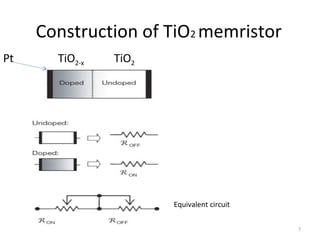
Memristor is a proposed fourth fundamental circuit element. It is a two-terminal passive device whose resistance depends on the amount of charge that has passed through it. In 2008, a team led by HP Labs created the first physical memristor, fulfilling the proposal made by Leon Chua in 1971. Memristors have potential applications as non-volatile memory replacements, and in artificial neural networks due to their ability to mimic synaptic behavior. Their unique properties may enable novel computing architectures in the future.