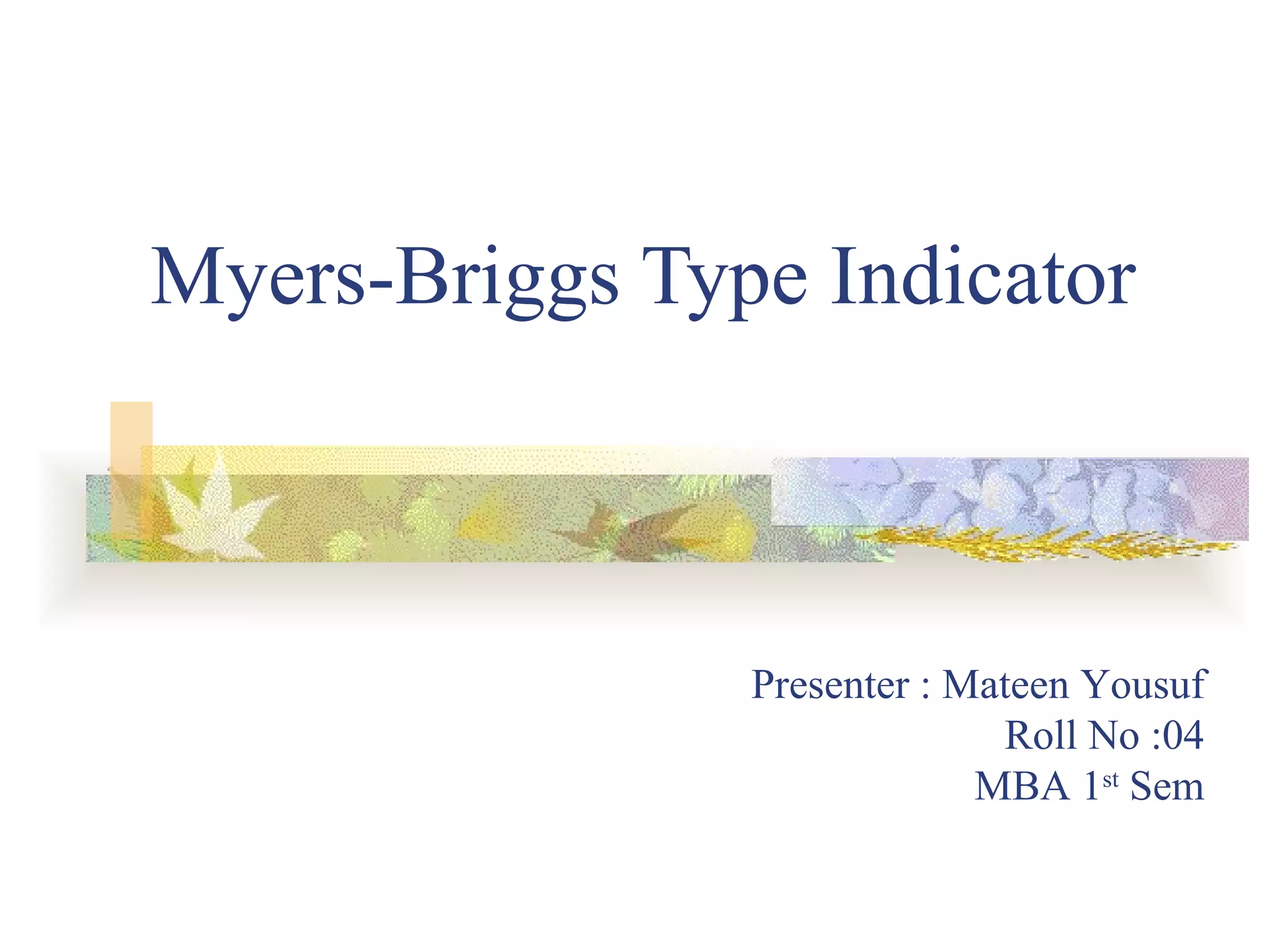
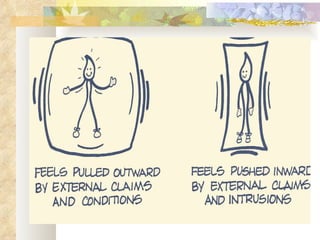
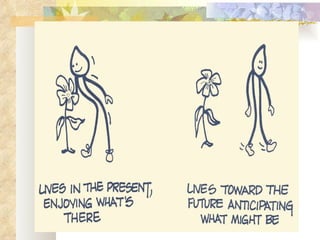
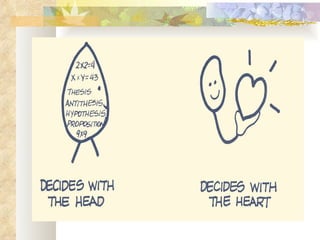
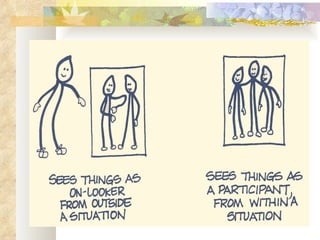
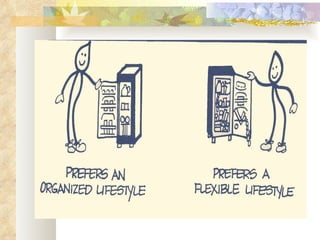
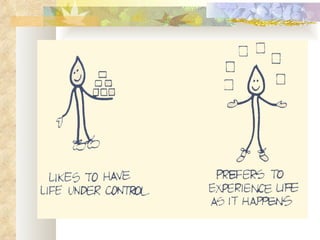
The Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (MBTI) is a psychological questionnaire that measures psychological preferences in how people perceive the world and make decisions. It was developed during World War II to help identify suitable jobs for women entering the workforce. The MBTI identifies a person's natural tendencies across four scales that represent preferences in how people focus their attention, take in information, make decisions, and adopt lifestyles. Over 30 million people have taken the MBTI, which is used to help with career choices, relationships, communication, leadership, and learning. Skeptics view the MBTI as unscientific and argue it oversimplifies personalities into strict types rather than recognizing people use different thinking styles in different situations.