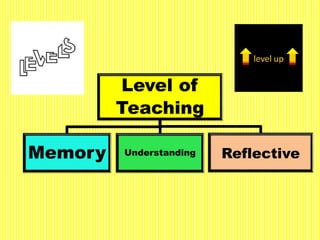
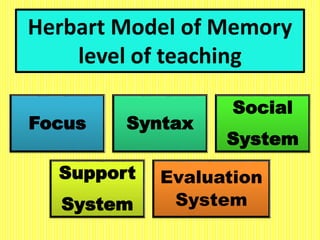
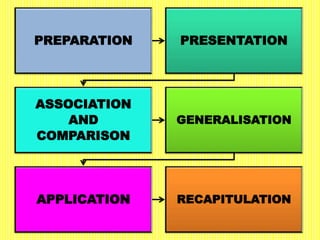
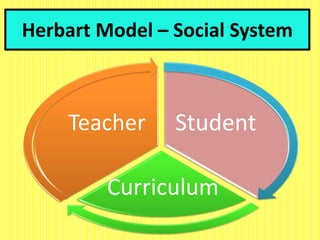
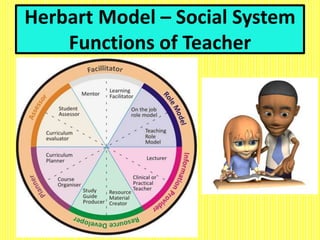
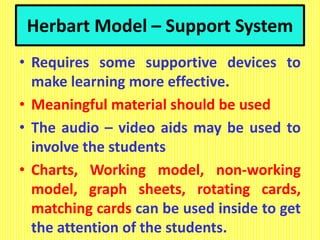
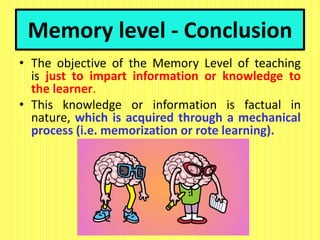
The document discusses the Herbartian model of memory-level teaching in mathematics, emphasizing the role of the teacher in imparting factual knowledge through structured processes. It outlines six key steps of teaching: preparation, presentation, association/comparison, generalization, application, and recapitulation, which support the effective retention and recall of information. The model also stresses the importance of evaluating student comprehension and employing supportive materials and techniques to enhance learning.