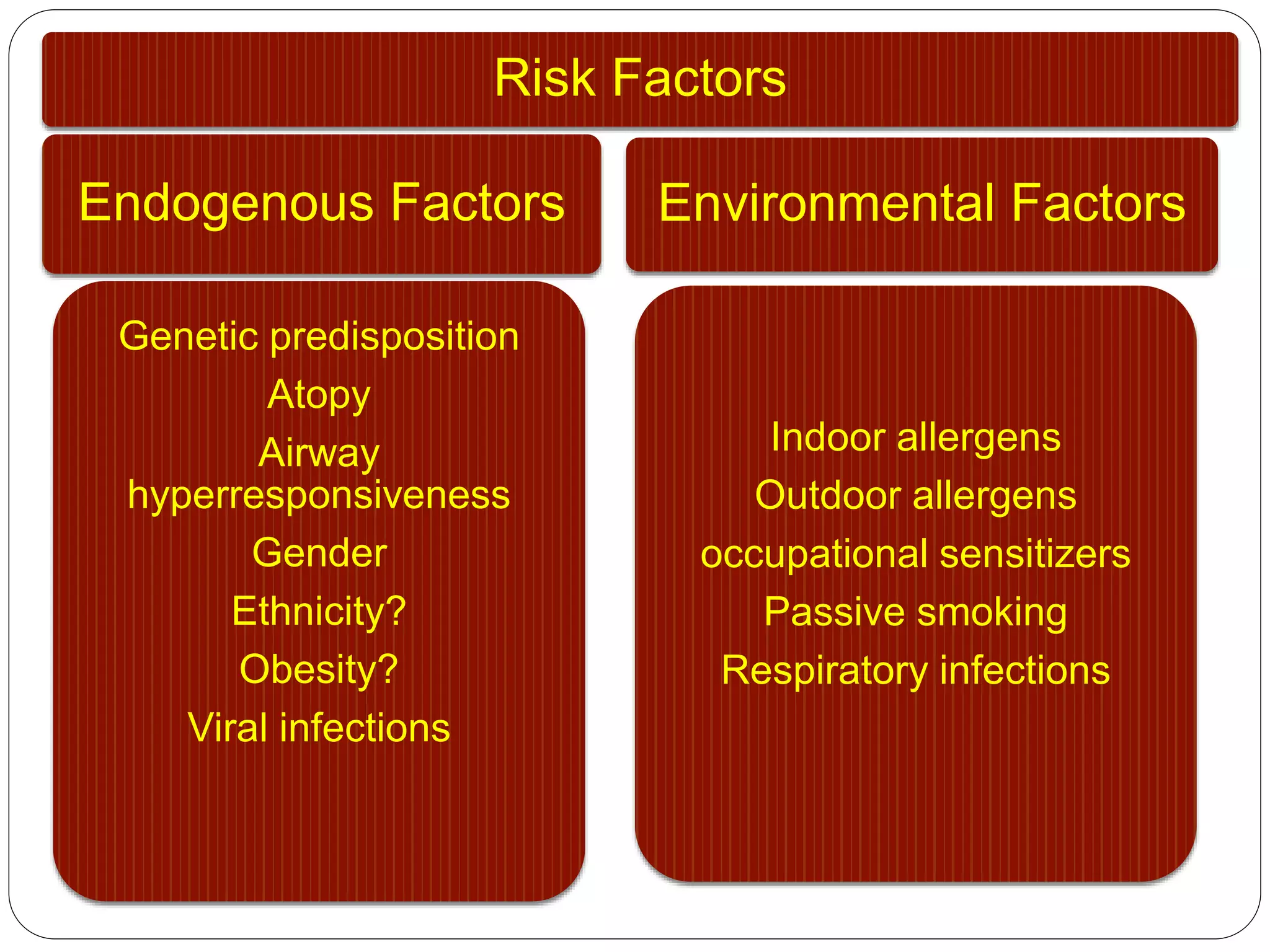
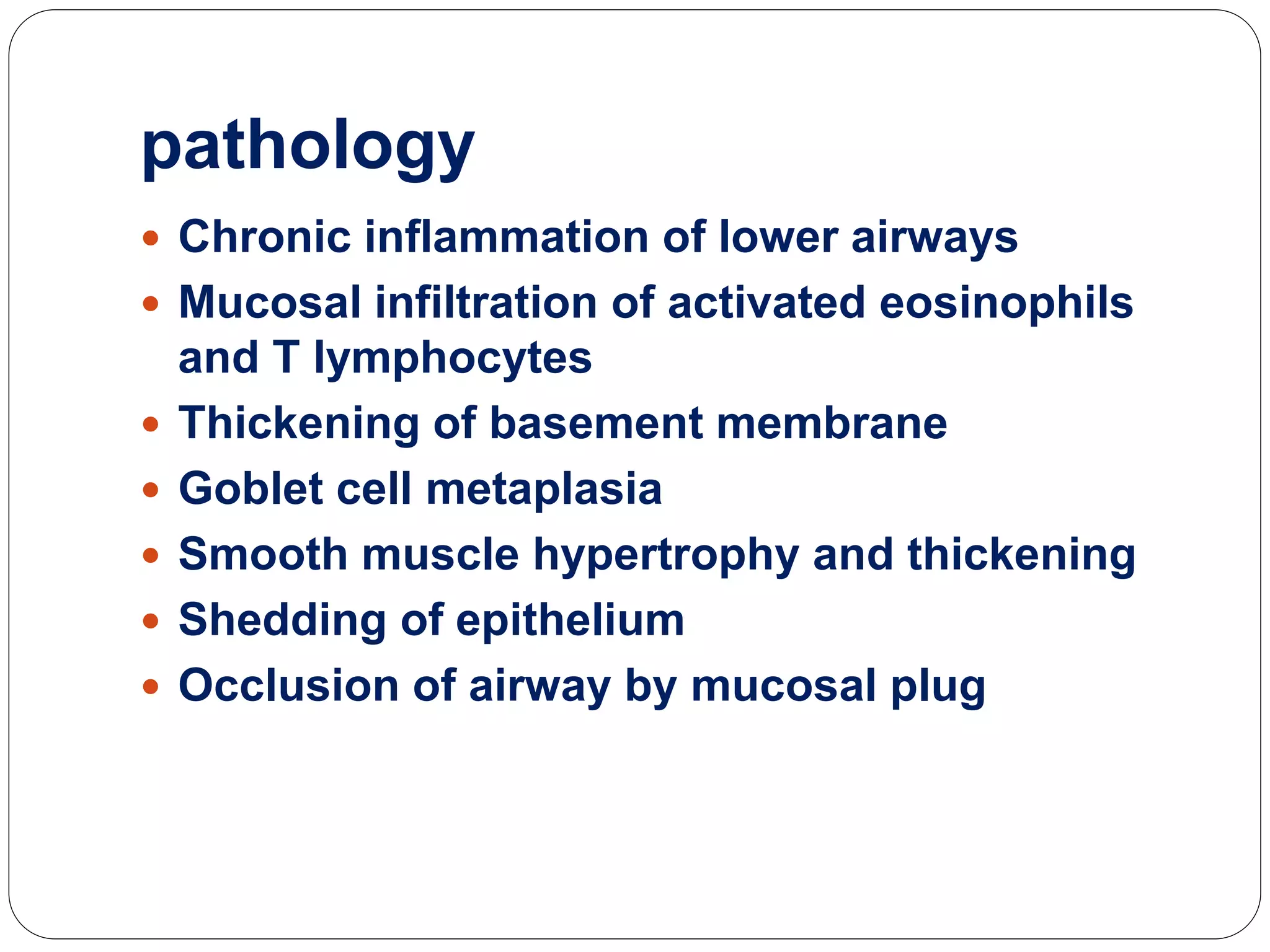
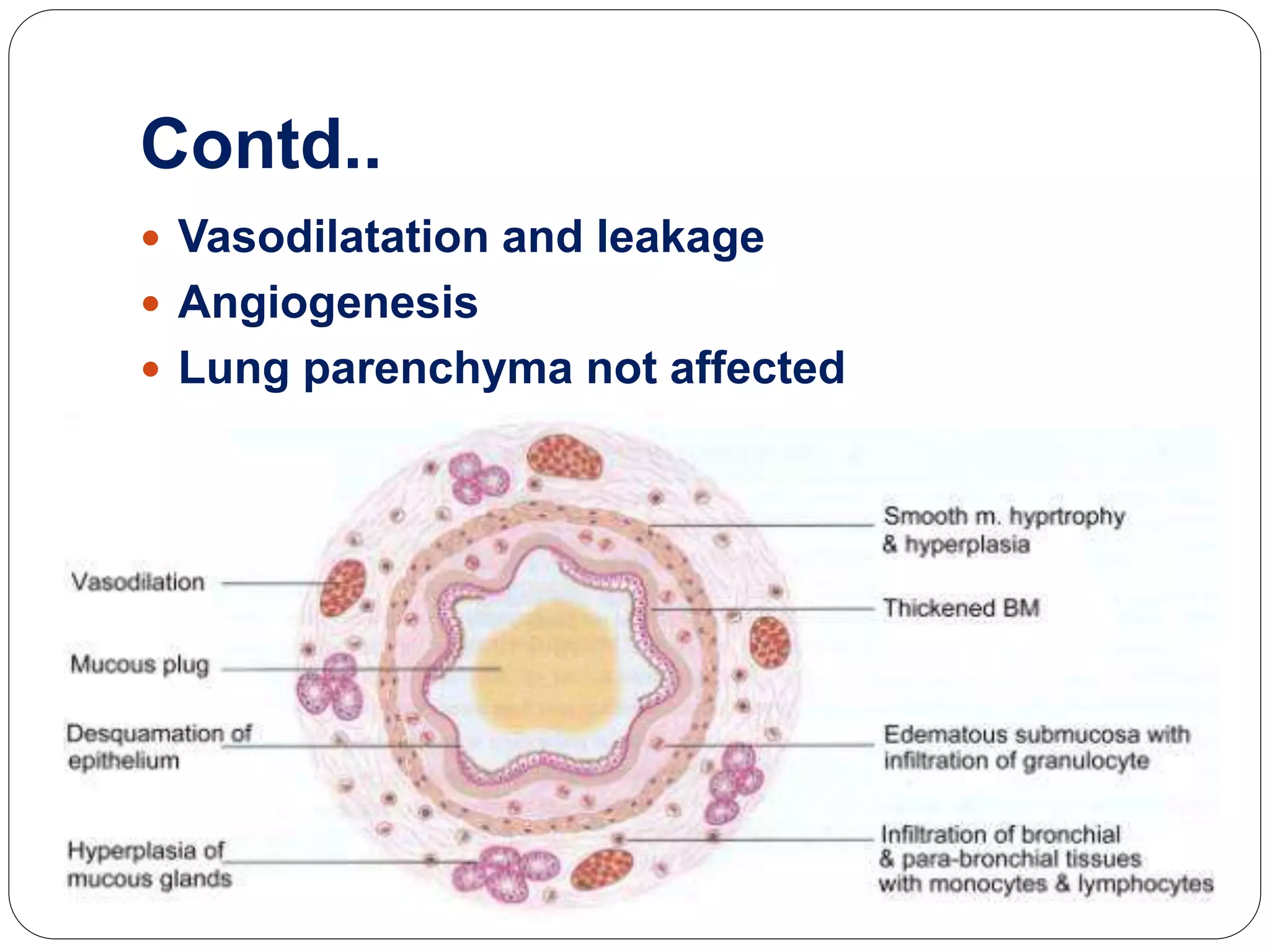
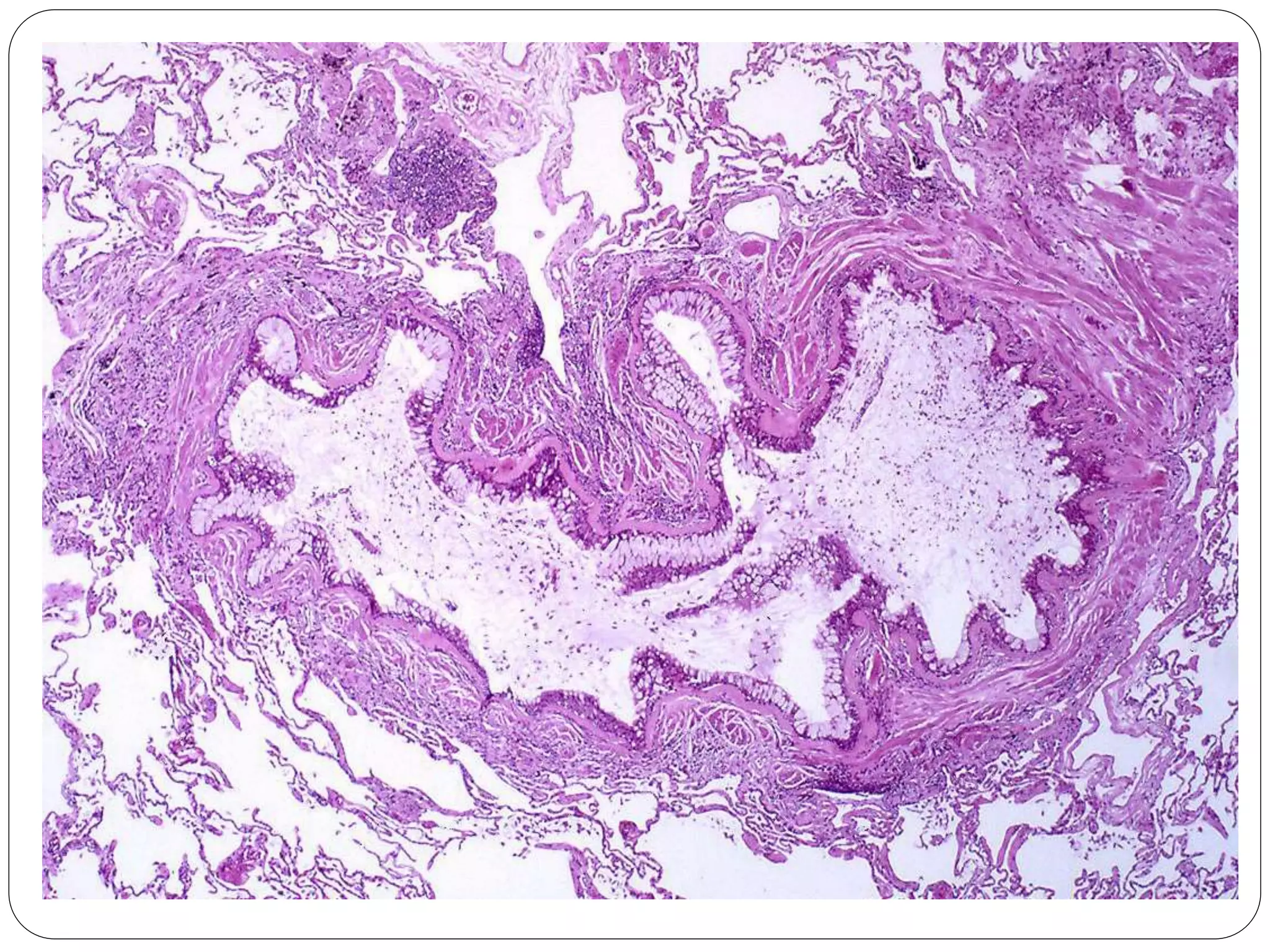
