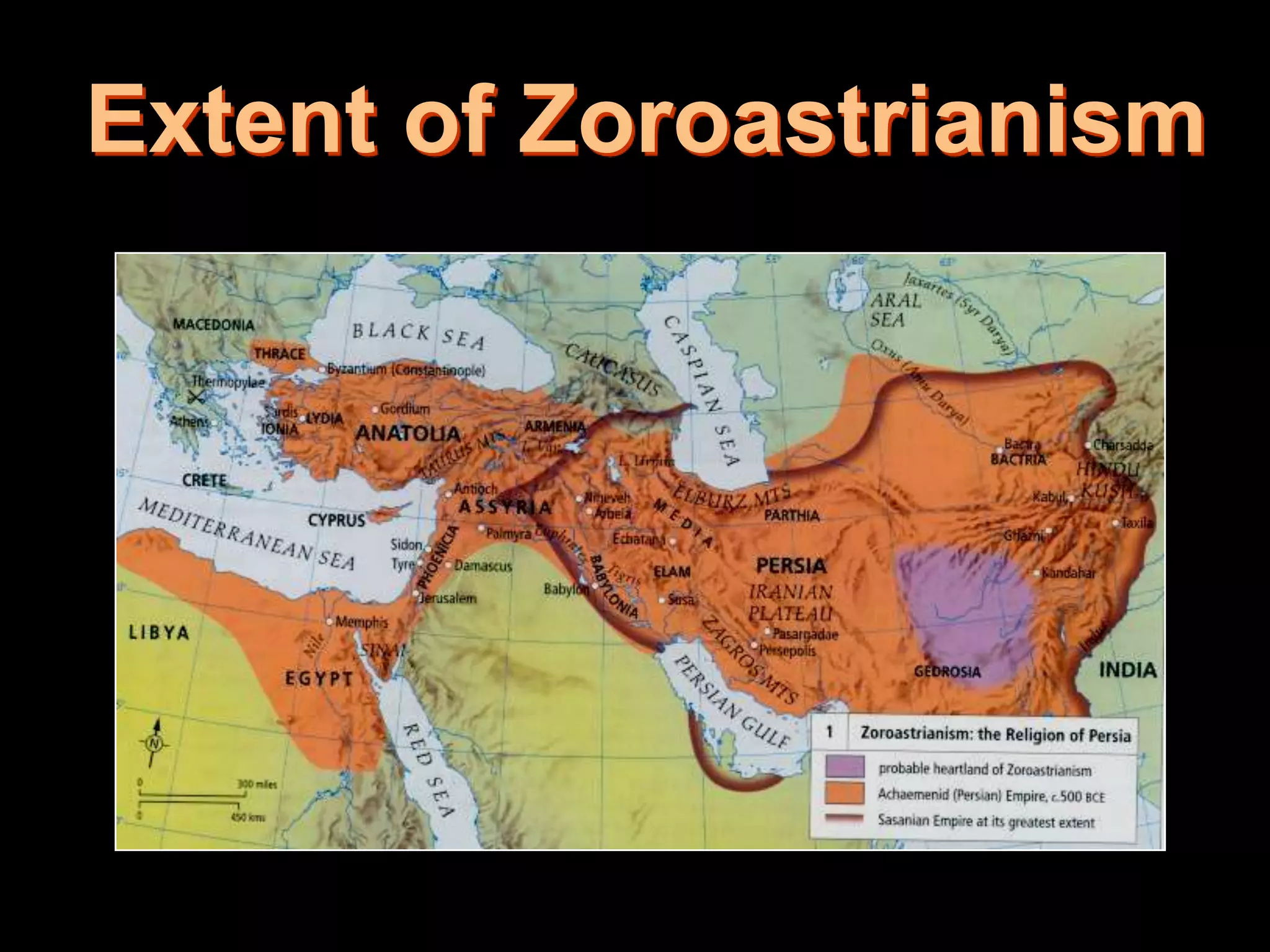
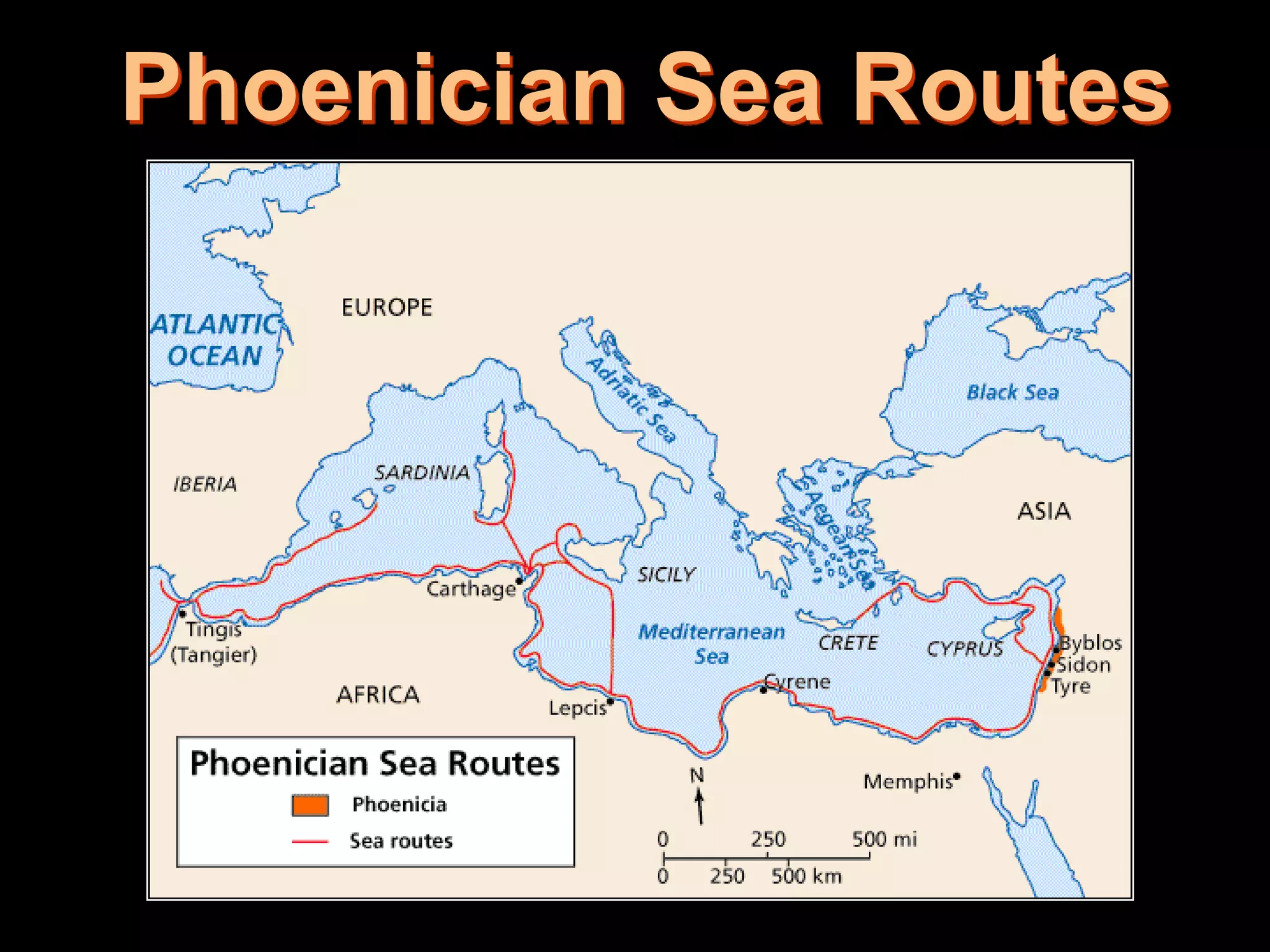
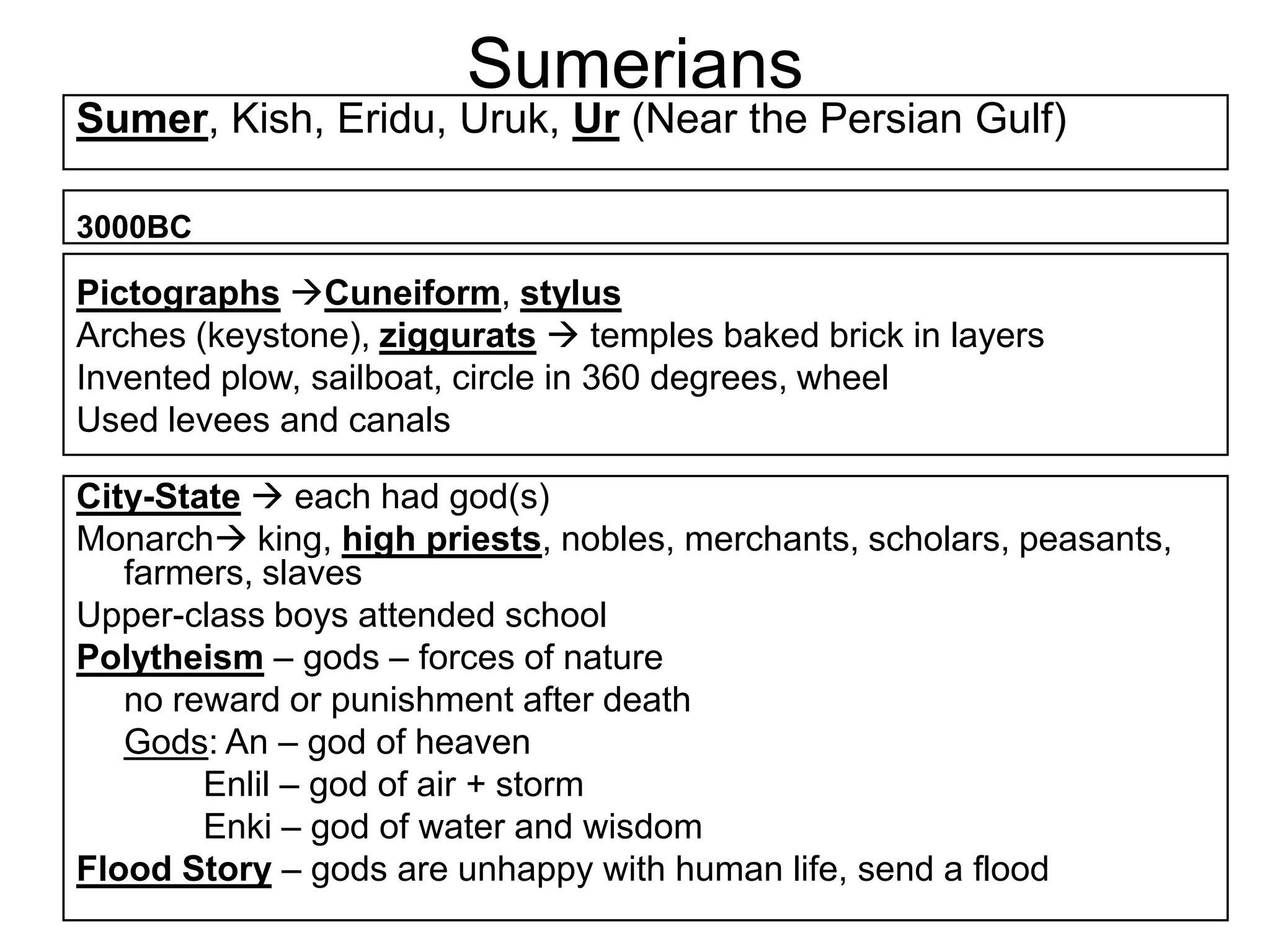
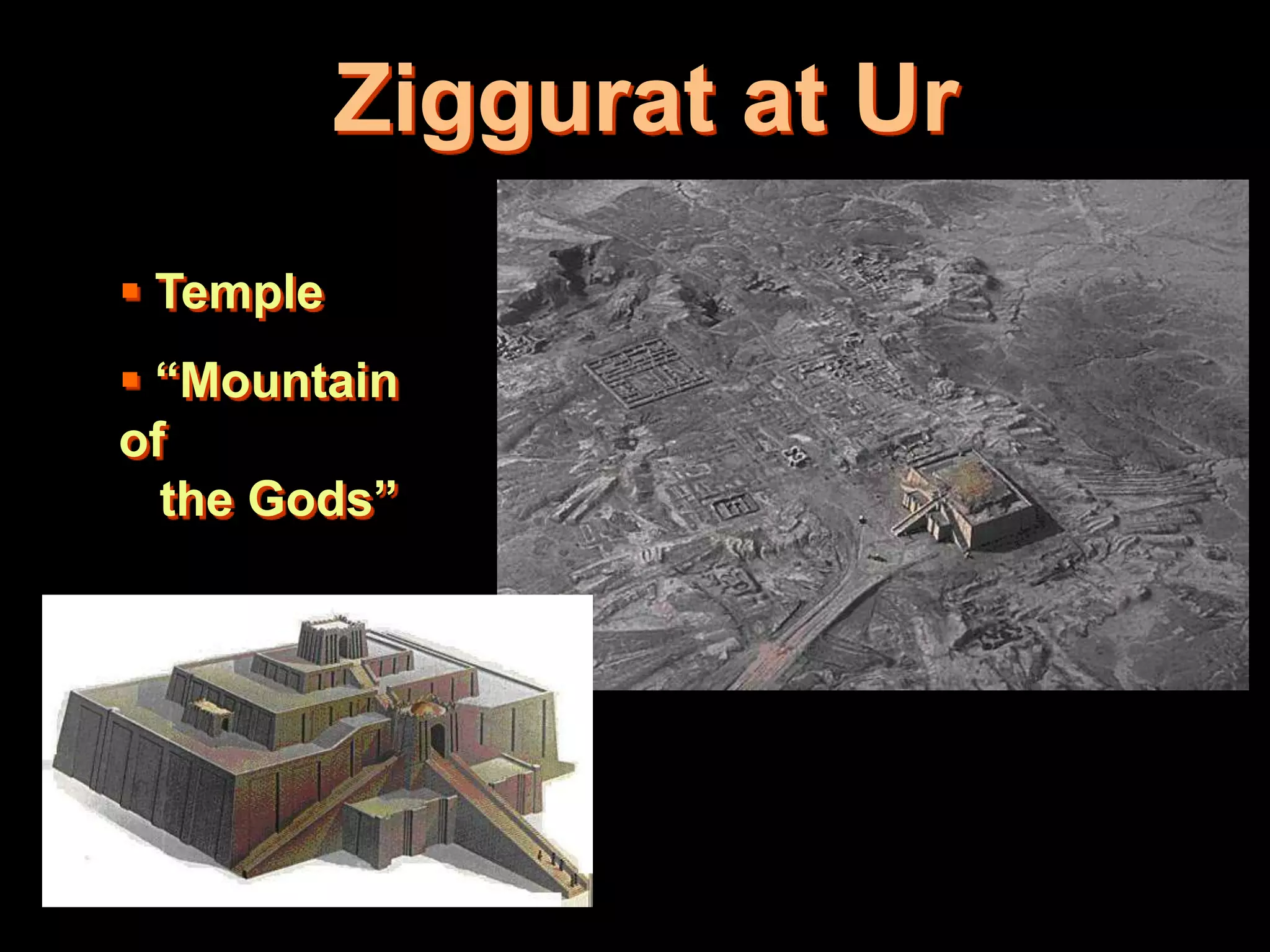
