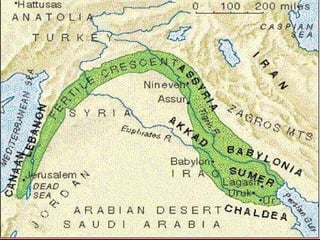
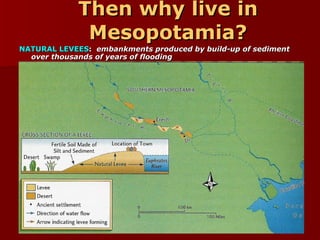
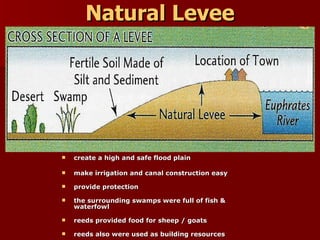
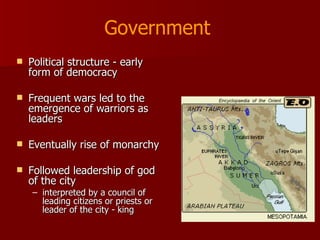
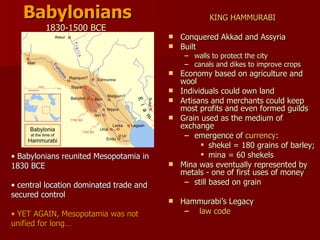
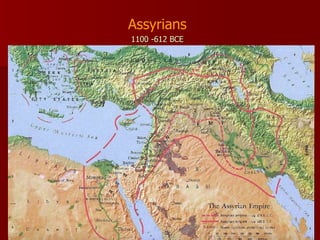
Mesopotamia, located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers in modern-day Iraq, was the site of some of the earliest human civilizations beginning around 3500 BCE. It had a favorable environment for agriculture due to natural levees and floodplains created by seasonal flooding. Mesopotamian civilizations such as the Sumerians, Akkadians, Babylonians, and Assyrians developed systems of irrigation, law, writing, mathematics, and organized religion centered around gods like Ishtar and Enki. Writing began as pictograms and evolved into the cuneiform script, while legal codes like Hammurabi's established early systems of law.