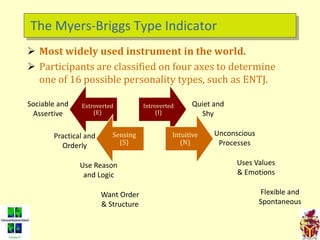
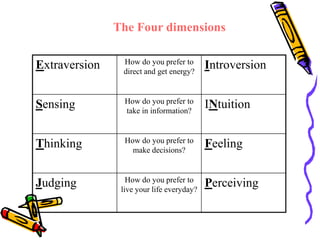
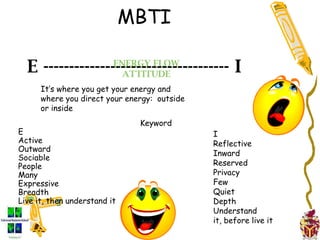
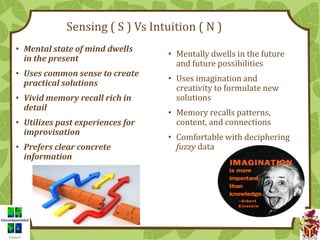
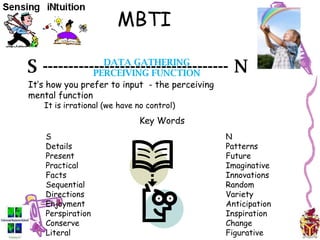
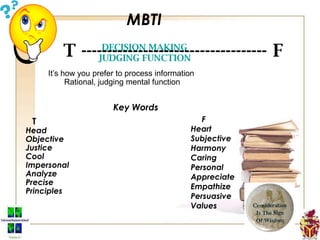
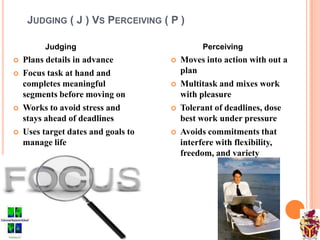
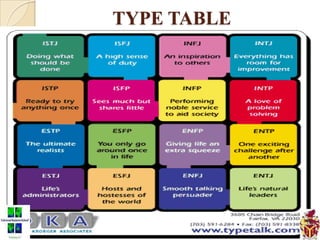
The document provides an overview of the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) personality assessment. It describes how the MBTI was developed in the 1940s by Isabel Briggs Myers and her mother based on Carl Jung's theory of psychological types. The MBTI aims to sort people into one of 16 personality types based on their preferences on four dichotomous scales: Extraversion vs Introversion, Sensing vs Intuition, Thinking vs Feeling, and Judging vs Perceiving. Over 600 dissertations and thousands of articles and books have been written on the MBTI since its creation.