Embed presentation
Downloaded 328 times
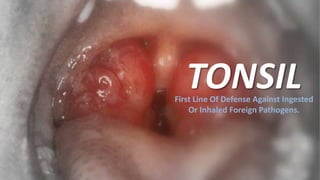







Tonsils are collections of lymphoid tissue located in the aerodigestive tract that form Waldeyer's ring and act as the immune system's first line of defense. Waldeyer's ring includes the adenoid tonsils, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsil. Tonsils contain specialized cells called M cells that capture pathogens and alert the immune system, stimulating B cells and T cells to respond. This leads to the production of antibodies and memory B cells in germinal centers within the tonsils. Tonsils can also become inflamed or infected, leading to tonsillitis, or develop calcified material known as tonsilloliths.






