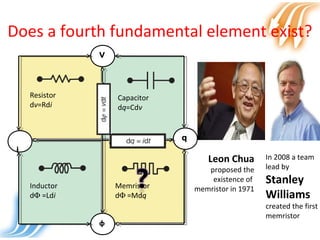
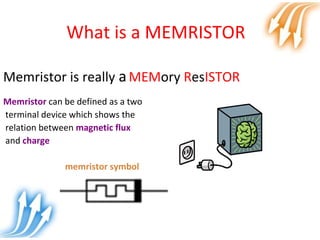
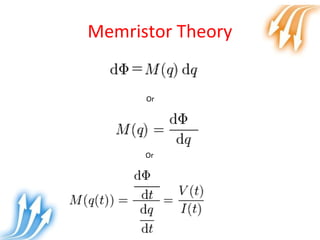
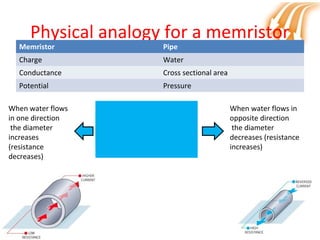
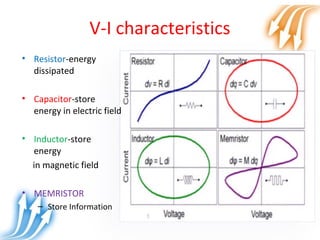
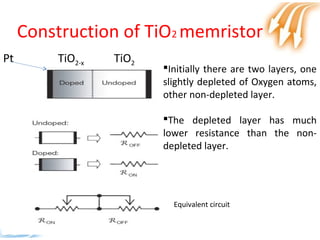
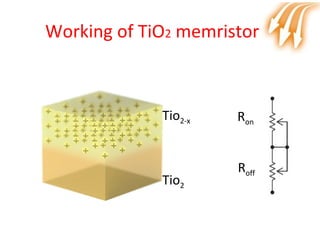
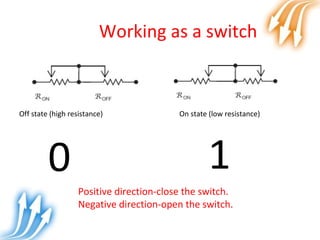
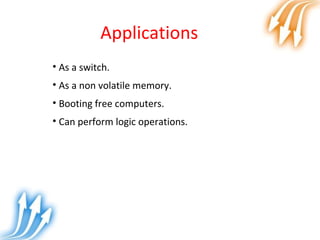
Memristor is proposed as the fourth fundamental circuit element along with resistor, inductor and capacitor. It relates magnetic flux and charge, and its memristance can be switched to different states, giving it memory properties. Physically, a memristor can be analogous to a pipe that changes diameter based on direction of water flow, retaining its size when flow stops. Its ability to store information qualifies it as a fundamental circuit element, and it has applications as switches, non-volatile memory and more compact logic circuits.