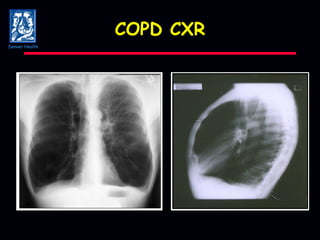
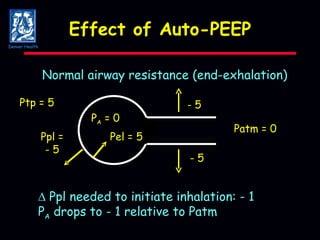
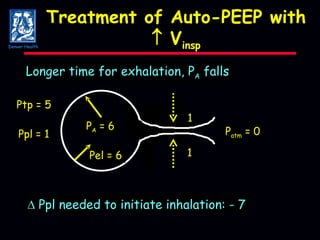
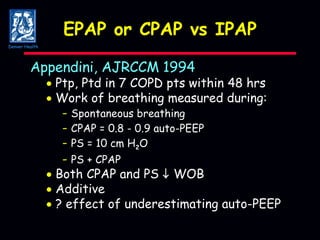
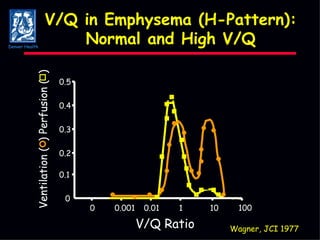
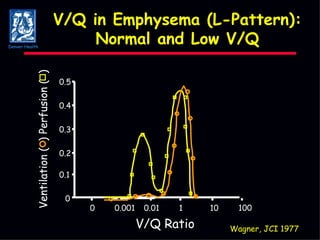
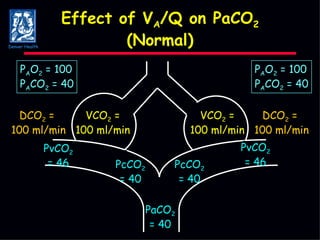
The document discusses mechanical ventilation strategies for patients with COPD and asthma exacerbations, emphasizing key aspects such as pathophysiology, determinants of Paco2, and the role of NIPPV in treatment. It highlights the impact of factors like auto-peep, work of breathing, and ventilator settings on patient outcomes. Recommendations include using low tidal volumes and appropriate PEEP to manage ventilation effectively.