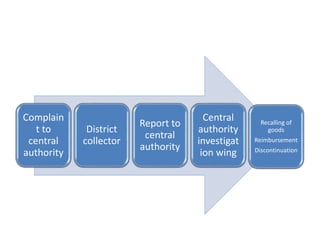
The Consumer Protection Act 2019 repealed and replaced the previous COPRA act of 1986. It established authorities at the central, state, and district levels to protect consumer interests and effectively handle consumer disputes. The central authority is headed by a Chief Commissioner based in New Delhi. Consumer disputes redressal commissions were established at the national, state, and district levels to handle consumer complaint cases depending on the amount in dispute. The act allows individuals to file complaints within 21 days with the appropriate commission. It also defines limitations periods for reporting negligence or defects. The Transplantation of Human Organs Act 1994 regulates the removal, storage, and transportation of human organs for therapeutic purposes. It prohibits commercial dealings in organs and established an authorization committee to regulate