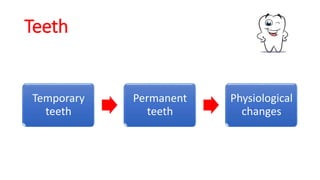
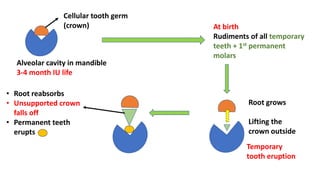
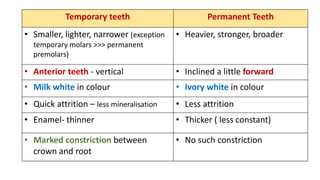
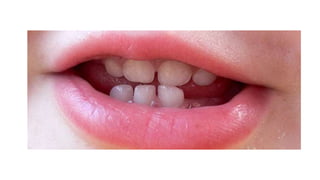
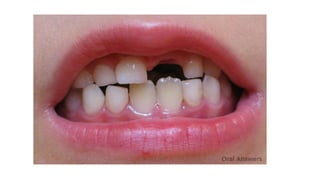
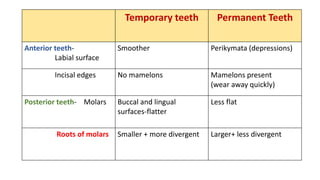
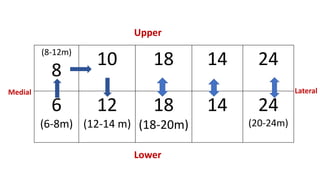
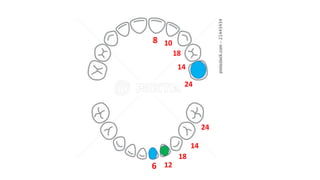
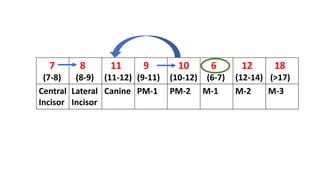
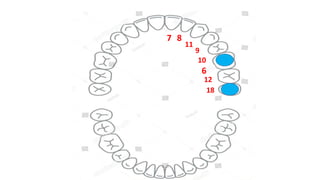
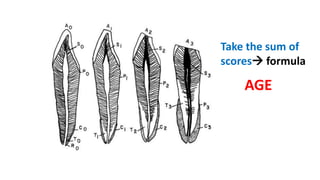
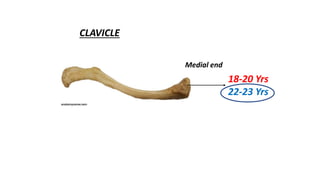
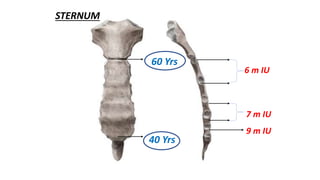
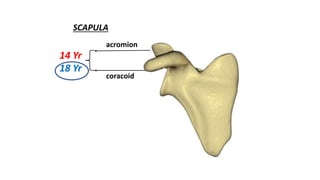
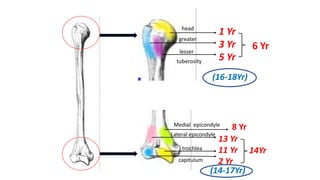
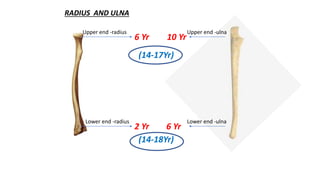
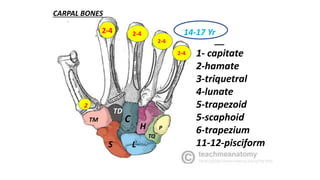
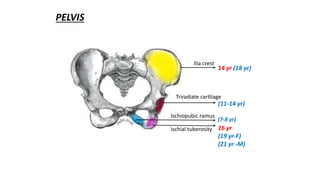
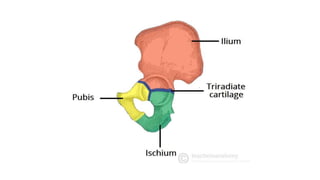
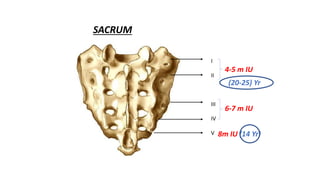
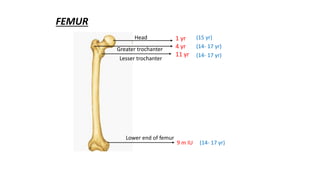
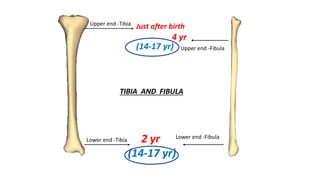
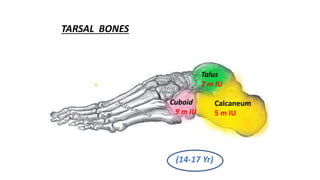
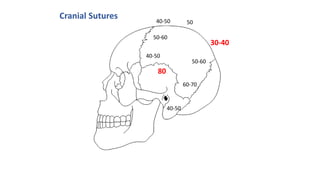
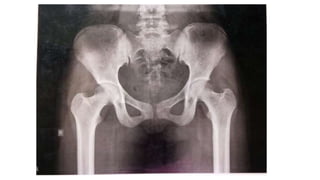
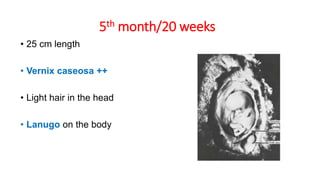
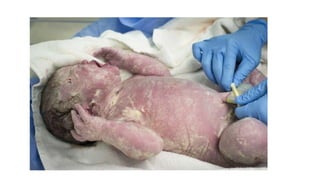
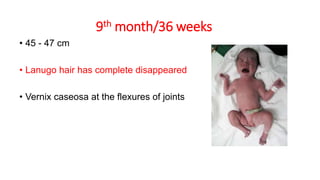
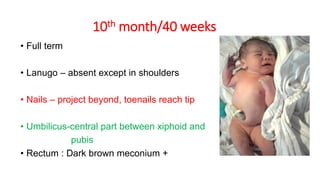
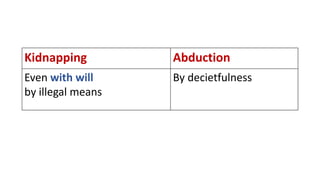
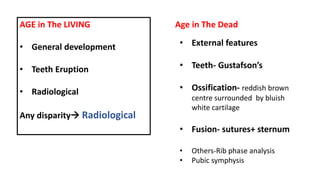
This document discusses methods for estimating age in the living and deceased. It covers dental development, ossification of bones, and secondary sexual characteristics as indicators. For teeth, it describes the eruption schedule of both primary and permanent teeth. It also discusses Gustafson's method for estimating age based on characteristics in dental tissues seen in radiographs. For bones, it provides timelines for ossification at various sites. It notes the medicolegal importance of accurately determining age for issues like legal consent, criminal responsibility, and definitions of infant, child, juvenile, and adult. Overall, the document serves as a reference for the key physical indicators used to assess age in forensic cases.