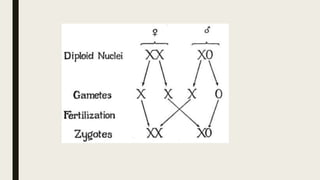
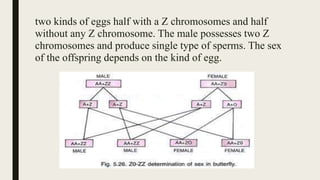
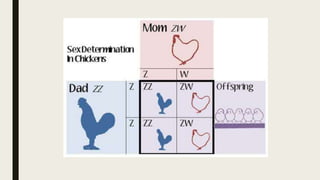
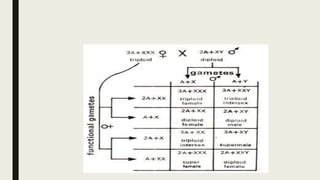
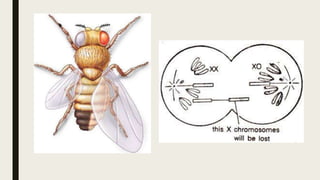
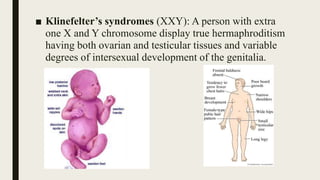
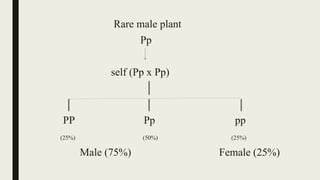
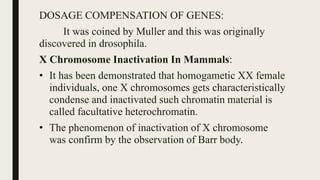
Sex determination is controlled by sex chromosomes. In humans and many other species, females have two X chromosomes (XX) while males have one X and one Y chromosome (XY). The presence of a Y chromosome determines maleness, while its absence results in femaleness. There are two main systems - heterogametic males which include humans and heterogametic females found in some insects and fish. The ratio between X chromosomes and autosomes also influences sex determination in some species through a genic balance mechanism.