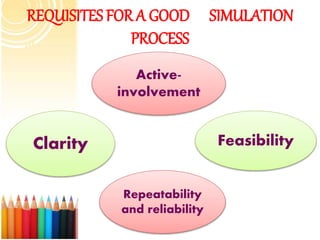
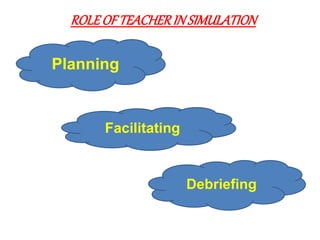
Simulation is a technique that allows learners to gain skills and competencies by participating in realistic simulated situations. It can be used to practice decision making, problem solving, and human interaction skills in a safe and controlled environment. There are various types of simulations ranging from low to high fidelity that incorporate different levels of realism. Simulation provides many benefits for nursing education such as allowing students to experience real situations without risk to patients, receiving immediate feedback, and building confidence. It is an effective method to help students transition from the classroom to clinical practice.







![2] Standardized patient-
standardized patient or sample patient (SP)( also known as patient
instructor), in health care, is an individual who is trained to act as a real
patient in order to stimulate a set of symptoms or problems.
• Used for-
Physical assessment skills.
History taking.
Teaching communication skills
Teaching clinical skills.
Interaction with psychiatric client
Clinical examination.
• Example-. Teach the student how to collect history from psychiatric
patient.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simulation-200814065001/85/SIMULATION-8-320.jpg)
![3] Screened based computer simulator-
This include computer application for simulation.
• Use-
Model various aspects of human physiology.
Model of specific task or environment.
Making clinical decision.
Observe the result in action.
• Example- computer –assisted instruction programs or
web-based programs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simulation-200814065001/85/SIMULATION-9-320.jpg)
![4] Complex task trainer-
i. Haptic systems- this type of technology is particularly useful
in learning environments where the faculty cannot clearly see
where the student is assessing the patient. It allow a learner to
perceive tactile and other stimuli to the senses through a
complex , computer generated environment .
ii. Virtual reality- These virtually- reality scenarios offer an
opportunity for the learner to practice skill via computer- based
traning, including-
Surgical skills.
Bronchoscopy.
Intravenous.
Central line catheterization.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simulation-200814065001/85/SIMULATION-10-320.jpg)
![5] Integrated simulators (Human Patient
simulator)- or human patient simulators(HPS) combine
computer technology and part-or whole-body mannequins to
provide a more realistic learning experience. Integrated
computer technology housed in the mannequins to respond in
real time to specific care intervention and treatment.
• Example-
Medications, Chest compressions, Needle decompressions.
Chest tube placement, and other physiologic interventions
and subsequent responses..
• These interactive mannequins are capable of realistic
physiologic responses, including
Respiration, pulses, heart sounds, breath sounds, urinary
output, and pupil reaction.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/simulation-200814065001/85/SIMULATION-11-320.jpg)