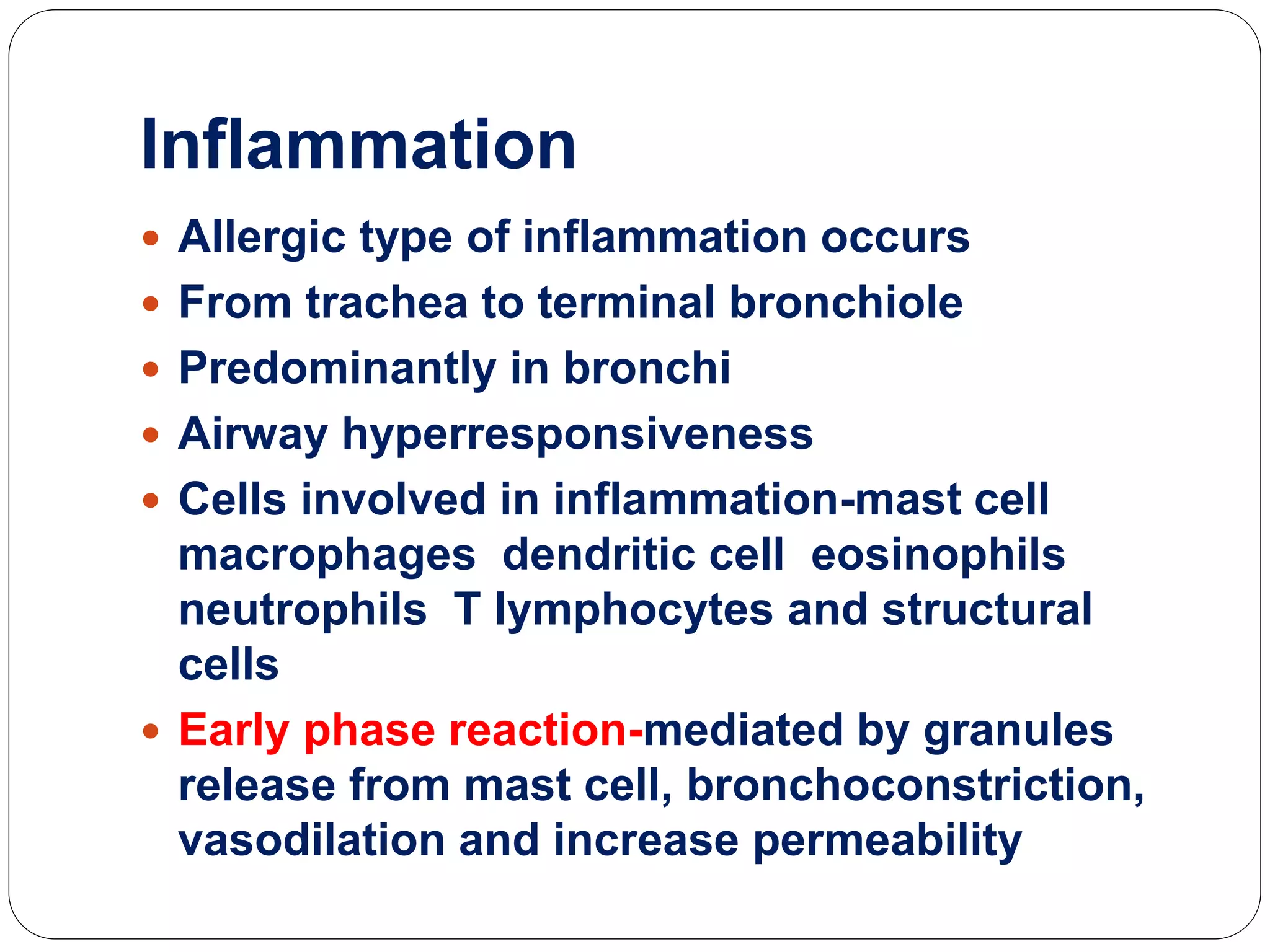
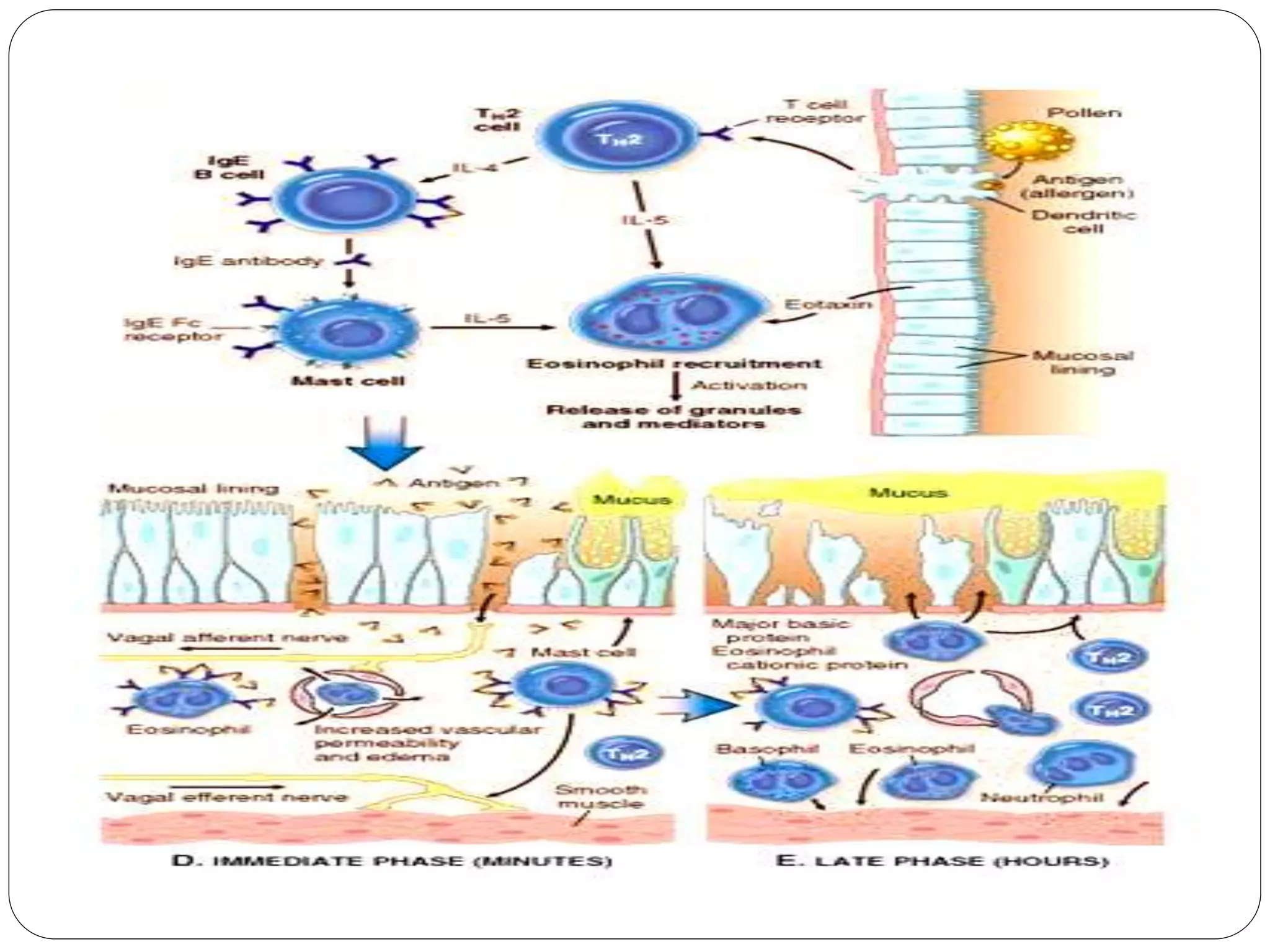
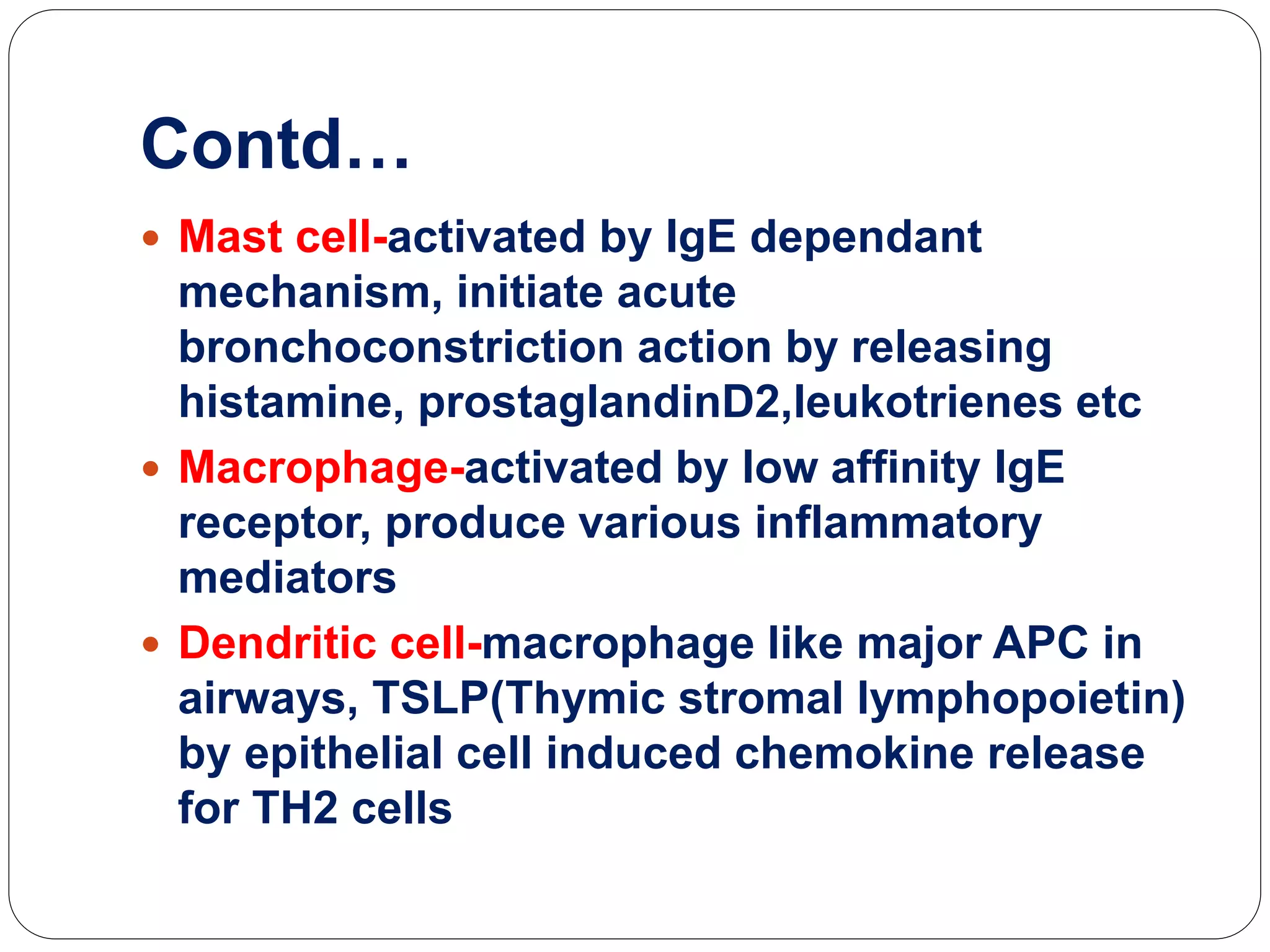
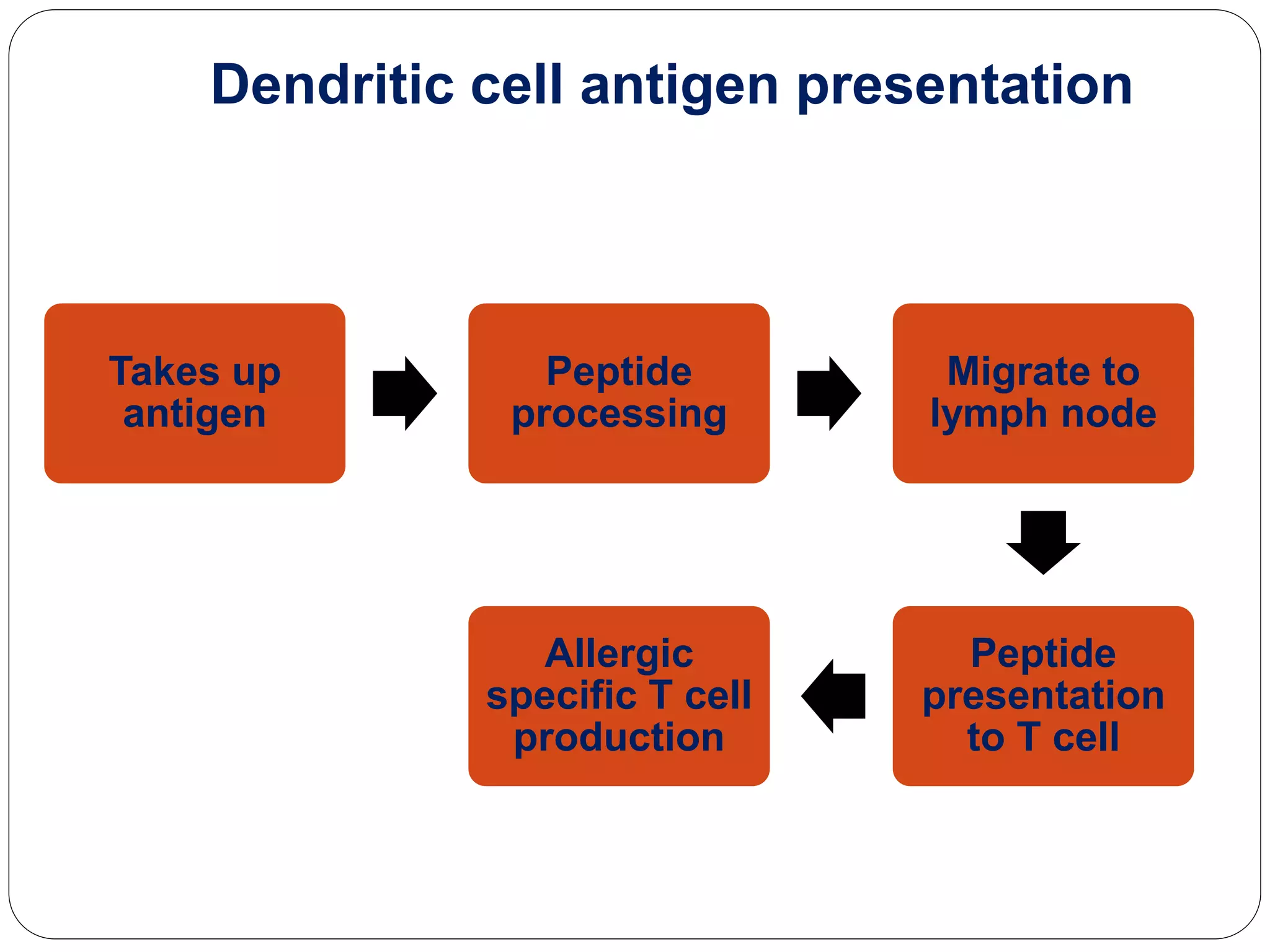