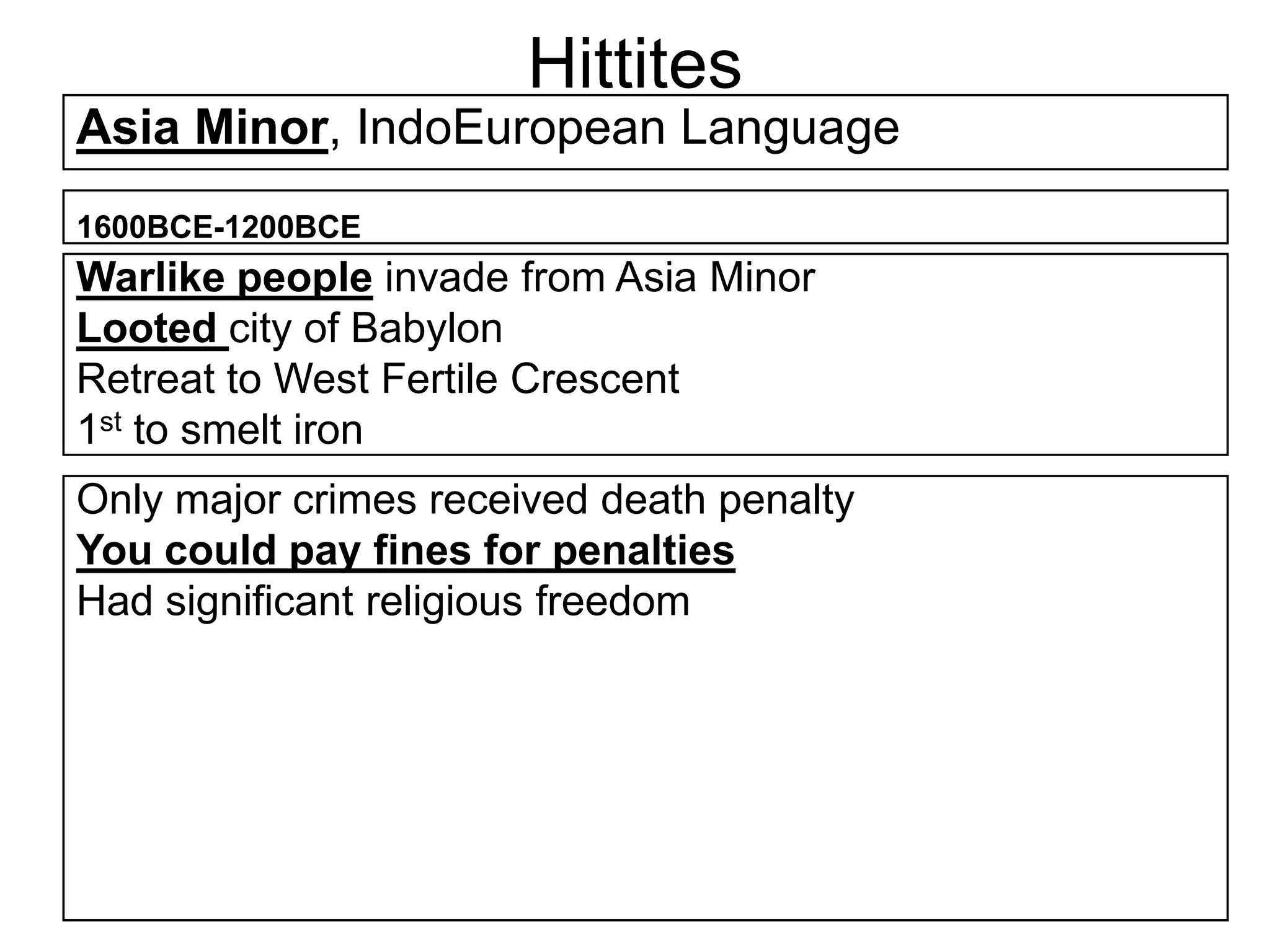
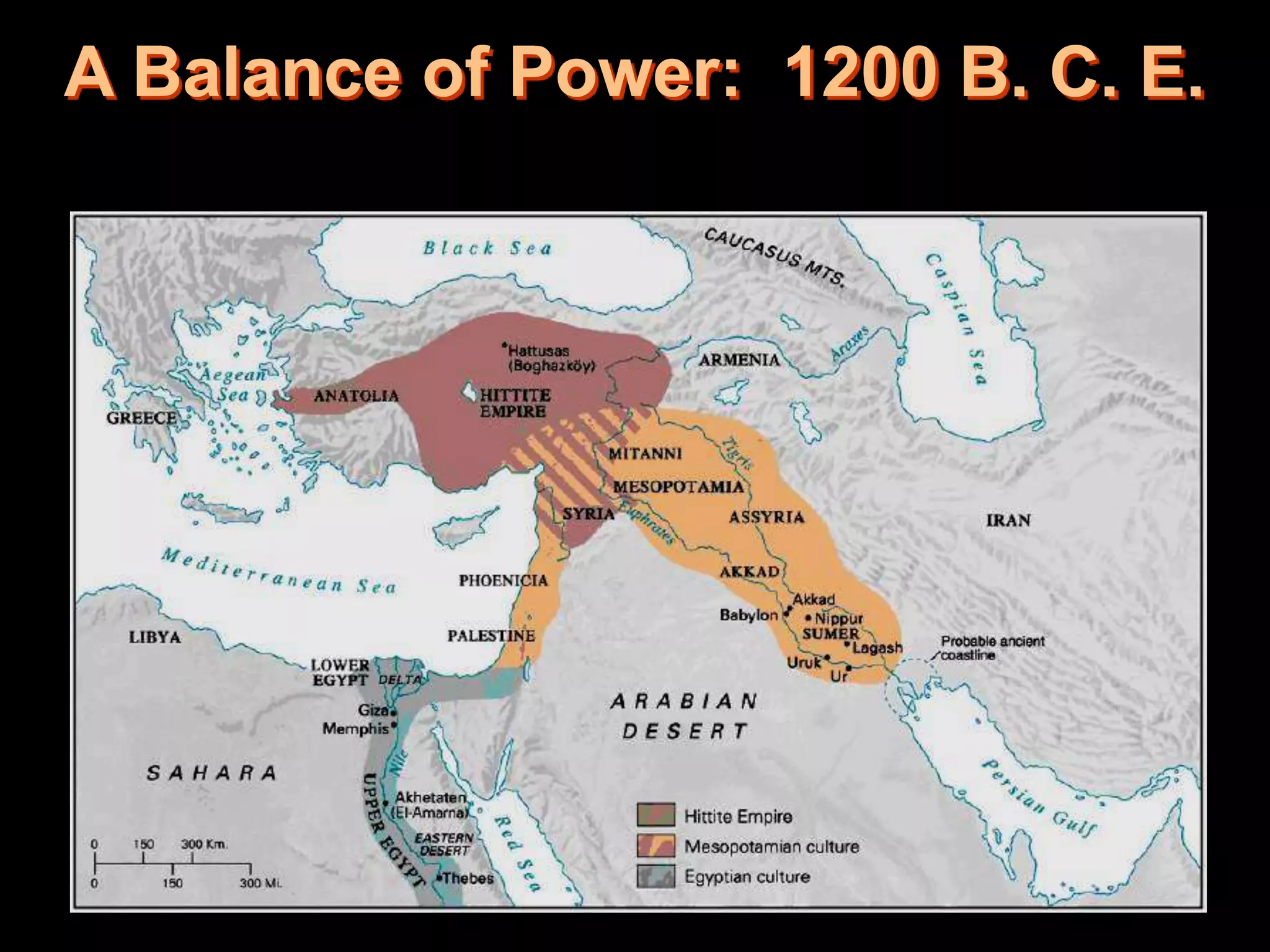
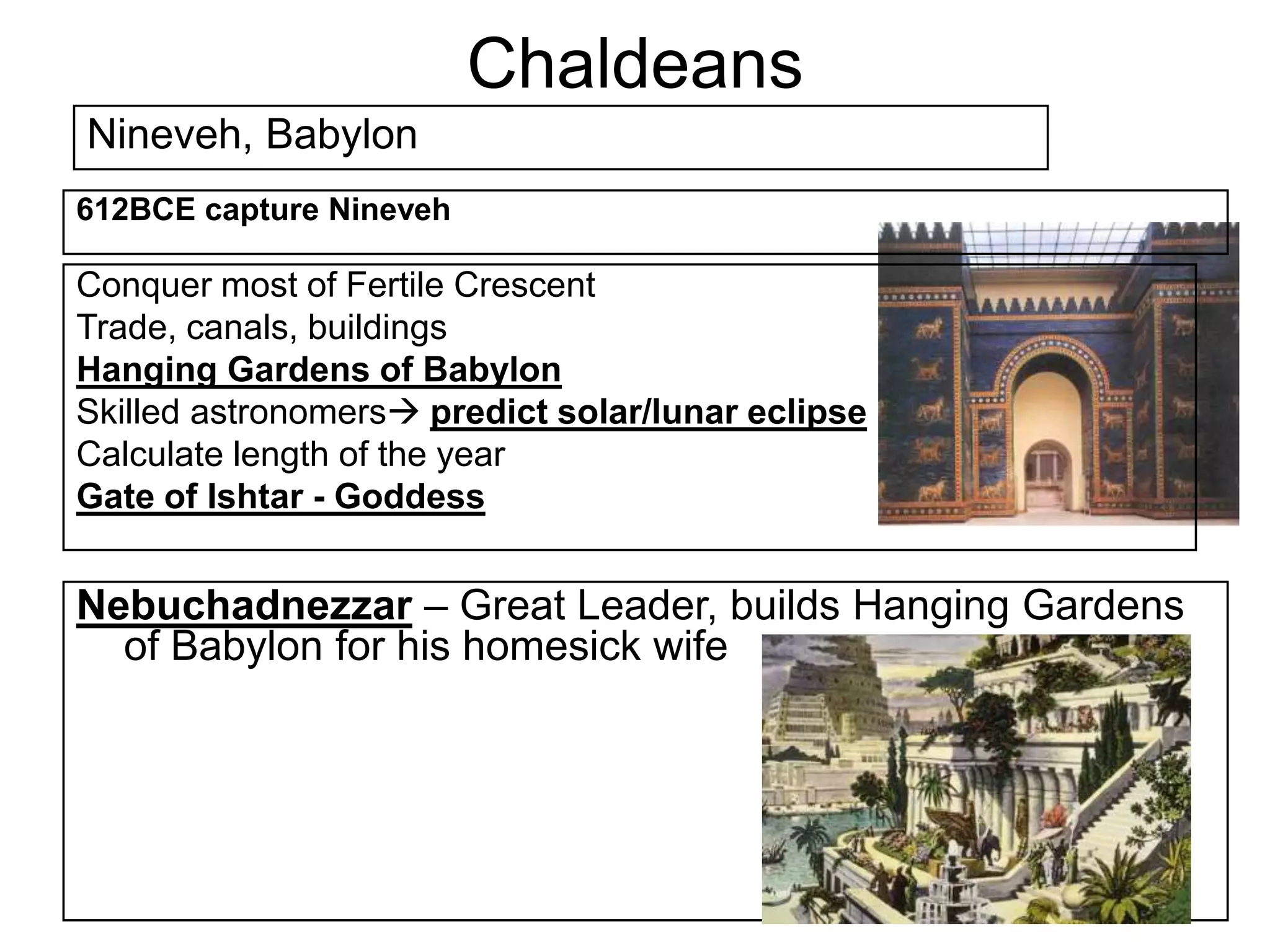
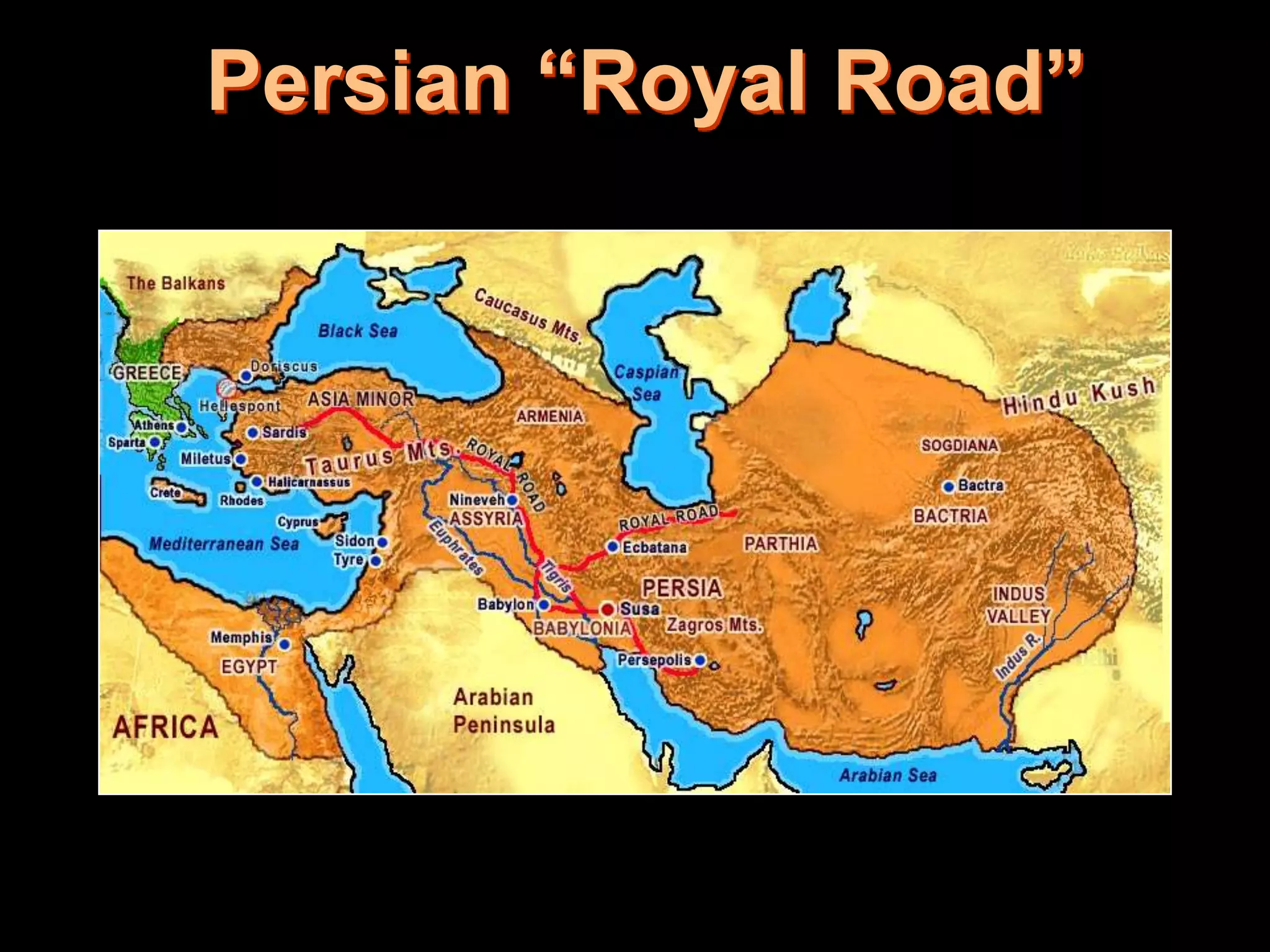
This document provides an overview of several early civilizations that emerged in Mesopotamia between 3000 BC and 100 BC, including the Sumerians, Babylonians, Assyrians, Chaldeans, Persians, Phoenicians, Lydians, and Hebrews/Jews. It describes their origins, locations, cultures, religions, innovations, and important leaders. Key developments discussed include the Sumerians inventing cuneiform writing and innovations like the plow, wheel, and ziggurat temples. The document also outlines the Babylonian code of Hammurabi, Assyrian and Persian empires, Phoenician trade routes, and foundations of Judaism under Moses and the Torah




![Hammurabi’s [r. 1792-1750 B. C. E.]
Code](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mesopotamiachartwpics-130925140559-phpapp01/75/Mesopotamian-Groups-Chart-with-Pictures-7-2048.jpg)




![Zarathustra [Zoroaster], 6c
BCE:
Good Thoughts, Good Deed, Good Words
“Tree of Life”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mesopotamiachartwpics-130925140559-phpapp01/75/Mesopotamian-Groups-Chart-with-Pictures-16-2048.jpg)