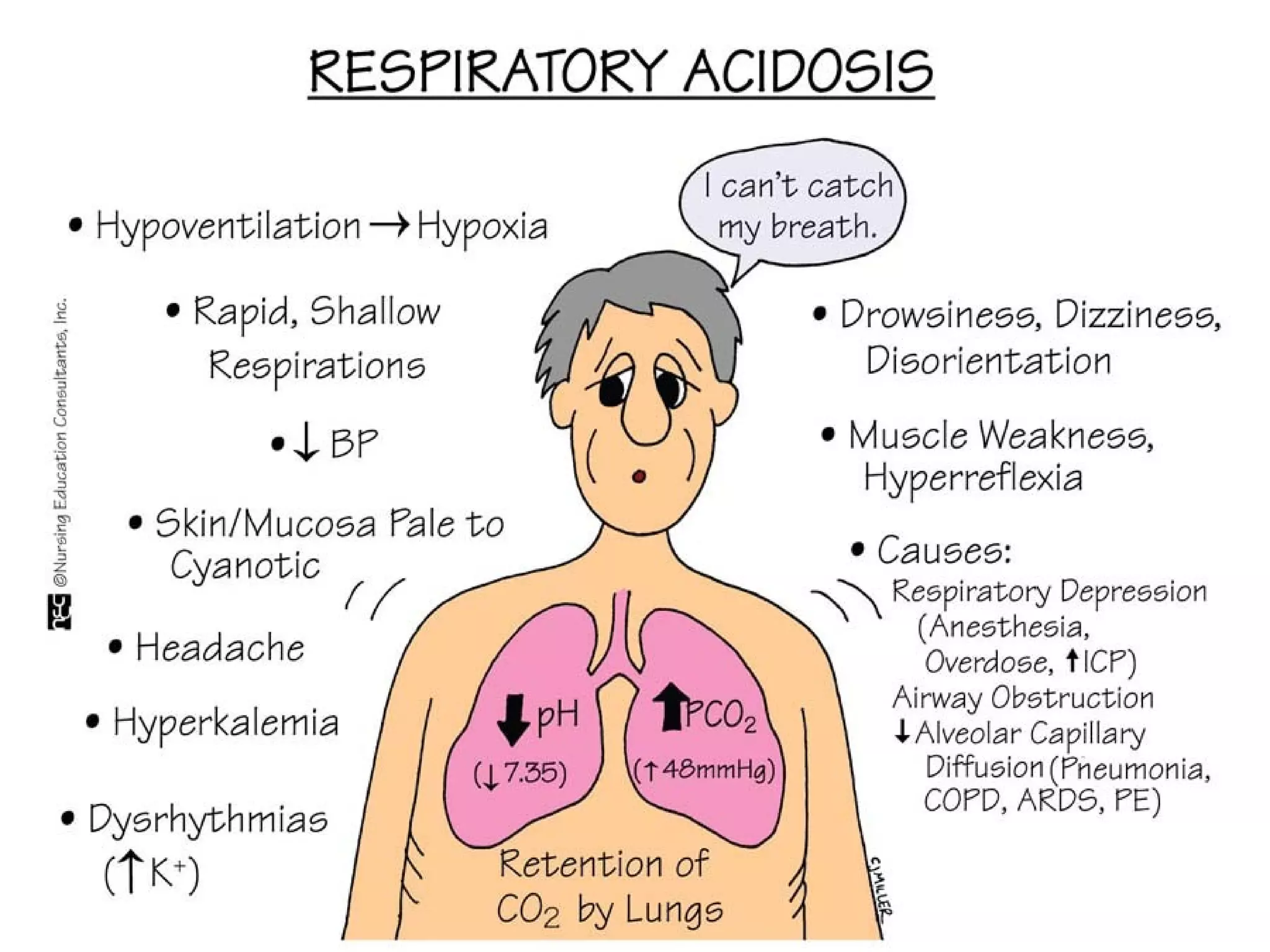
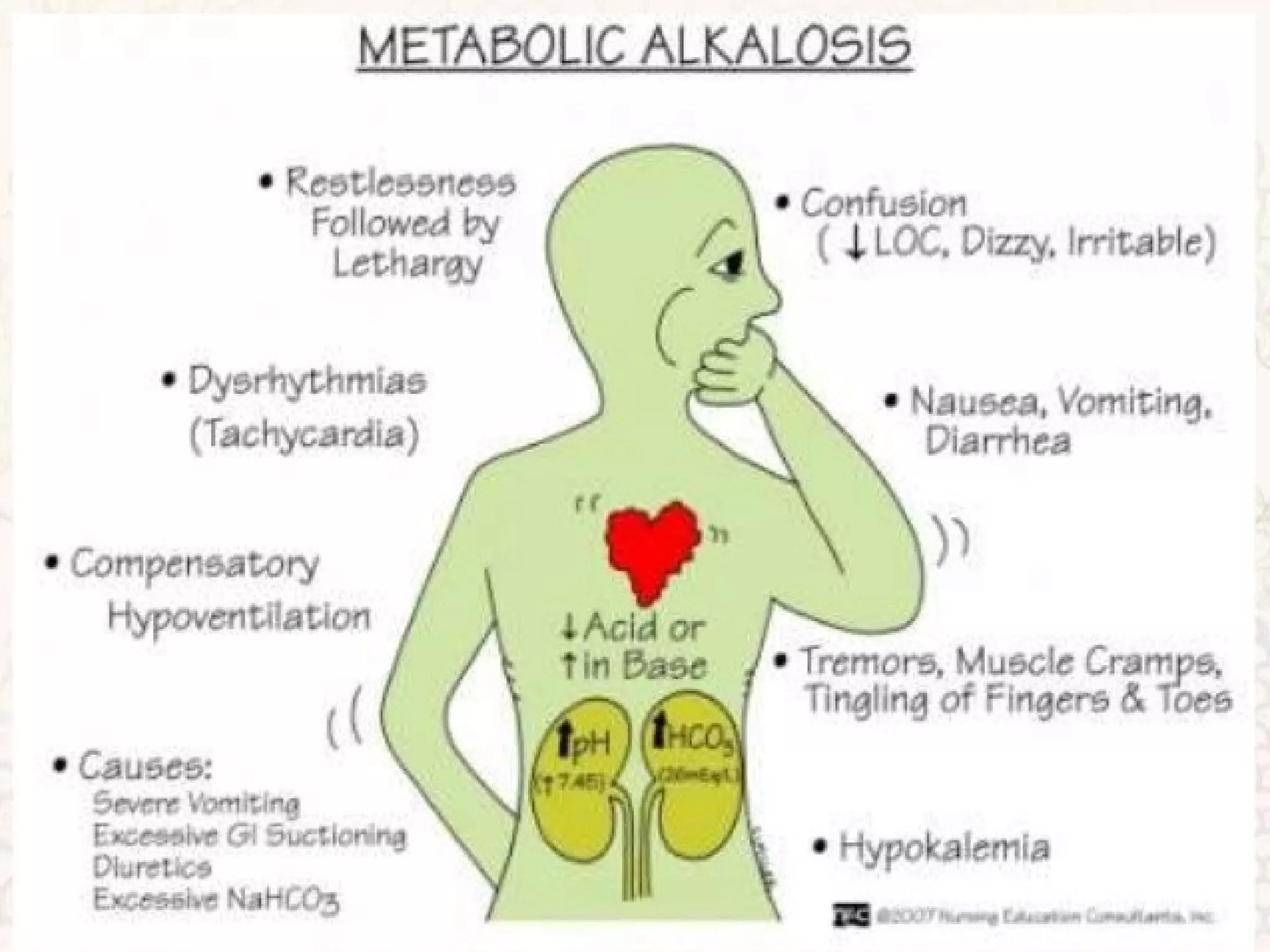
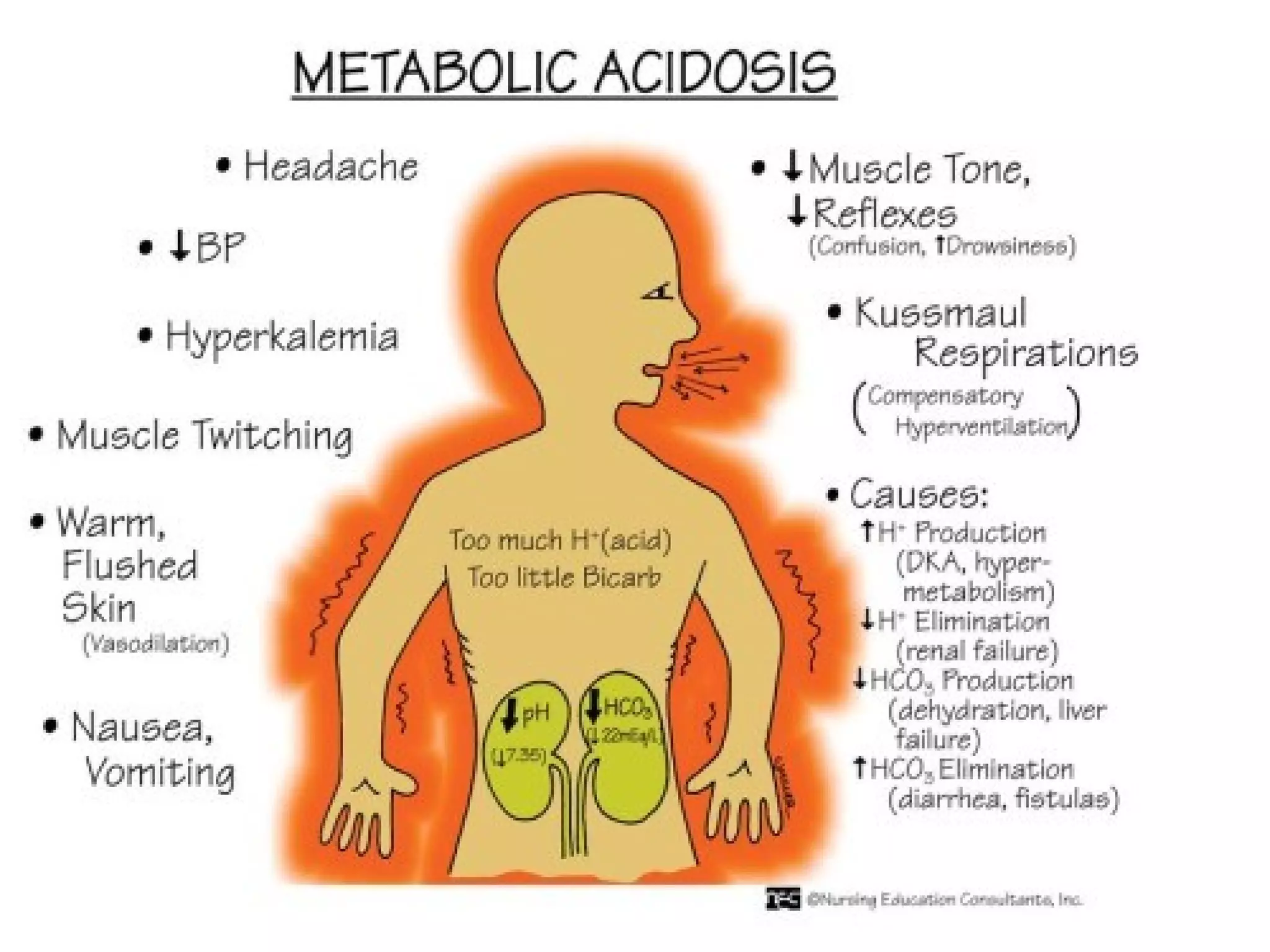
An arterial blood gas (ABG) test measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH and bicarbonate levels in blood drawn from an artery. It is used to evaluate ventilation, oxygenation and acid-base balance, especially in patients on ventilators or with breathing issues. Key components measured include pH, partial pressures of carbon dioxide (PCO2) and oxygen (PO2), and bicarbonate (HCO3). The test involves puncturing an artery, usually the radial artery, to collect a blood sample which is immediately tested or preserved on ice. Abnormal results can indicate respiratory or metabolic acidosis or alkalosis with various underlying causes. Complications are rare but include bleeding, bruising and distal