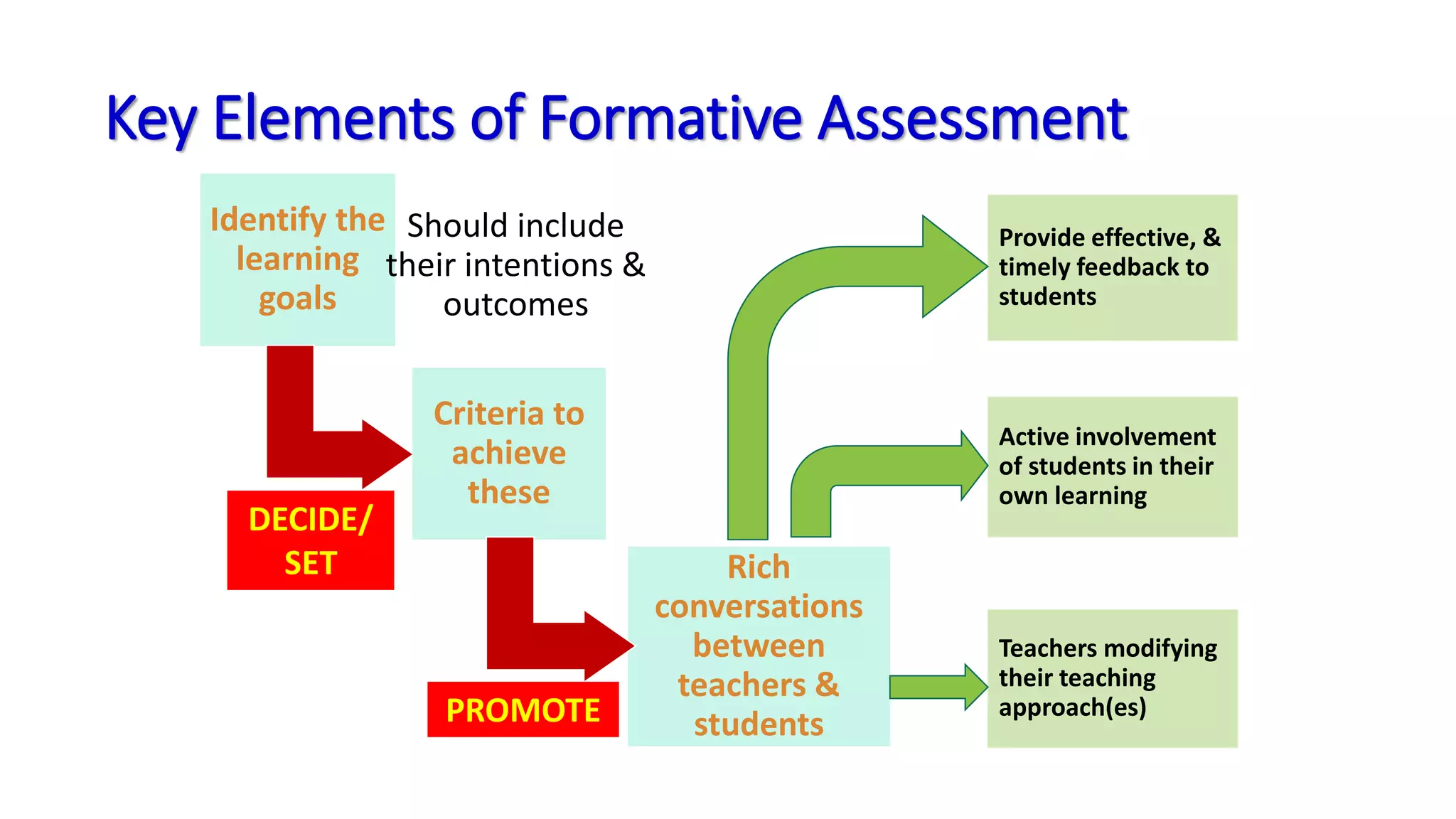
This document discusses internal and formative assessment in medical education. It defines internal assessment as assessment done by teachers who have taught a subject, and notes its benefits include overcoming day-to-day variability and allowing for larger sampling of topics. Formative assessment is defined as assessment for learning that provides ongoing feedback to both teachers and students. The key elements of effective formative assessment are identifying learning goals, involving students in self-assessment, and providing timely feedback. The document provides examples of how to incorporate more formative assessment into an existing system focused on summative assessment and internal exams.

















![RBC WORKSHOP ON MEDICAL EDUCATION TECHNOLOGIES
What happens after GMER 2019
Internal Assessments to be used for appearing in the
University Exam.
Marks will not be added in the final marks
[IA marks will reflect as a separate head of passing at the University exam.]
***
35% - appearance
50% - result publication
Less than 50% - remedial measures
[In subjects that have two papers - at least 40% marks in each paper with
minimum 50% of marks in aggregate to pass]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internalassessmentformativeassessment-210904041434/75/Internal-assessment-formative-assessment-20-2048.jpg)


![Internal Assessment
• Priority can be given to psychomotor, communication and
affective domains.[usually not assessed by traditional
assessment methods]
• Can be a very useful tool for assessing the competencies in any
competency based curriculum.
• Multiple tools can be used for a given competency - helps to
improve validity and reliability of the assessment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/internalassessmentformativeassessment-210904041434/75/Internal-assessment-formative-assessment-23-2048.jpg)