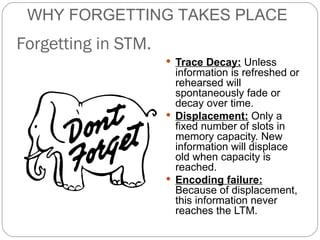
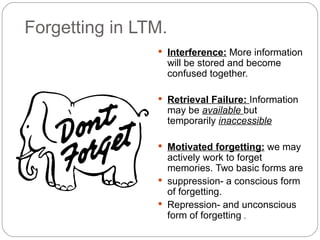
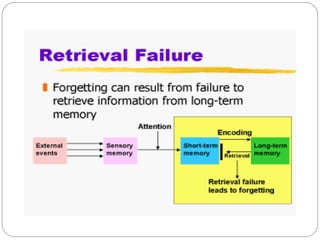
The document discusses several theories of forgetting. It defines different types of forgetting such as natural forgetting, morbid forgetting, general forgetting, and specific forgetting. It also outlines some key theories of why forgetting takes place, including trace decay theory, displacement in short-term memory, encoding failure, interference and retrieval failure in long-term memory, and motivated forgetting through suppression and repression.