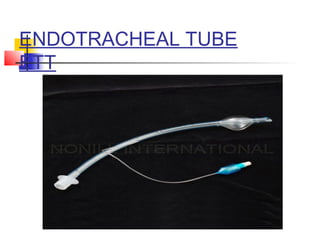
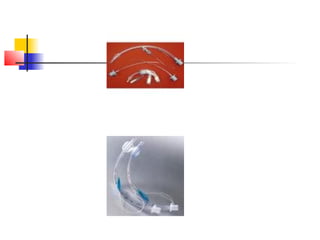
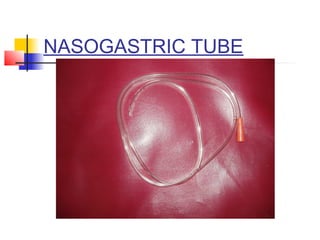
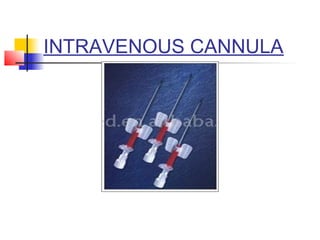
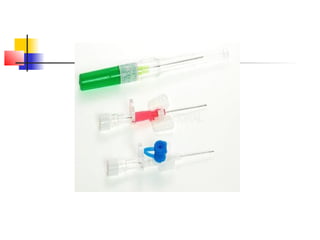
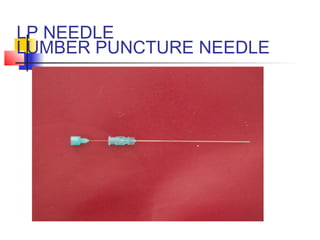
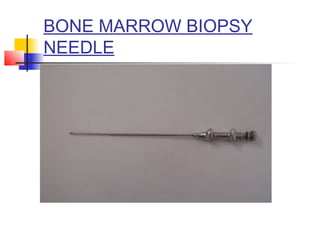
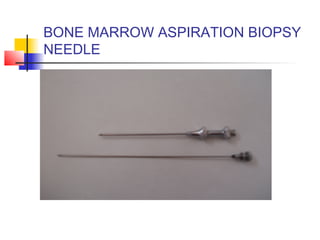
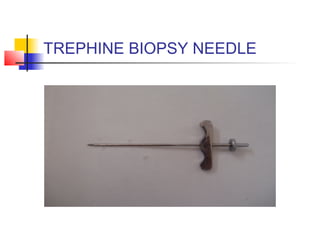
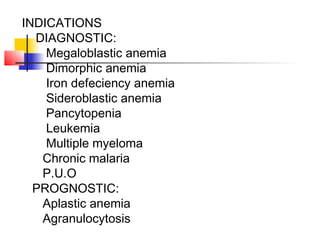
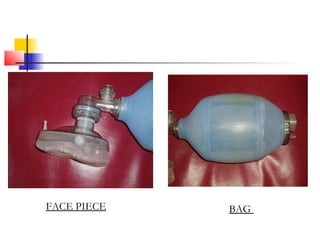
This document lists and describes various common medical instruments. It discusses endotracheal tubes, airways, Ambu bags, Foley catheters, nasogastric tubes, intravenous cannulas, lumbar puncture needles, liver biopsy needles, laryngoscopes, chest tubes, bone marrow needles, ESR tubes, ophthalmoscopes, and provides information on their features, indications, contraindications and complications.