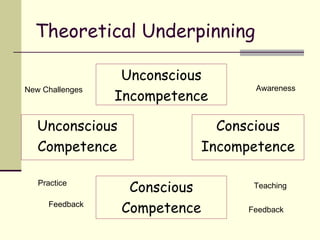
The document discusses the use of medical simulations in teaching, outlining four types: simple, mechanical, hybrid standardized patients, and virtual scenarios. It highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each type, focusing on how simulations can enhance learning by allowing students to practice skills, receive feedback, and improve their medical competencies. The document emphasizes the importance of structured learning objectives and the role of feedback in developing medical professionals.