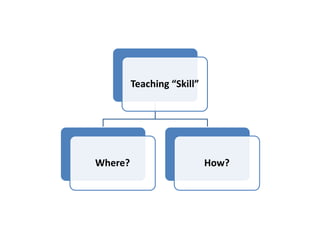
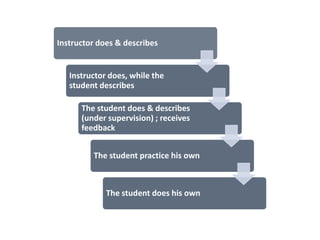
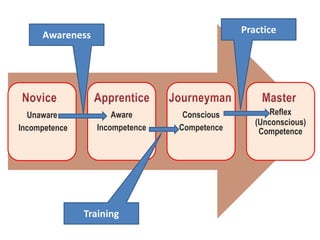
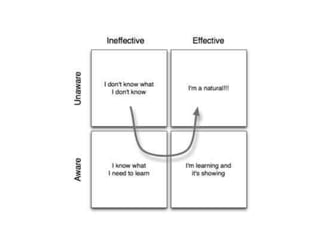
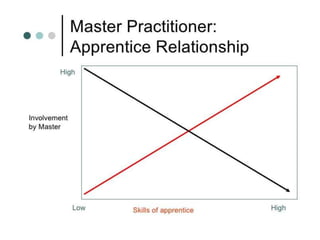
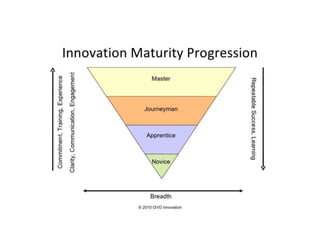
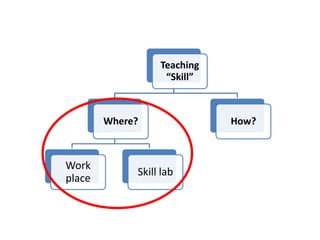
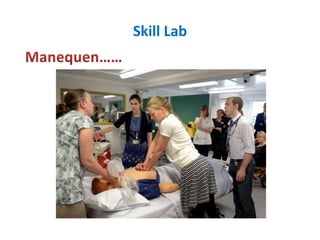
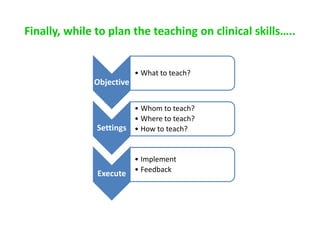
The document discusses the effective teaching of clinical skills, emphasizing the importance of active participation and a master-apprentice model over passive observation. It outlines various skill types required for medical professionals and highlights current teaching challenges, such as unclear objectives and inadequate supervision. The document also weighs the advantages and disadvantages of skill labs and workplace-based training in developing these essential competencies.