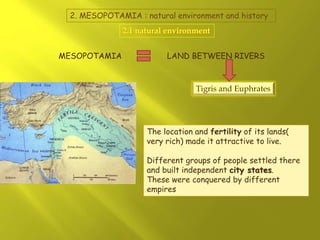
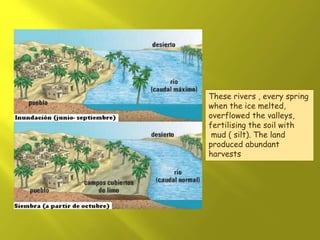
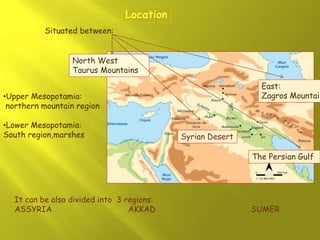
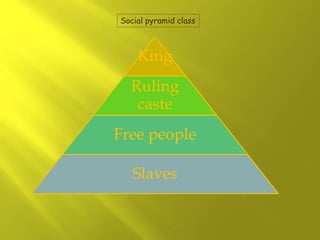
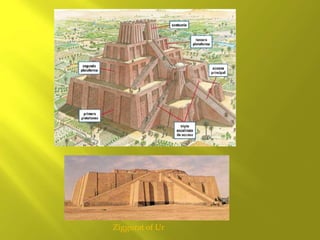
Mesopotamia and Egypt were early civilizations that emerged around 6000 BC along major river valleys, developing irrigation, cities, social hierarchy, governments, and early forms of writing. Mesopotamia emerged between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in an area known as the Fertile Crescent. Early civilizations like Sumer and Akkad developed, and empires like Babylon and Assyria rose and fell over time in Mesopotamia before it was conquered by Persia. Mesopotamian culture included polytheistic religions centered around temples, advances in math, astronomy, and medicine, and architectural achievements like ziggurats and palaces built from mudbricks and decorated