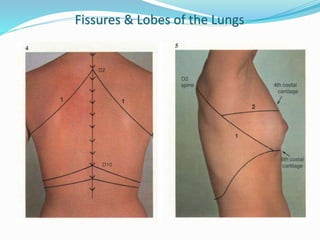
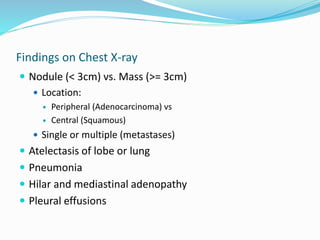
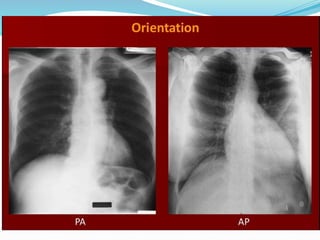
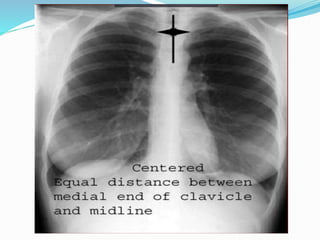
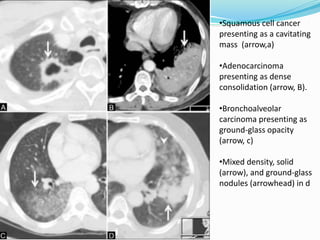
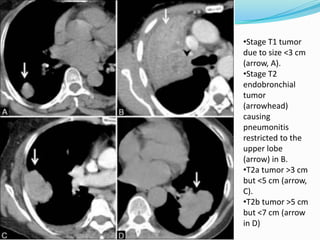
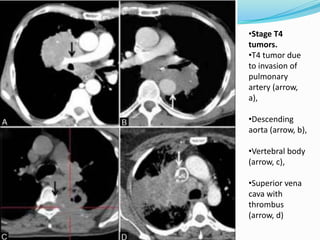
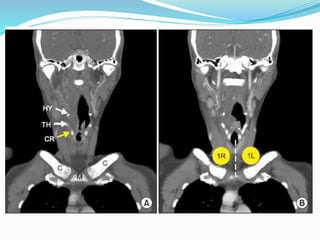
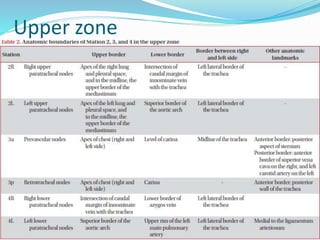
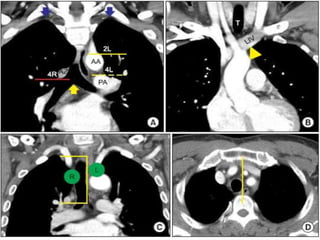
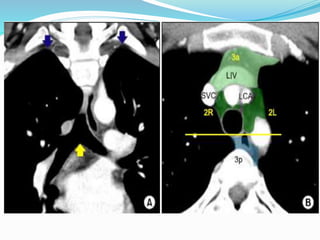
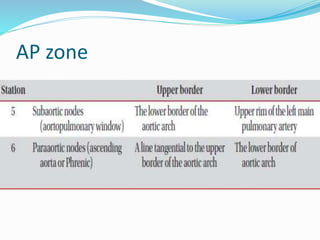
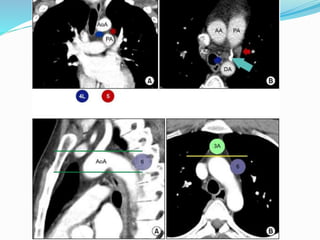
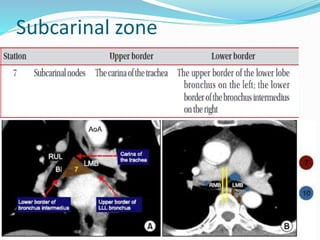
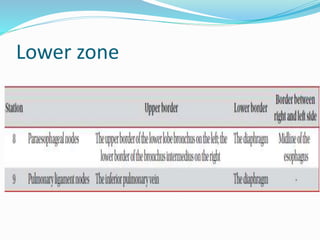
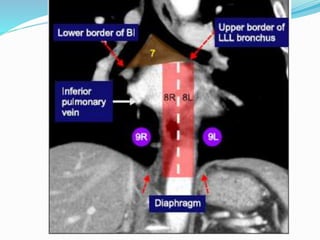
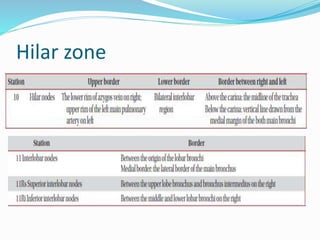
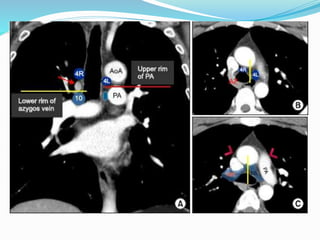
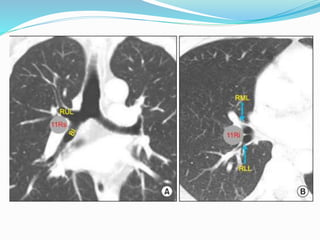
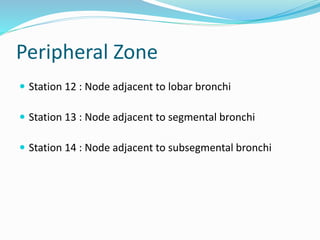
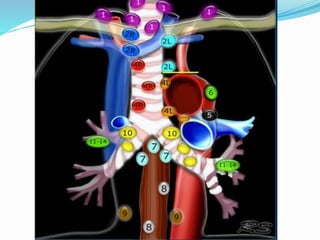
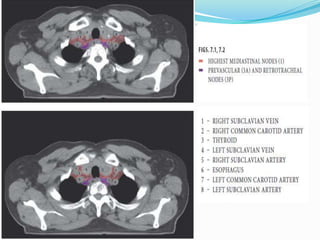
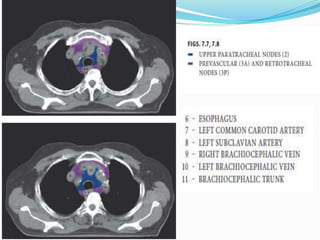
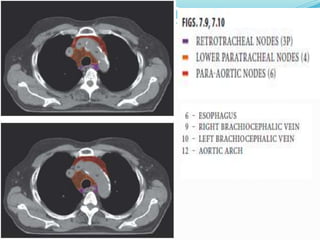
The document summarizes the borders and fissures of the lungs. It describes how the apex is located about 2cm above the medial 1/3 of the clavicle. It also outlines how the anterior borders of the right and left lungs descend and meet in the midline behind the angle of Louis, with the right lung continuing down to the 6th costochondral junction and the left lung curving laterally to form the cardiac notch before descending to the 6th costochondral junction. The lower border is represented by a line starting from the 6th rib in the MCL, 8th rib in the MAL, and 10th rib in the mid scapular line. Oblique and transverse fissures