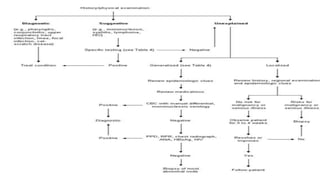
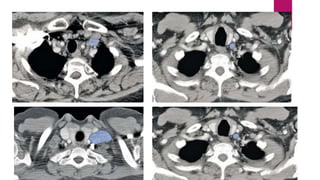
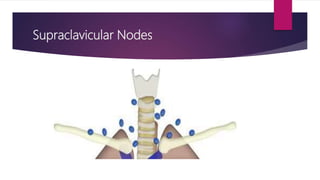
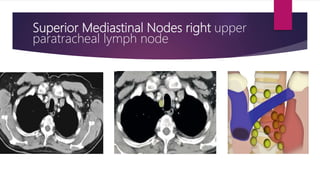
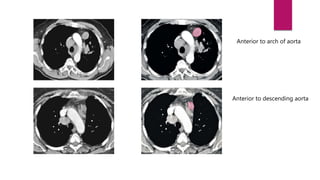
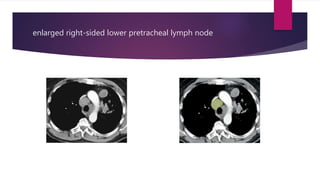
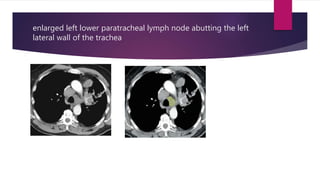
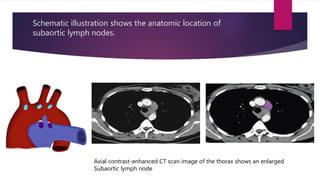
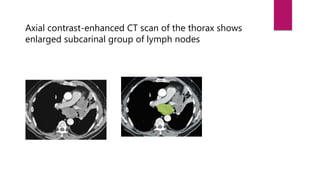
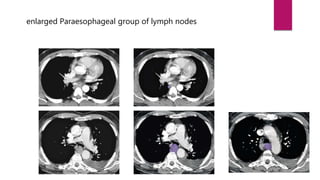
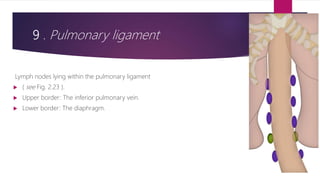
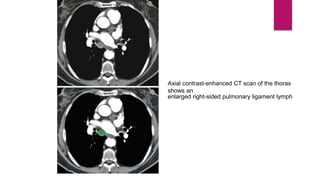
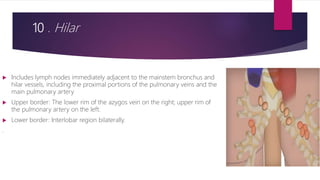
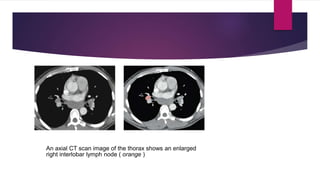
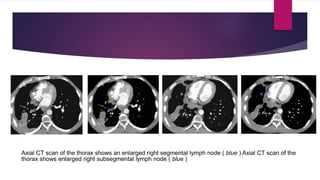
This document describes the mediastinal lymph node stations according to the 2009 IASLC lymph node map. It provides detailed definitions for each lymph node station, including anatomical boundaries and examples of enlarged lymph nodes in each station seen on CT scans. Key lymph node stations described include supraclavicular (1), superior mediastinal (2-4), aortic (5-6), inferior mediastinal (7-9), hilar (10), interlobar (11), lobar (12), segmental (13), and subsegmental (14) nodes. Diagrams and CT images are provided to illustrate lymph node locations.