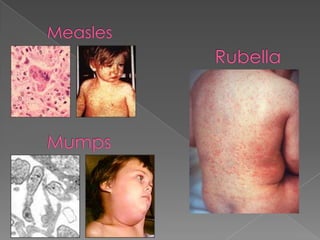
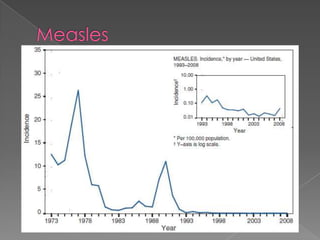
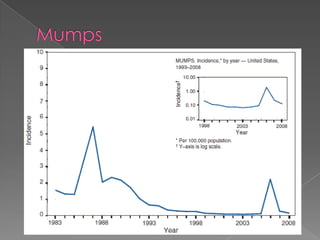
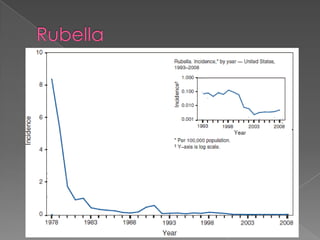
This document discusses measles, mumps, and rubella. Measles causes a rash and is spread through respiratory droplets. It can lead to complications like pneumonia or encephalitis. Mumps causes swelling of the salivary glands and is common in children ages 2-12. It spreads through respiratory droplets. Rubella, also called German measles, causes a rash and inflammation and is spread through the air or close contact. All three diseases can be prevented through routine immunization with the MMR vaccine.