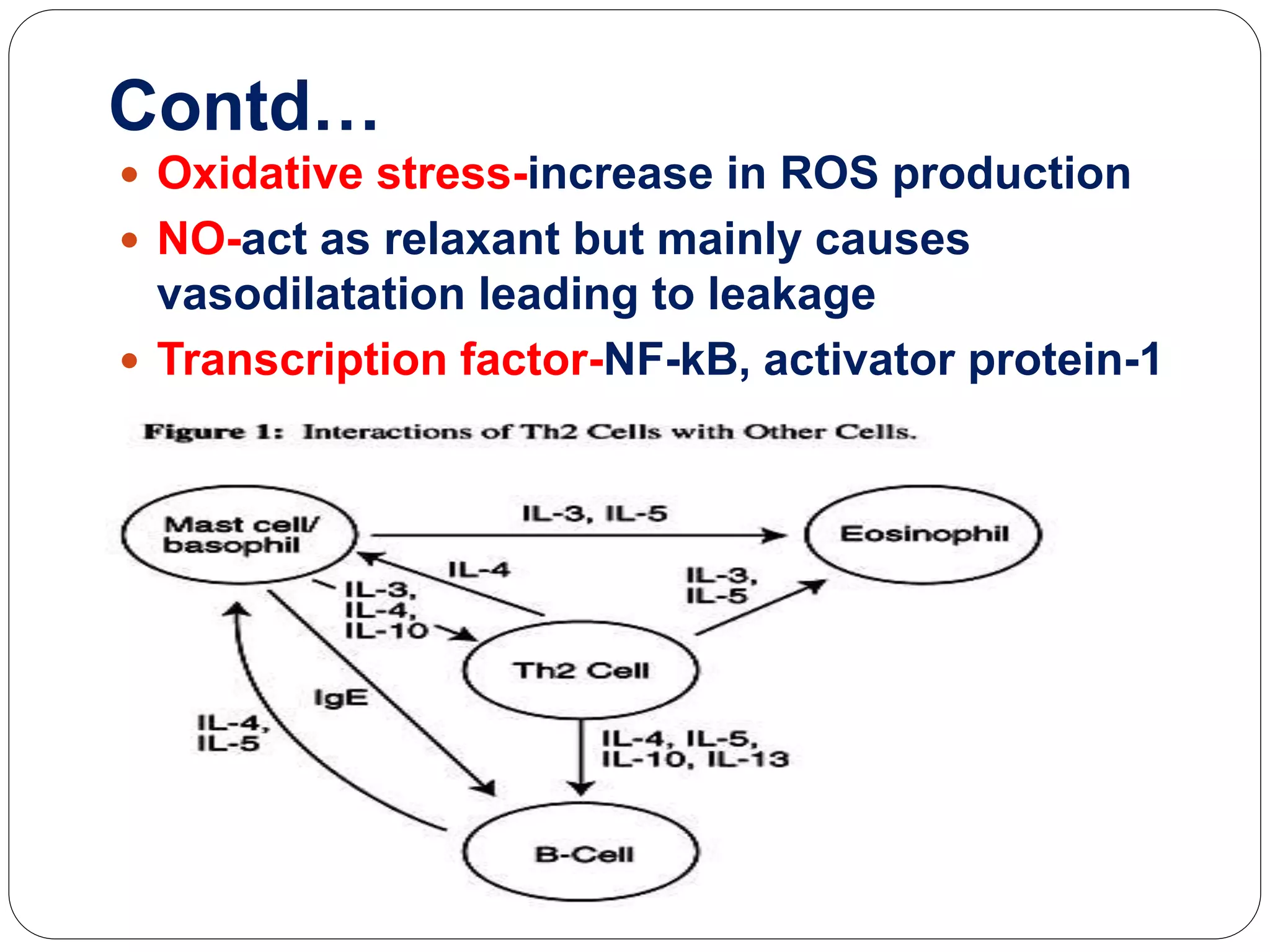
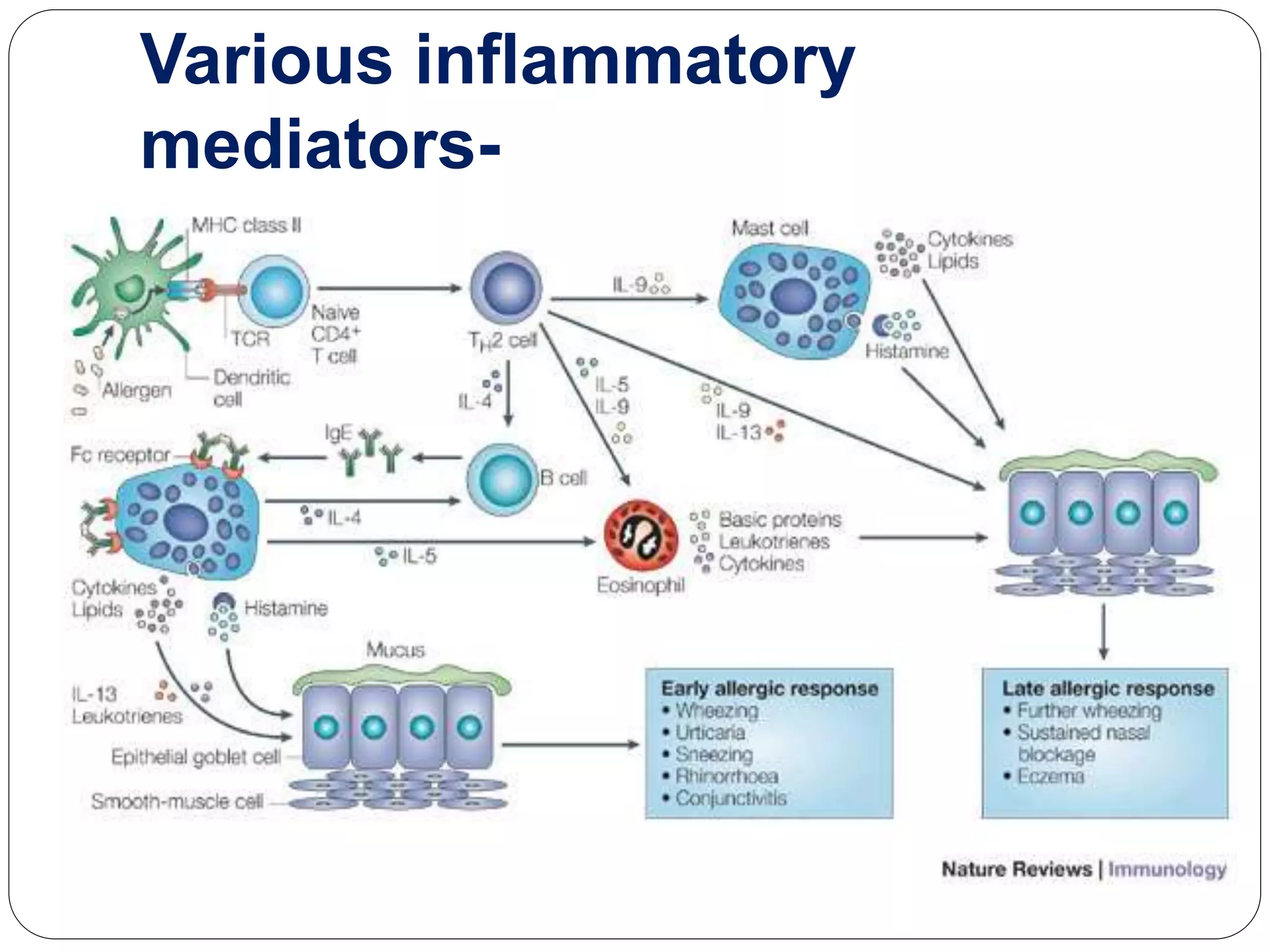
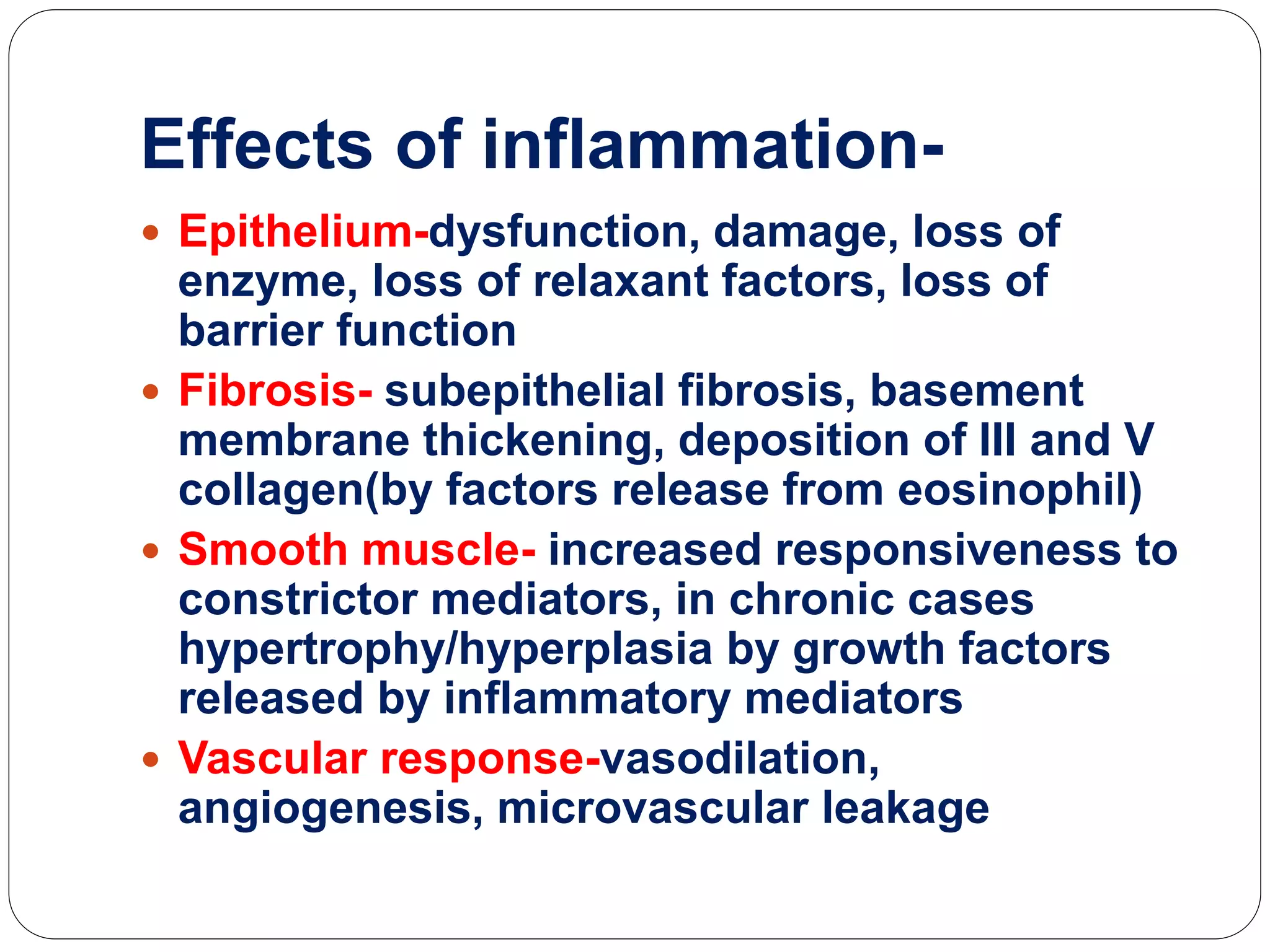
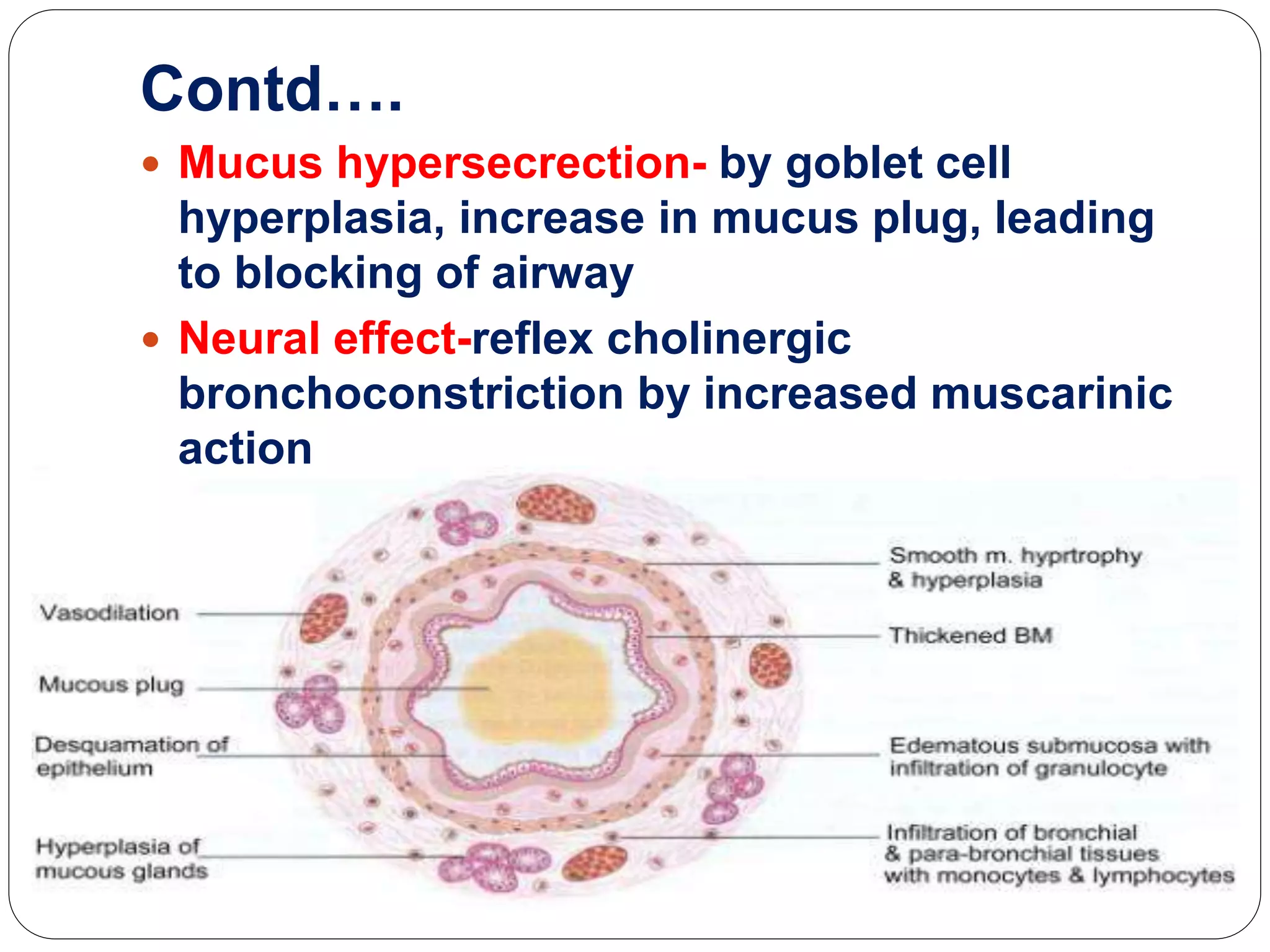
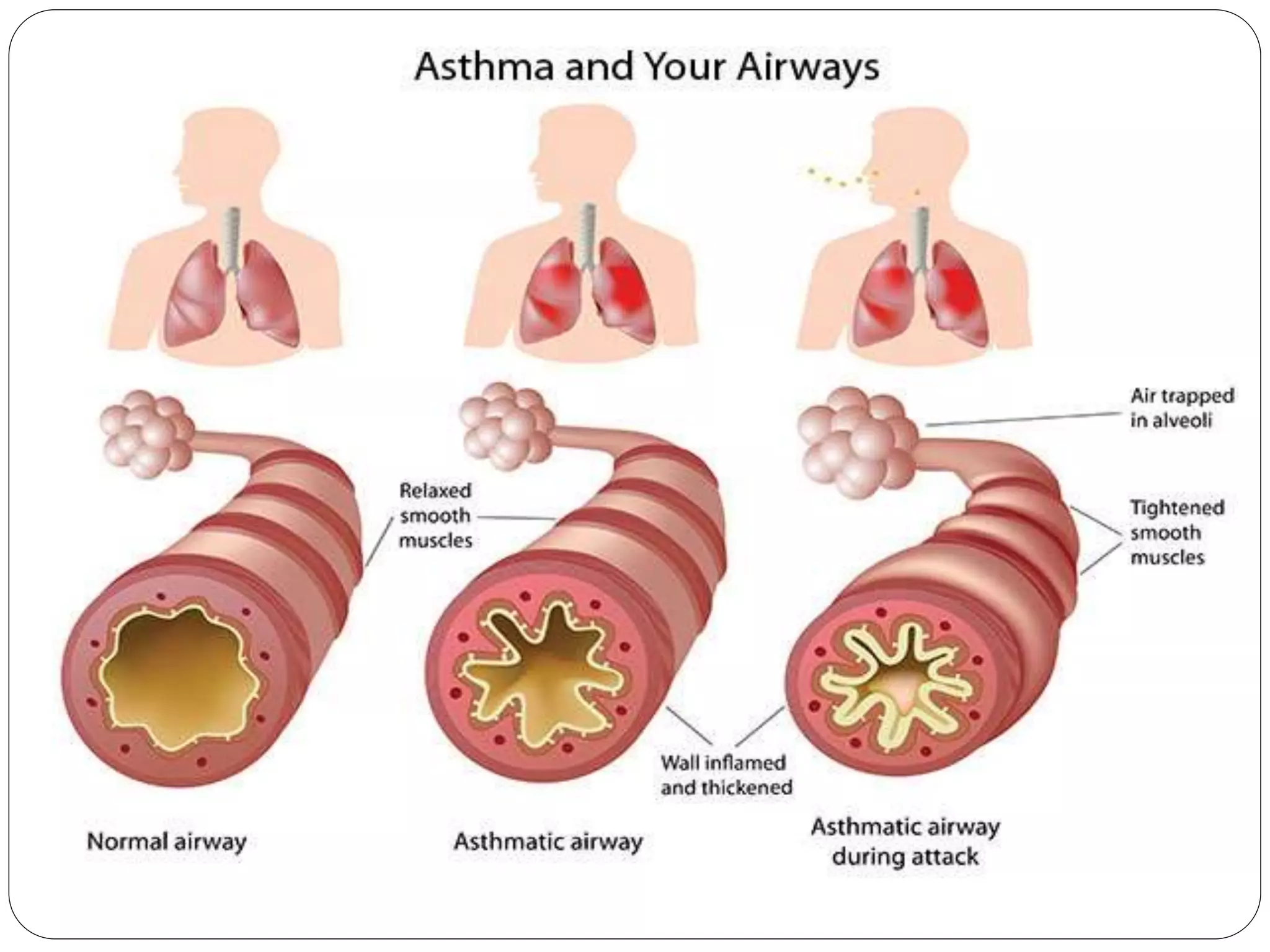
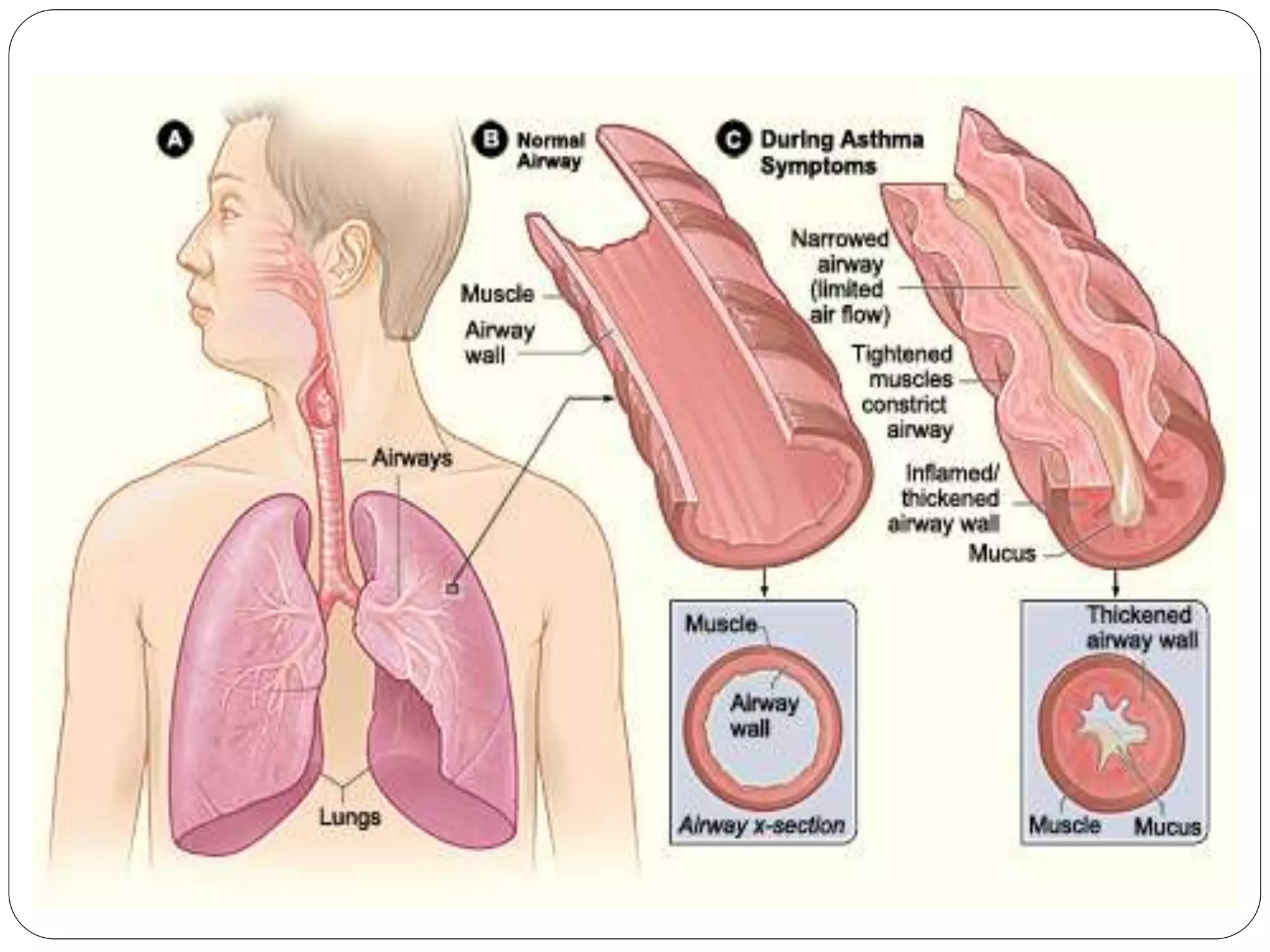
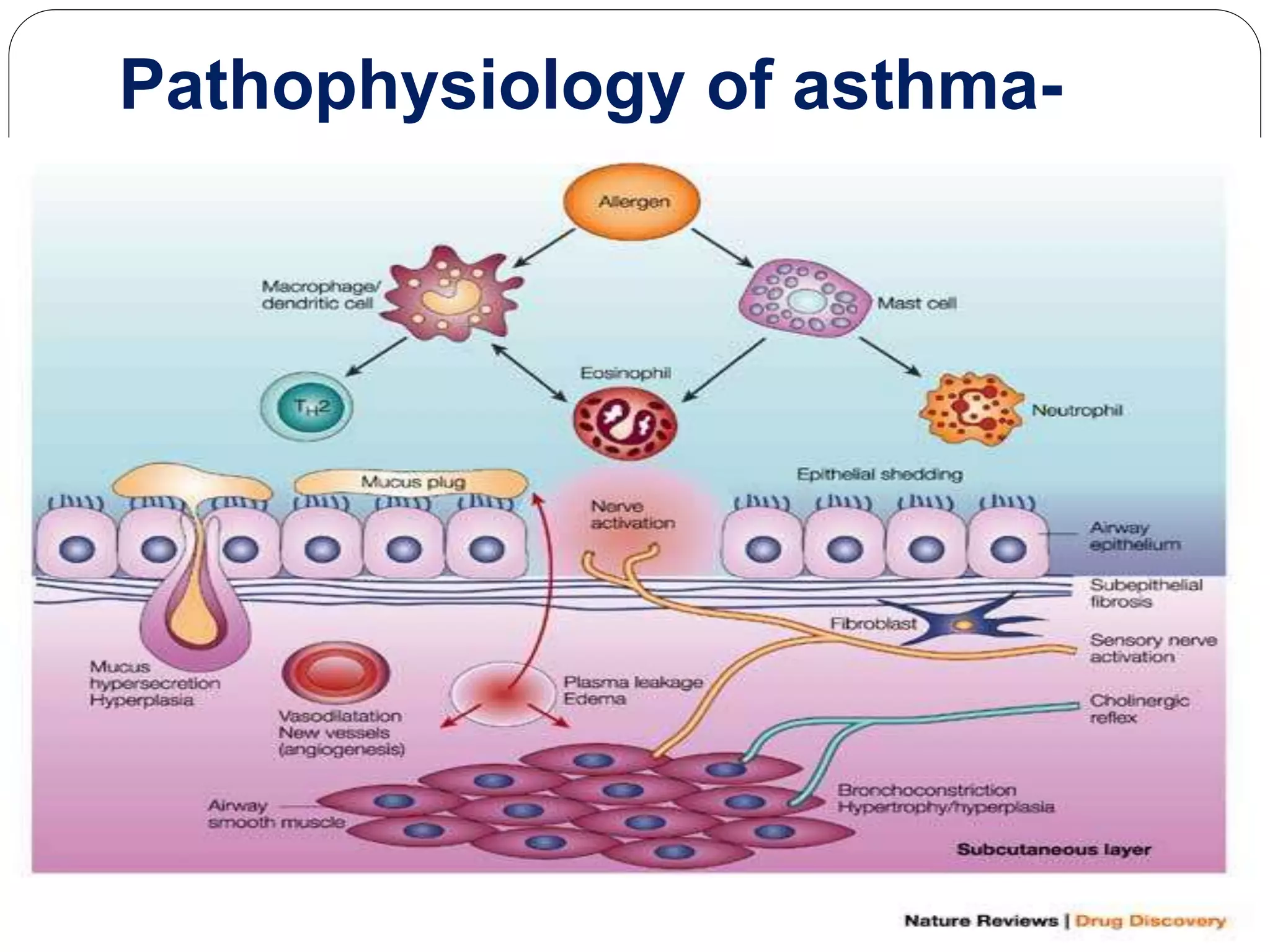
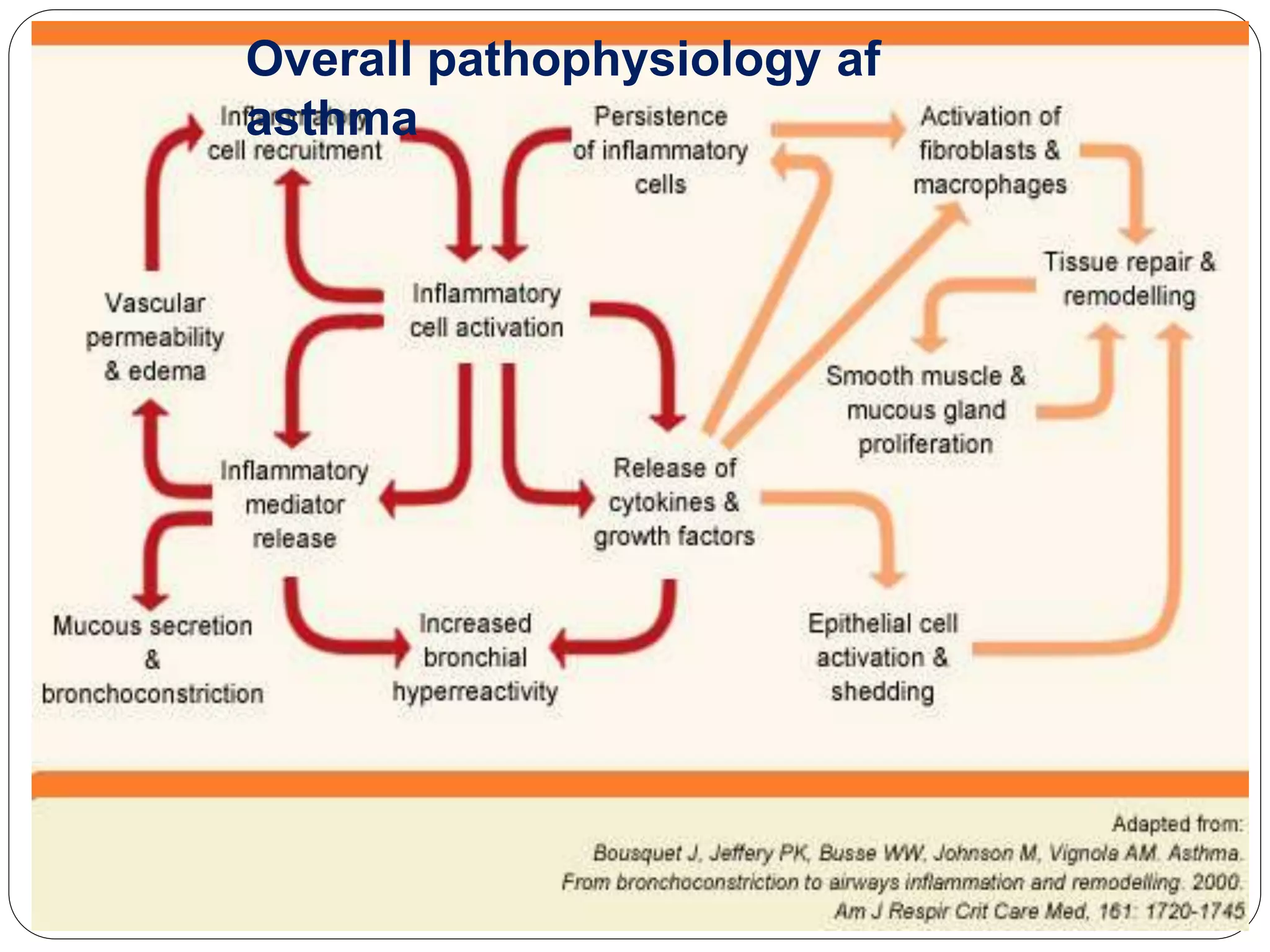
Asthma is a syndrome characterized by variable and reversible airflow obstruction. It involves chronic inflammation of the lower airways. Various risk factors and triggers can cause an immune response involving mast cell activation and release of inflammatory mediators like histamine and leukotrienes. This leads to early and late phase reactions with recruitment of cells like eosinophils that release additional mediators causing symptoms like wheezing. Over time, remodeling of the airways occurs due to thickening of the basement membrane, fibrosis, and smooth muscle hypertrophy resulting in irreversible narrowing.